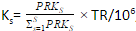Page History
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Normalization Methods
Below is the notation that will be used to explain each method:
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| S | Sample (or cell for single cell data node) |
| F | Feature |
| Xsf | Value of sample S from feature F (if normalization is performed on a quantification data node, this would be the raw read counts) |
| TXsf | transformed value of Xsf |
| C | Constant value |
| b | Base of log |
...
- Absolute value
TXsf = | Xsf | - Add
TXsf = Xsf + C
a constant value C needs to be specified - Antilog
TXsf = bxsf
A log base value b needs to be specified from the drop-down list; any positive number can be specified when Custom value is chosen - CPM (counts per million)
TXsf = (106 x Xsf)/TMRs
where Xsf here is the raw read of sample S on feature F, and TMRs is the total mapped reads of sample S.
If quantification is performed on an aligned reads data node, total mapped reads is the aligned reads. If quantification is generated from imported read count text file, the total mapped reads is the sum of all feature reads in the sample. - Divided by
When mean, median, Q1, Q3, std dev, or sum is selected, the corresponding statistics will be calculated based on the transform on sample or features option
Example: If transform on Samples is selected, Divide by mean is calculated as:
TXsf = Xsf/Ms
where Ms is the mean of the sample.
Example: If transform on Features is selected, Divide by mean is calculated as:
TXsf = Xsf/Mf
where Mf is the mean of the feature. - Log
TXsf = logbXsf
A log base value b needs to be specified from the drop-down list; any positive number can be specified when Custom value is chosen - Logit
TXsf=logb(Xsf/(1-Xsf))
A log base value b needs to be specified from the drop-down list; any positive number can be specified when Custom value is chosen - Lower bound
A constant value C needs to be specified,
if Xsf is smaller than C, then TXsf= C; otherwise, TXsf = Xsf - Multiply by
TXsf = Xsf x C
A constant value C needs to be specified - Quantile normalization, a rank based normalization method.
For instance, if transformation is performed on samples, it first ranks all the features in each sample. Say vector Vs is the sorted feature values of sample S in ascending order, it calculates a vector that is the average of the sorted vectors across all samples --- Vm, then the values in Vs is replaced by the value in Vm in the same rank. Detailed information can be found in [1]. - RPKM (Reads per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads [2])
TXsf = (109 * Xsf)/(TMRs*Lf)
Where Xsf is the raw read of sample S on feature F,
TMRs is the total mapped reads of sample S,
Lf is the length of the feature F,
If quantification is performed on an aligned reads data node, total mapped reads is the aligned reads. If quantification is generated from imported read count text file, the total mapped reads is the sum of all feature reads in the sample.
If the feature is a transcript, transcript length Lf is the sum of the lengths of all the exons. If the feature is a gene, gene length is the distance between the start position of the most downstream exon and the stop position of the most upstream exon. See Bullard et al. for additional comparisons with other normalization packages [3]
For paired reads, the normalization option will show up as FPKM (Fragments per kilobase per million mapped reads) rather than RPKM. However, the calculations are the same.
...
- Normalize the reads by the length of feature, it generate reads per kilobase
RPKsf = Xsf / Lf; - Sum up all the RPKsf in a sample
PRKs = ∑Ff=1 FRPKsf - Generate a scaling factor for each sample by normalizing the PRK of the sample to the sum PRK of all the samples
,
where TR is the total reads across all samples - Divide raw reads by the scaling factor to get TPM
TXsf = Xsf/Ks
- Normalize the reads by the length of feature, it generate reads per kilobase
- Total count(Reads per million)
TXsf = (106 x Xsf)/TMRs
where Xsf here is the raw read of sample S on feature F, and
TMRs is the total mapped reads of sample S.
If quantification is performed on an aligned reads data node, total mapped reads is the aligned reads. If quantification is generated from imported read count text file, the total mapped reads is the sum of all feature reads in the sample.
Upper quartile - The method is exactly the same as the LIMMA package [7].
The following is the simple summarization of the calculation:
- Remove all the features that have 0 reads in all samples.
- Calculate the effective library size per sample: effective library size = (raw library size (in millions))*((upper quartile for a particular sample)/ (geometric mean of upper quartiles in all the samples) * (raw library size (in millions))
- Get the normalized counts by dividing the raw counts per feature by the effective library size (for the respective sample)
Normalization Report
The Normalization report includes the Normalization methods used, a Feature distribution table, Box-whisker plots of the Expression signal before and after normalization, and Sample histogram charts before and after normalization. Note that all visualizations are disabled for results with more than 30 samples.
...
Overview
Content Tools