ChIP-Seq and ATAC-Seq identify enriched regions or peaks in genome. Depending on the assay, the biological meaning of enrichment changes; in ChIP-Seq, enrichment indicates protein binding, while in ATAC-Seq, enrichment indicates open chromatin. To understand the importance of enriched regions in regulating gene expression, we can add information about overlapping or nearby genomic features.
What is Annotate peaks?
Annotate peaks takes an input set of regions and checks for overlap between those regions and a gene/feature annotation. This gives regulatory context for enriched regions.
Running Annotate peaks
The input for Annotate peaks is a Peaks type data node.
- Click a Peaks data node
- Click the Peak analysis section in the toolbox
- Click Annotate peaks
- Set the Genomic overlaps parameter
The Genomics overlaps parameter lets you choose one of two options.
Report one gene region per peak (precedence applies) chooses one gene section for each peak using the precedence order to settle cases where more than one gene section overlaps a peak. The order of precedence is TSS, TTS, CDS Exon, 5' UTR Exon, 3' UTR Exon, Intron, Intergenic.
Report all gene regions per peak creates a row for each gene section that overlaps a peak in the task report.
- Choose a gene/feature annotation from the drop-down menu
- Click Finish to run
Annotate peaks output
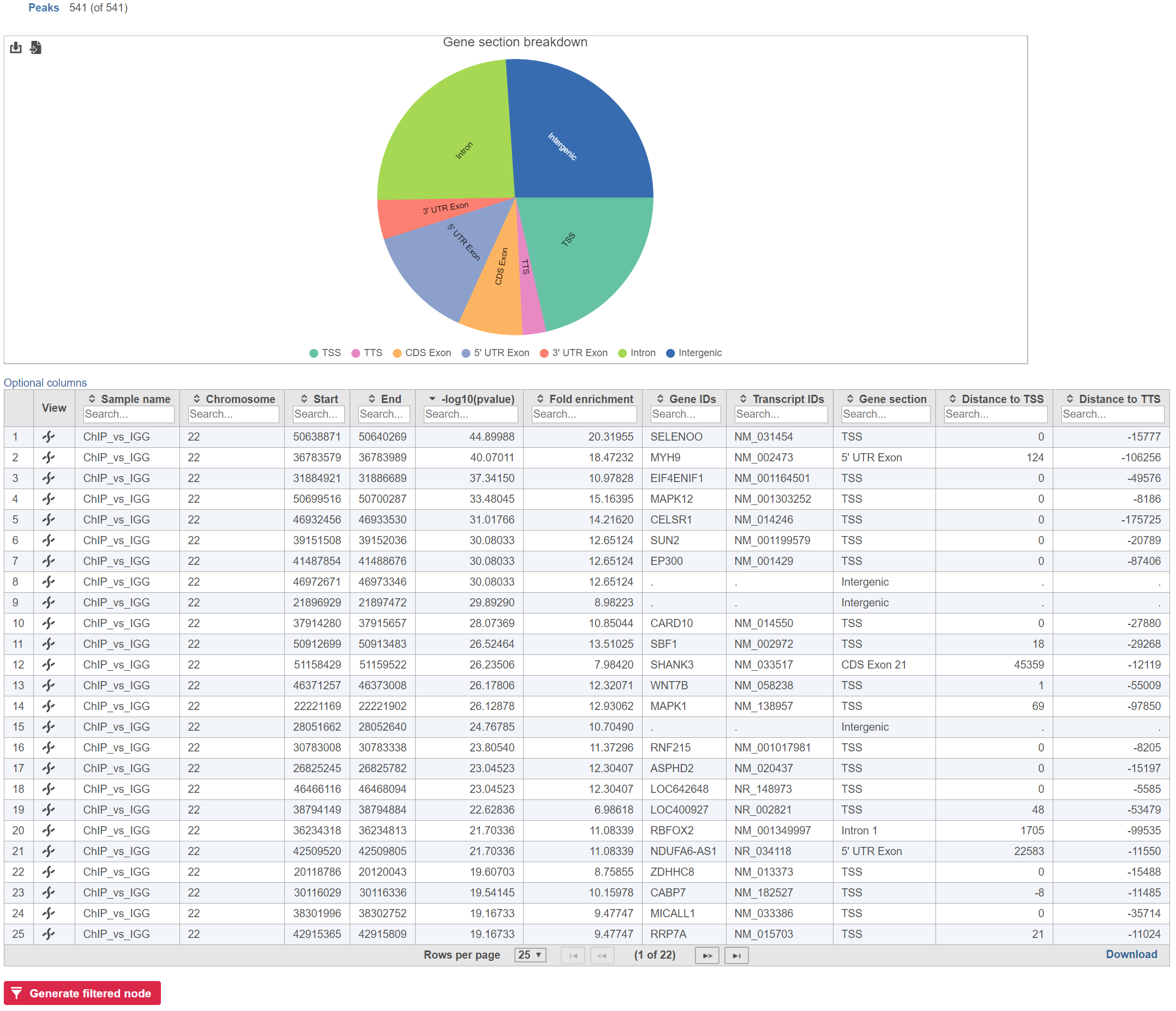
Annotate peaks produces an Annotated peaks data node. The Annotated peaks task report adds a Gene section breakdown pie chart and adds columns with information about the Gene IDs, Transcript IDs, Gene section, Distance to TSS, and Distance to TTS of each peak to the standard Peaks report (Figure 1). If