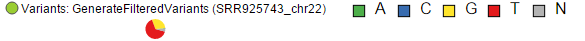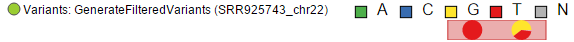Page History
Data tracks section of the Select tracks dialog enables you to specify the tracks for visualization on the canvas. An overview of the available track types is provided in Figure 161. Note that not all tracks are visible at all times and that their presence depends on the whether specific data types are present in the project as well as the zoom level. The tracks can be customised customized and their appearance changed by using the control panel on the right.left. Different track also has it own specific configuration settings which allow you to pin the track to move the track, pin the track, change the styles of the track and hide the track using the settings options on the left of each track ( )
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Alignments track Isoform proportion track Variants track Amino acids track Reads pileup track Probe intensities track Peaks track |
Alignments Track
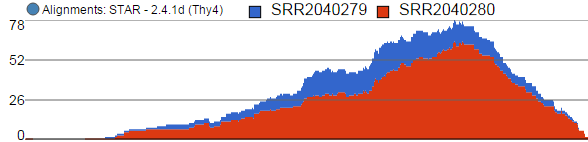
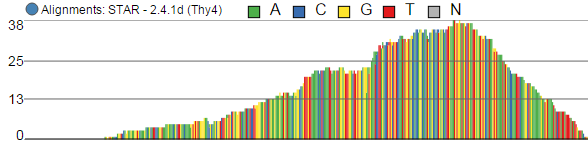
Alignments track displays a histogram view of alignments present in .bam files in a stacked histogram fashion (similar to Partek® Partek® Genomics Suite®Suite®). The y-axis shows number of (raw) base calls per position. By default, reads are coloured by sample; the exception is invocation of the chromosome view on a variant table, when the reads are coloured by base calls. The difference is shown in Figure 17.
...
. Variations on the track are displayed below. They can be configured in the following ways:
- The histogram can be colored by sample, attribute groups or by base call. By default, it is colored by sample except when the chromosome viewer is invoked from a variant data table.
- When colouring reads by sample, the reads are stacked (on top of each other), i.e. in the example
...
- below there are more reads in the red sample than in the blue sample. This is an example of a Sum histogram type. This can also be configured to display overlays or averages.
...
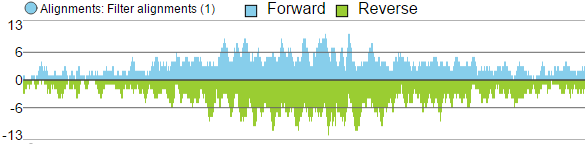
- Reads can be split into two tracks corresponding to the strand that they map to. This can be invoked by clicking the Split read histogram by strand checkbox.
- Y-axis can be scaled for all samples to have the same max or each sample has its own specific max
For more information on configuring tracks see our page on Customizing the chromosome viewer
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Reads coloured by sample Reads coloured by base calls Reads split by strand |
Isoform Proportion Track
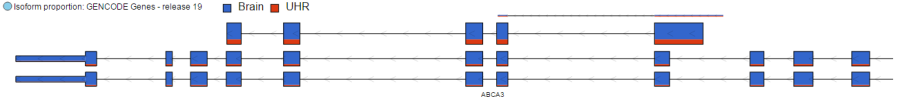
The Isoform proportion track displays the reads mapped to transcripts and helps to visualize differential expression and alternative splicing, using this track is only available on the feature list data node which is generated from differential expression analysis. It uses standard symbols for exons (boxes) and introns (lines connecting the boxes). The size height and color of each transcript is proportional to the number of reads that map to that transcript. The color indicates the samples to which the reads belong. Figure 18 proprotional to its LS mean value. Figure 3 shows a gene with two transcripts in RefSeq database; the top transcript is more abundant than the bottom transcript and is preferentially expressed in the "blue" condition (labeled as 0 uM). The bottom transcript, on the other hand, seems to be expressed at the same level across all three conditions (i.e. 0 uM, 5 uM, 10 uM). The number and structure of transcripts on the plot depend on the transcript model that was used for mapping.
For more information on configuring tracks see our page on Customizing the chromosome viewer
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Variants Track
Variant tracks show single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and indels, and appear in the Select track dialog if Detect variants task has been performed. Presentation of variants depends on the level of zoom. With low power magnification, SNVs are seen as purple columns and indels are bars (insertions: green bars; deletions: red bars) (Figure 194).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Upon zoom-in, SNVs are drawn as pie charts, representing the proportion of each base call at that locus (Figure 205)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
At higher modification, insertions are seen as green boxes, with individual inserted bases presented using a pie chart, while deletions look like red boxes and the affected bases are also presented by a pie (Figure 216).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Insertion Deletion |
Amino Acids Track
...
When you zoom closer to the genome, all the amino acids become visible as colored boxes (Figure 227) and labeled using the single-letter amino acid code. Alternative amino acids are depicted as additional boxe on box on the top of the consensus sequence.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
If an amino acid spans two exons, its box will be truncated and the line connecting the exons will be dashed. An example is in Figure 238.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
An empty gray box on the top of consensus sequence is used to indicate a STOP codon, which is a consequence of a mutation (Figure 249).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Untranslated bases, such as ones downstream of a STOP codon are depicted by lighter shades. Figure 25 10 shows two transcripts in an amino acid track; the direction is from left to right, so amino acids downstream of a STOP codon (P > G > L) are lightly shaded.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Reads Pileup Track
...
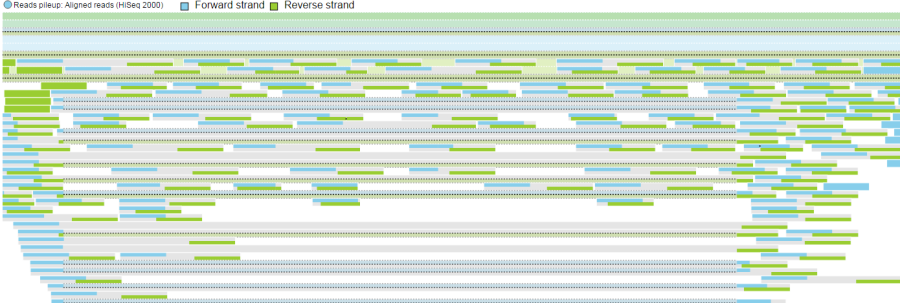
Forward strand reads are in sky blue, while reverse strand reads are in parakeet green. If paired-end chemistry was used, the paired reads will be depicted as half reads within a gray rectangle encompassing the pair (Figure 2611). Singletons will be depicted as thicker reads.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
If you used a junction-aware aligner (such as TopHat or STAR), the junction reads will be depicted using dashed lines, which connect exon-spanning parts of the same read (Figure 2712).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Deleted bases can also be seen on a Reads pileup track, as fat black lines (Figure 2813).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Probe Intensities Track
Microarray probes are visualised by the Probe intensities track. The probes are shown as bars and their colour depends on the probe intensity, ranging from white (low) to admiral blue (high) (Figure 2914).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
As with the Reads pileup track, probes may not be visible with low power magnification and you will see a message - Zoom in to view individual microarray probes.
Peaks Track
The Peaks track displays the results of peak caller tasks. It displays a bar that spans genomic location of each peak call. If summits are identified by the peak caller, such as the MACS2 algorithm, then its genomic location is marked by a vertical line. The color marks either the pair being compared by the peak caller or, if present, the sample attribute associated with the sample.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Additional assistance |
|---|
|
| Page Turner | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Rate Macro |
|---|