Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a very powerful technique for identifying differentially expressed genes in a multi-factor experiment. In this data set, ANOVA will be used to generate a list of genes that are significantly regulated by each treatment by two-fold.
Adding Factor and Interactions
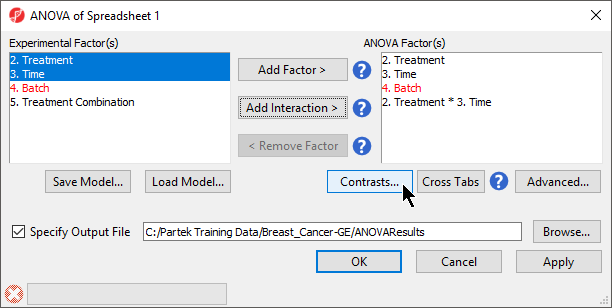
When setting up the ANOVA, the primary factors of interest, Treatment and Time, should be included. We will also include the interaction between Treatment and Time, Treatment * Time, because we are interested in whether different treatments behave differently over time. From our exploratory analysis using the PCA, we also know that Batch is a major source of variation and needs to be included. Including Batch as a random factor will allow us to account for the batch effect.
- Select Detect differentially expressed genes from the Analysis section of the Gene Expression workflow
- Select Treatment, Time, and Batch in the Experimental Factor(s) panel
- Select Add Factor > to move the selections to the ANOVA Factor(s) panel
- Select both Treatment and Time in the Experimental Factor(s) panel by holding Ctrl on the keyboard while selecting each
- Select Add Interaction > to add the Treatment * Time interaction to the ANOVA Factor(s) panel (Figure 1)
- Do not select OK or Apply. We still need to add linear contrasts to the ANOVA model
Fixed vs. Random Effects - Mixed Model ANOVA
Fixed effects
Additional Assistance
If you need additional assistance, please visit our support page to submit a help ticket or find phone numbers for regional support.


| Your Rating: |
    
|
Results: |
    
|
0 | rates |