Page History
...
- Gene counts
- Transcript counts
- MicroRNA counts
- Cufflinks quantification
- Quantification
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The format of the output is the same as the input data format, the node is called Normalized counts. This data node can be selected and normalized further using the same task.
...
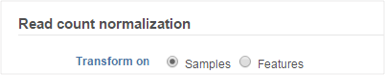
Select whether you want your data normalized on a per sample or per feature basis (Figure 2). Some transformations are performed on each value independently of others e.g. log transformation, and you will get an identical result regardless of your choice.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The following normalization methods will generate different results depending on whether the transformation was performed on samples or on features:
- Divided by mean, median, Q1, Q3, std dev, sum
...
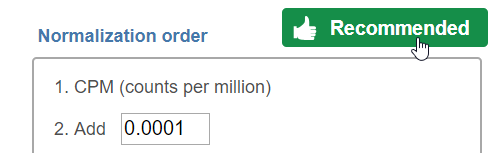
If available, the Recommended button will appear. Clicking the button will populate the right panel (Figure 3).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Normalization Methods
Below is the notation that will be used to explain each method:
...
These box-whisker plots show the expression signal distribution for each sample before and after normalization. When you mouse over on each bar in the plot, a balloon would show detailed percentile information (Figure 5).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
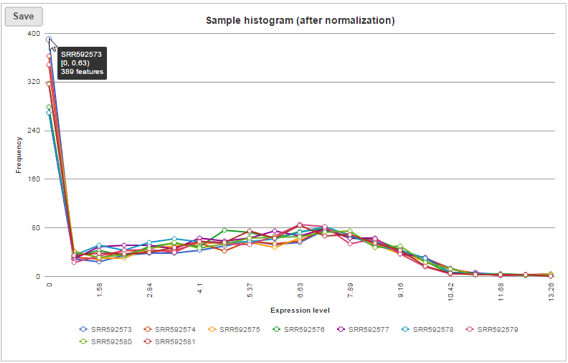
Sample histogram
A histogram is displayed for data before and after it is normalized. Each line is a sample, where the X axis is the range of the data in the node and the Y-axis is the frequency of the value within the range. When you mouse over a circle which represent a center of an interval, detailed information will appear in a balloon (Figure 6). It includes:
- The sample name.
- The range of the interval, “[ “represent inclusive, “)” represent exclusive.
- The frequency value within the interval
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
References
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed, TP. A Comparison of Normalization Methods for High Density Oligonucleotide Array Data Based on Bias and Variance. Bioinformatics. 2003; 19(2): 185-193.
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 2008; 5(7): 621–628.
- Bullard JH, Purdom E, Hansen KD, Dudoit S. Evaluation of statistical methods for normalization and differential expression in mRNA-Seq experiments. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010; 11: 94.
- Robinson MD, Oshlack A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010; 11: R25.
- Dillies MA, Rau A, Aubert J et al. A comprehensive evaluation of normalization methods for Illumina high-throughput RNA sequencing data analysis. Brief Bioinform. 2013; 14(6): 671-83.
- Wagner GP, Kin K, Lynch VJ. Measurement of mRNA abundance using RNA-seq data. Theory Biosci. 2012; 131(4): 281-5.
- Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015; 43(15):e97.
| Additional assistance |
|---|
|
| Page Turner | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Rate Macro | ||
|---|---|---|
|