Page History
...
If there is more than one factor in the model, more complex criteria combining the factors can be specified using Tools>List Manager menu Advanced tab. For example, to find categories that are significant and changed by at least two fold, make two criteria: one for a low p-value and the other for a minimum of two fold change, and take the intersection of the two criteria.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
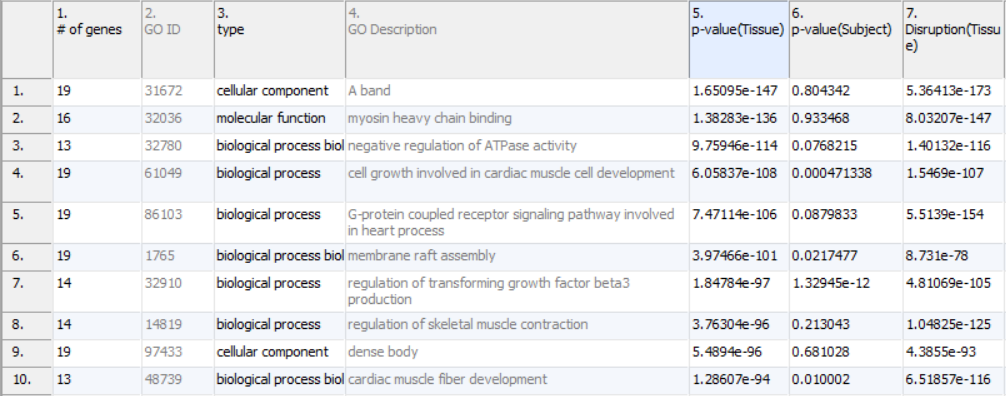
If the disruption (factor*gene interaction) is tested, the filters can become more complicated. The most pressing need for complex filters is that when analyzing larger functional groups it is not expected that the entire functional group will behave the same. Looking back at Figure 1, notice how the low values in column 7 are present because not every gene is equally differentially expressed even in the most differentially expressed of groups. That is, when there is significant differential expression, it is likely that there will also be disruption as at least a single gene is likely participating in a role beyond that of the functional group and will not follow the pattern of the rest of the group. This situation is expected and leads to a new type of filter.
...