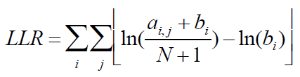Motif detection tasks allow to extract binding motifs from peak region generated from ChIP-seq data. It allows users to search for know motifs from provided database as well as detect noval motifs. These tasks are available when click on region data node.
Search for know motifs
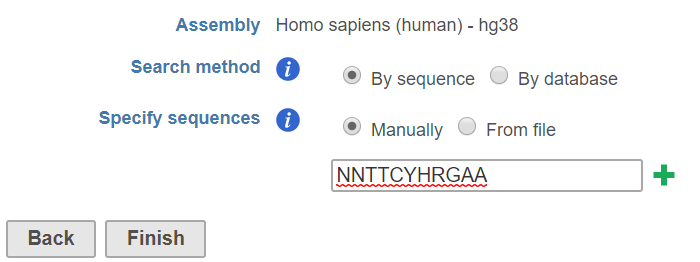
Given a set of genomic regions, sequence motif can be search based on a string provided by user or alignment matrix from a database like JASPAR. Click on a peak data node, choose Search for known motifs from Motif detection section on the pop-up menu (Figure 1).
The string search tool will retrun all positions in the set of genomic regions that match the given string
Detect de novo motifs
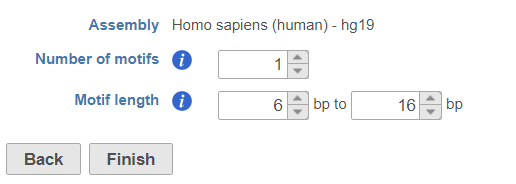
Click on Peak data node, select Detect de novo motifs from Motif detection section in the pop-up menu (Figure 1), specify the number of motifs to detect and the length of the motifs.
This is done by repeating the below two steps until convergences:
A. Given the alignment matrix from step B, search for location in the set of regions that score highly compared to the alignment matrix using equation
Reference
- Neuwald, A.F., Liu, J.S., & Lawrence, C.E. Gibbs motif sampling: detection of bacterial outer membrane protein repeats. Protein Science 1995, 4: 1618-1632.


| Your Rating: |
    
|
Results: |
    
|
1 | rates |