While processing 10x Chromium Single Cell Multiome ATAC + Gene Expression sequencing data via ‘cellranger-arc count’ pipeline, Feature linkages analysis is performed as pairs of genomic features, such as peaks and genes, that have significant correlation in signals across cells. Because it provides a basis for inferring enhancer-gene targeting relationships and constructing transcriptional networks. The features with strong linkages are considered to be “co-expressed” and enriched for a shared regulatory mechanism.
Partek Flow provides the opportunity to our users to explore the linkage relationships among different features including peaks and genes, peaks and peaks, and genes and genes. A tab-delimited file containing information of feature linkages inferred from Flow Cell Ranger - ATAC task will be loaded into Integrative Genome Viewer (IGV)[1] for exploration if Feature linkage analysis task has been completed successfully.
Running Feature linkage analysis
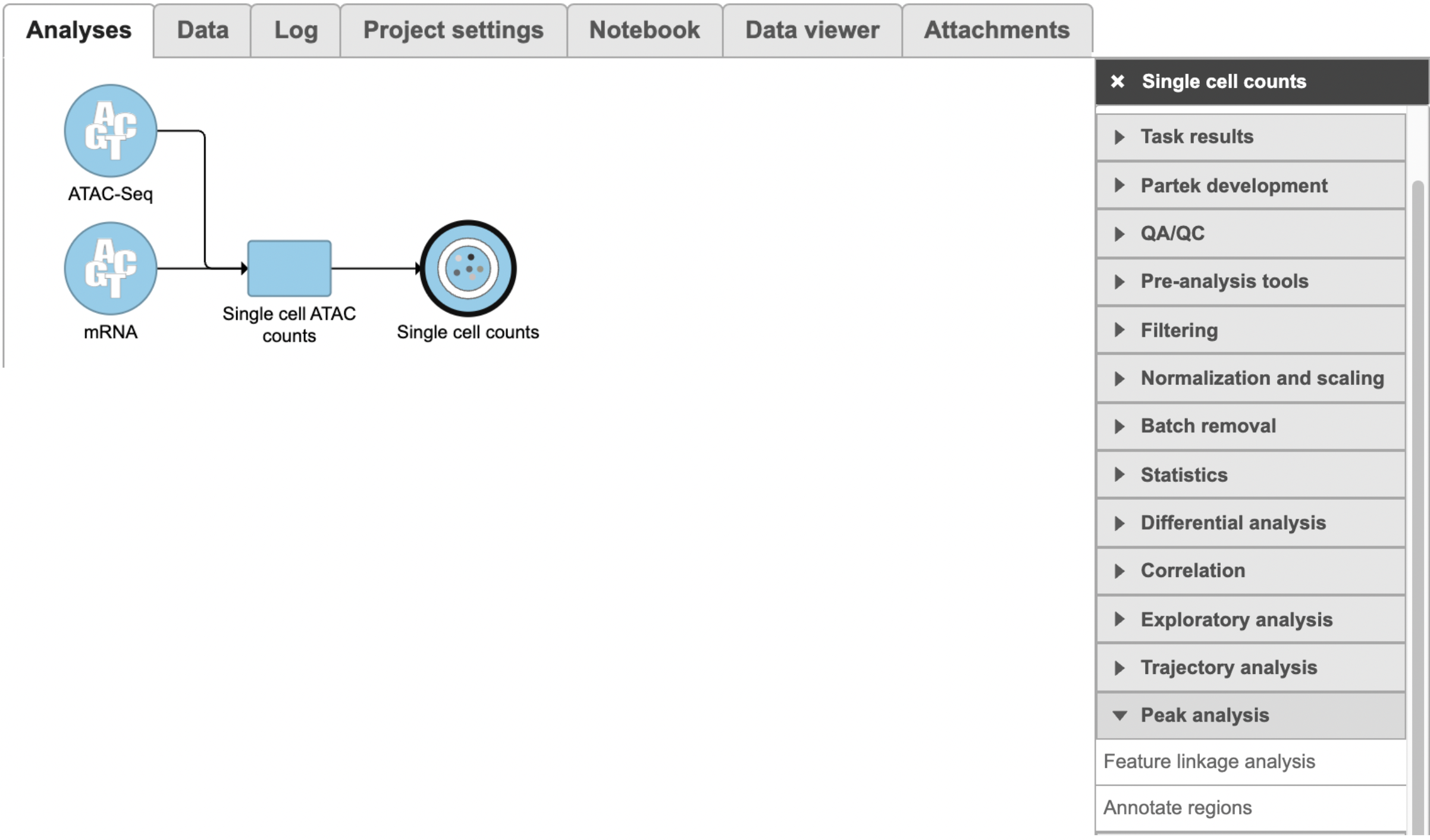
To run Feature linkage analysis task (Figure 1),
- Click one datanode that has both features of ATAC and gene expression;
- Click the Feature linkage analysis task under Peak analysis section in the toolbox;
- Click the Finish button to complete the submission.
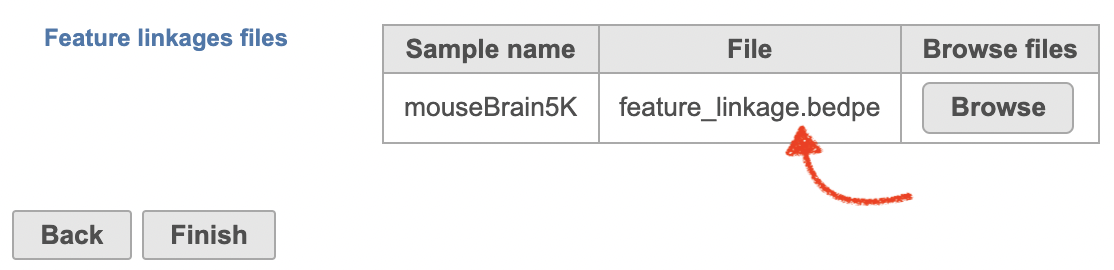
There will be no inputs needed if the FASTQ is converted to counts matrix within Flow. However, if users processed the FASTQ files outside of Partek, and imported the counts matrix into Flow later. The feature_linkage.bedpe file in outs/analysis/feature_linkage from Cell Ranger output will be needed for each sample (Figure 2) to complete the analysis.
For data where no sample attributes are specified, the peak detection pairs need to be manually defined. In the example in Figure 1, there only two samples. Under the Define pairs section, the left panel lists all the sample names uploaded to the project (H3K27 and Mock). Add one pair at a time by dragging the corresponding samples to either the IP panel on the top-right or the Control panel on the bottom-right. If no control samples are present in the experiment, leave the Control panel blank. If more than one ChIP or Control samples are added, the samples will be combined (or pooled) during the analysis. After defining a pair, click the Add pair button.
