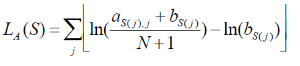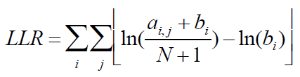Motif detection tasks allow to extract binding motifs from peak region generated from ChIP-seq data. It allows users to search for know motifs from provided database as well as detect noval motifs. These tasks are available when click on region data node.
Search for know motifs
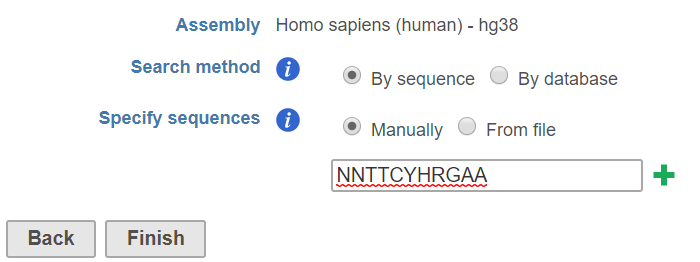
Given a set of genomic regions, sequence motif can be search based on a string provided by user or alignment matrix from a database like JASPAR. Click on a peak data node, choose Search for known motifs from Motif detection section on the pop-up menu (Figure 1).
Manually: user can manually specify the sequences, click on green plus button to add multiple sequences to search.
From file: use can specify a text file (.txt) contains a list of sequences, one row per sequence.
The string search tool will return all positions in the set of genomic regions that match the given strings. The string match is case insensitive, meaning if you search for ATCG, you may get atcG as a match. Nucleotides that are lower case have been "repeat masked", meaning they are located in a repetitive region of the genome. Your search string may contain any of the characters from the IUPAC nucleotide code . For example, if you search for WAAA, you may get back AAAA or TAAA (or any variantion of upper and lower cases), since W represents A or T.
Alignment matrices are often used in literature to model transcription factor binding sites, alignment matrices are matrices of nucleotide counts per position [1]. Each instance of the motif is aligned to each other and the number of nucleotides at eac hposition is counted and summarized in an alignment matrix. All positions from the set of genomic regions are scored against the alignment matrix. The scroe represents how likely the position is an instance of the motif. A quality cutoff is used to determine which sequences in the regions are instances of the motif. The scoring scheme and quality cutoff are similar to [2] and it briefly described below:
Let M be a motif of length L consisting of N motif instances.Let A be a 4XL alignment matrix such that ai,j is the count of letter i at position j. Let Bi be the background frequency of letter i (calculated as the number of nucleotides i in the regions divided by the total oligonucleotides in the regions). Let S be a sequence of length L. The score of S given the alignment matrix is
Detect de novo motifs
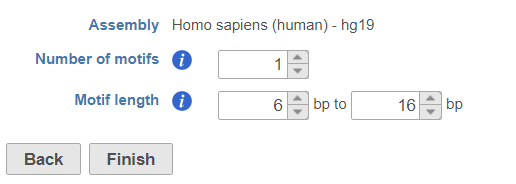
Click on Peak data node, select Detect de novo motifs from Motif detection section in the pop-up menu (Figure 1), specify the number of motifs to detect and the length of the motifs.
This is done by repeating the below two steps until convergences:
A. Given the alignment matrix from step B, search for location in the set of regions that score highly compared to the alignment matrix using equation
Reference
- Hertz, GZ., & Stormo, G.D. Identifying DNA and protein patterns with statistically significant alignments of multiple sequences. Bioinformatics 1999, 15, 563-577
- Schug, J., & Overton, C.G. TESS, Transcription Element Search Software on WWW. Technical Report CBIL-TR-1997-1001-v0.0, of the Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory, School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, 1997
- Neuwald, A.F., Liu, J.S., & Lawrence, C.E. Gibbs motif sampling: detection of bacterial outer membrane protein repeats. Protein Science 1995, 4: 1618-1632.


| Your Rating: |
    
|
Results: |
    
|
1 | rates |