The Single-cell QA/QC task in Partek Flow enables you to visualize several useful metrics that will help you include only high-quality cells. To invoke the Single-cell QA/QC task:
- Click a Single cell counts data node
- Click the QA/QC section of the task menu
- Click Single cell QA/QC
If your Single cell counts data node has been annotated with a gene/transcript annotation, the task will run without a task configuration dialog. However, if you imported a single cell counts matrix without specifying a gene/transcript annotation file, you will be prompted to choose the genome assembly and annotation file by the Single cell QA/QC configuration dialog (Figure 1). Note, it is still possible to run the task without specifying an annotation file. If you choose not to specify an annotation file, the detection of mitochondrial counts will not be possible.
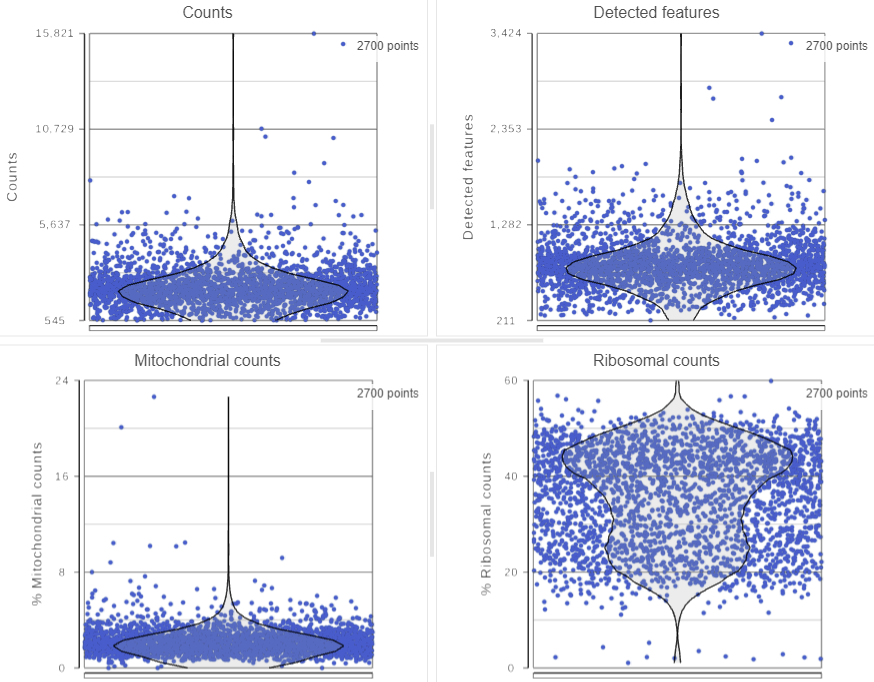
The Single cell QA/QC task report opens in a new data viewer session. Four dot and violin plots showing the value of every cell in the project are displayed on the canvas: counts per cell, detected features per cell, the percentage of mitochondrial counts per cell, and the percentage of ribosomal counts per cell (Figure 2).
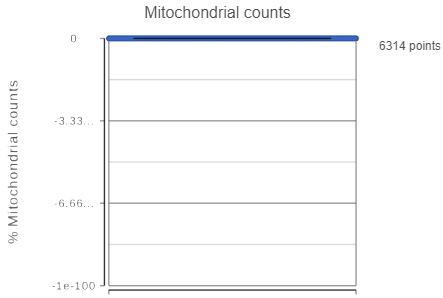
If your cells do not express any mitochondrial genes or an appropriate annotation file was not specified, the plot for the percentage of mitochondrial counts per cell will be non-informative (Figure 3).
Ribosomal genes are defined as genes that code for proteins in the large and small ribosomal subunits. Ribosomal genes are identified by searching their gene symbol against a list of 89 L & S ribosomal genes taken from HGNC. The search is case-insensitive and includes all known gene name aliases from HGNC. Identifying ribosomal genes is performed independent of the gene annotation file specified.
Total counts are calculated as the sum of the counts for all features in each cell from the input data node. The number of detected features is calculated as the number of features in each cell with greater than zero counts. The percentage of mitochondrial counts is calculated as the sum of counts for known mitochondrial genes divided by the sum of counts for all features and multiplied by 100. The percentage of ribosomal counts are calculated as the sum of counts for known ribosomal genes divided by the sum of counts for all features and multiplied by 100.
Each point on the plots is a cell. All cells from all samples are shown on the plots. The overlaid violins illustrate the distribution of cell values for the y-axis metric.
The appearance of a plot can be configured by selecting a plot and adjusting the settings in the Configuration cards on the left (Figure 4). Here are some suggestions, but feel free to explore the other options available:
- Open the Color card and reduce the Opacity using the slider. For data sets with very many cells, it may be helpful to decrease the dot opacity to better visualize the plot density.
- Open the Scale card and change the Y-axis scale to Logarithmic. This can be helpful to view the range of values better, although it is usually better to keep the Ribosomal counts plot in linear scale.
- Open the Summary card and switch on Box & Whiskers. Inspecting the median, Q1, Q3, upper 90%, and lower 10% quantiles of the distributions can be helpful in deciding appropriate thresholds.
Double click the Filtered counts data node to view the task report. The report includes a summary of the count distribution across all features for each sample; a detailed breakdown of the number of cells included in the filter for each sample; and the minimum and maximum values for each quality metric (expressed genes, total counts, etc) across the included cells for each sample (Figure 12).
Additional Assistance
If you need additional assistance, please visit our support page to submit a help ticket or find phone numbers for regional support.


| Your Rating: |
    
|
Results: |
    
|
5 | rates |