For data where the sample attributes are defined (Figure 3), you will have an additional option to add pairing or grouping based on sample attributes. Figure 3 shows an example dataset with 4 samples, 2 time points, and there is one IP sample and one Input sample in each time point.
When running the MACS2 task, sample attributes will be used to define the multiple pairs (Figure 4). There is an IP-Input pair for each time point, so the Pair attribute is the Time attribute. The Control attribute is the attribute that differentiates between the Input and IP groups, and in this example, it is the ChIP attribute. Finally, the Control term is labeled as Input in the example.
Click Generate pairs and the two pairs will be automatically added to the Pairs table (Figure 5).
Peaks report
In the task report, each pair will generate a list of peaks displayed in a table (Figure 6). Use the drop down menu next to Peaks detected for... to select the pair.
- Absolute summit: base pair location of peak summit
- Pileup: pileup height at peak summit
- -log10(pvalue): negative log10 pvalue for the peak summit
- Fold enrichment: fold enrichment for the peak summit against random Poisson distribution with local lambda
- -log10(qvalue): negative log10 qvalue at peak summit
- a peak name generated by the MACS2 algorithm
Click the browse to peak button () to invoke chromosome view and zoom into that location.
Click the Download button at the lower-right corner to download the peaks in a text file.
References
- Zhang Y, Liu T, et al. Model-based Analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 2008;9(9):R137.
Additional Assistance
If you need additional assistance, please visit our support page to submit a help ticket or find phone numbers for regional support.


| Your Rating: |
    
|
Results: |
    
|
2 | rates |