Page History
...
The Deduplicate UMIs task identifies and removes reads mapped to the same chromosomal location with duplicate unique molecular identifiers (UMIs). The details of the our UMI deduplication methods are outlined in our the UMI Deduplication in Partek Flow white paper.
...
UMIs and barcodes are detected and recorded by the Trim tags task in Partek Flow. You can choose whether to retain only one alignment per UMI or not (Figure 1). The default will depend on which prep kit was used in the Trim tags task.
...
If you do not select Retain only one alignment per UMI, UMI deduplication will proceed without filtering to exonic reads. Other differences between the two options are outlined in the UMI Deduplication in Partek Flow white paper.
Imported BAM
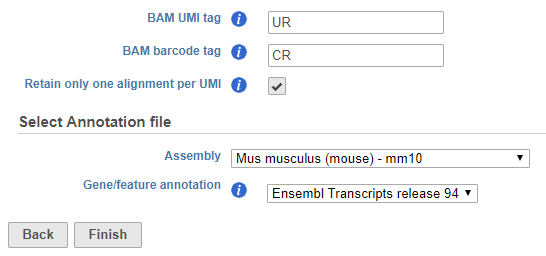
UMIs and barcodes are stored in the BAM headerImported BAMs generated by other tools can be imported into Partek Flow and deduplicated by the software. Additional options are available in the task configuration dialog to allow you to specify the location of the UMI and cell barcode information typically stored in the BAM header. Specify the BAM header tags in the text fields. For example, when processing a BAM file produced by CellRanger 3.0.1, the BAM identifier tag for the UMI sequence is UR and the BAM identifier for the barcode sequence is CR (Figure 2).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The option to Retain only one alignment per UMI is also available when starting from a BAM file.
Deduplicate UMIs task report
...