run with the option to report all gene sections selected, each peak will have a row for each gene section it overlaps. If run with the option to report one gene section selected, each peak will have one row with the gene section it overlaps chosen using the order of precedence.
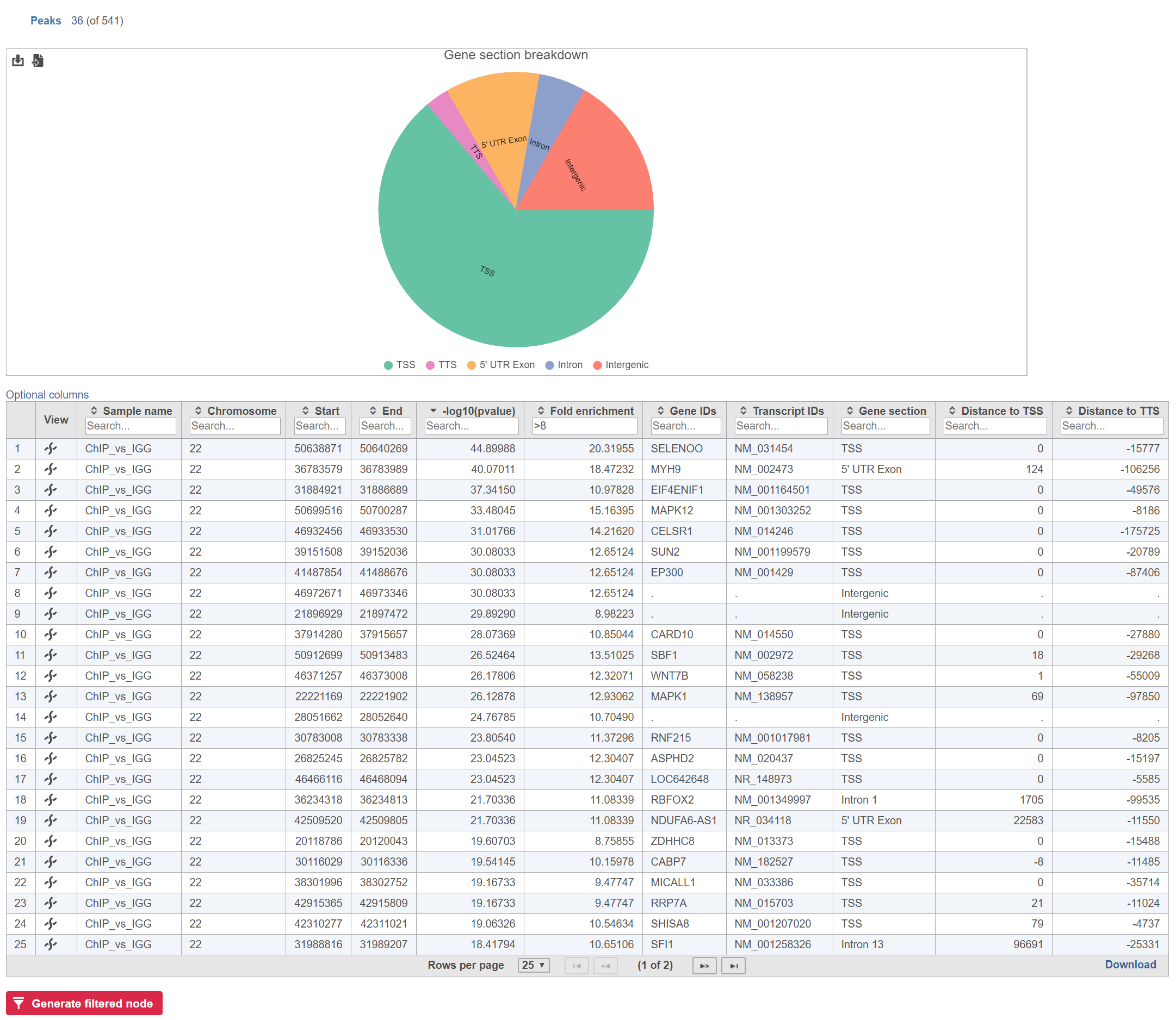
The table can be sorted and filtered by any of its columns (Figure 2). The Gene section breakdown pie chart will update as the table is filtered (the current (Peaks) and the total number of peaks (in parenthesis) are given in the upper left corner).
Gene sections
TSS
Transcription start site (TSS) is -1000bp and +100bp from the TSS for a transcript
TTS
Transcription termination site (TTS) is -100bp and +1000bp from the TTS for a transcript
CDS Exon
Coding sequence (CDS) Exon is overlapping a coding exon in a transcript
5' UTR Exon
5' Untranslated Region (UTR) Exon is overlapping an exon in the 5' UTR of a transcript
3' UTR Exon
3' Untranslated Region (UTR) Exon is overlapping an exon in the 3' UTR of a transcript
Intron
Intron is overlapping an intron in a transcript
Intergenic
Intergenic is not located within 1000bp of a transcript
Annotate peaks vs. Annotate regions
Annotate regions is almost identical to Annotate peaks. Annotate regions takes Region counts data as the input and outputs Annotated region counts. One important difference is that you cannot filter the Annotated region counts from the task report.
Run Annotate regions prior to performing differential analysis if you will want to be able to view gene section information and filter regions by gene section in the differential analysis task report.


| Your Rating: |
    
|
Results: |
    
|
2 | rates |