Page History
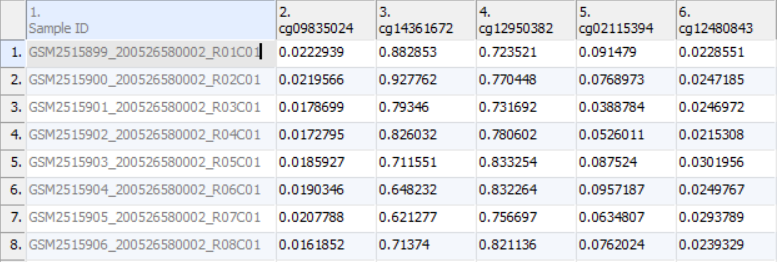
Once the .idat files are imported, you will be facing the Scatter Plot. To move forward with the tutorial, switch to the Analysis tab and take a look at the top level (i.e. initial) Each row of the spreadsheet (Figure 1) . Samples identifiers are corresponds to a single sample. The first column is the names of the .idat files as shown by the Sample ID column while all the and the remaining columns are the array probes. The table values are β-values, which correspond to the percentage methylation at each site. A β-value is calculated as the ratio of methylated probe intensity over the overall intensity at each site (the overall intensity is the sum of methylated and unmethylated probe intensities).
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
An alternative metric for measurement of methlyation levels are M-values. β-values can be easily converted to M-values using the following equation:
M-value = log2( β / (1 - β))
Here's the interpretation: a MAn M-value close to 0 for a CpG site indicates a similar intensity between the methylated and unmethylated probes, which means the CpG site is about half-methylated. Positive M-values mean that more molecules are methylated than unmethylated, while negative M-values mean that more molecules are unmethylated than methylated. As discussed by by Du and colleagues, the the β-value has a more intuitive biological interpretation, but the M-value is more statistically valid for the differential analysis of methylation levels.
Therefore, the Because we are performing differential methylation analysis of the tutorial data will be performed on the M-values; select , we need to convert our data to from β-values to M-values.
- Select Convert Beta Value to M Value
...
- from the Import section of the Illumina BeadArray Methylation workflow
The original data (β-values) will be overwritten.Before proceeding to exploratory data
- Select () from the icon bar to save the current spreadsheet
Before we can perform any analysis, the study samples need to be organized in four groups, two biological replicates each. In the Import section of the workflow, select Add Sample Attributes and, in the next into their experimental groups.
- Select Add Sample Attributes from the Import section of the Illumina BeadArray Methylation workflow
- Select Add a Categorical Attribute from the Add Sample Attributes dialog (Figure 2)
...
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
...
- Select OK
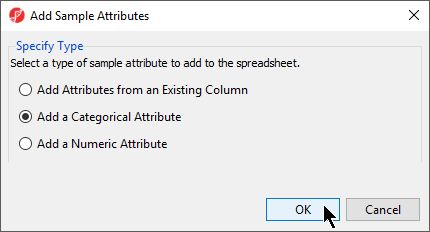
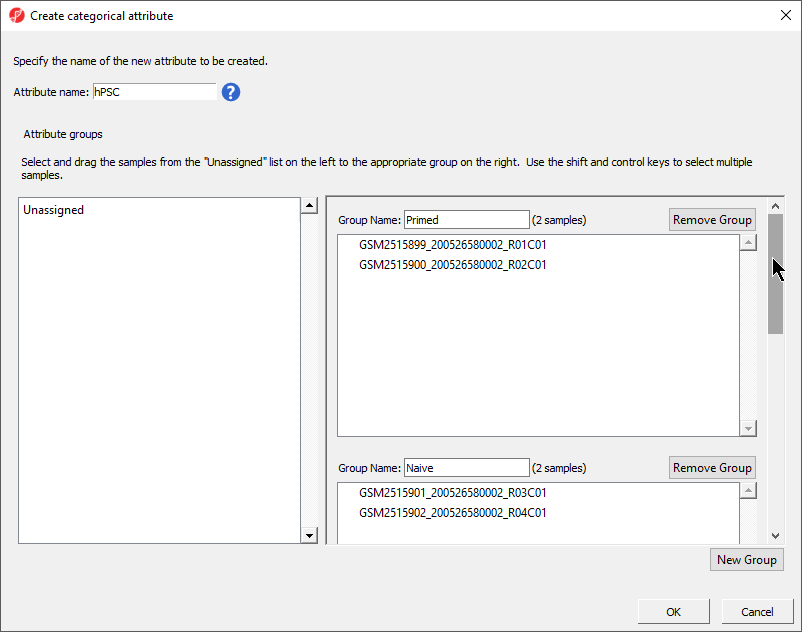
The Create categorical attribute dialog (Figure 3) . The Attribute name filed specifies the name of the new column (attribute), while the groups (levels of the attribute) are specified in the Group Name fieldsallows us to create groups for a categorical attribute. By default, two groups are created, but additional ones groups can be added using the New Group button. Finally, drag and drop the samples from the Unassigned list to their matching groups.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
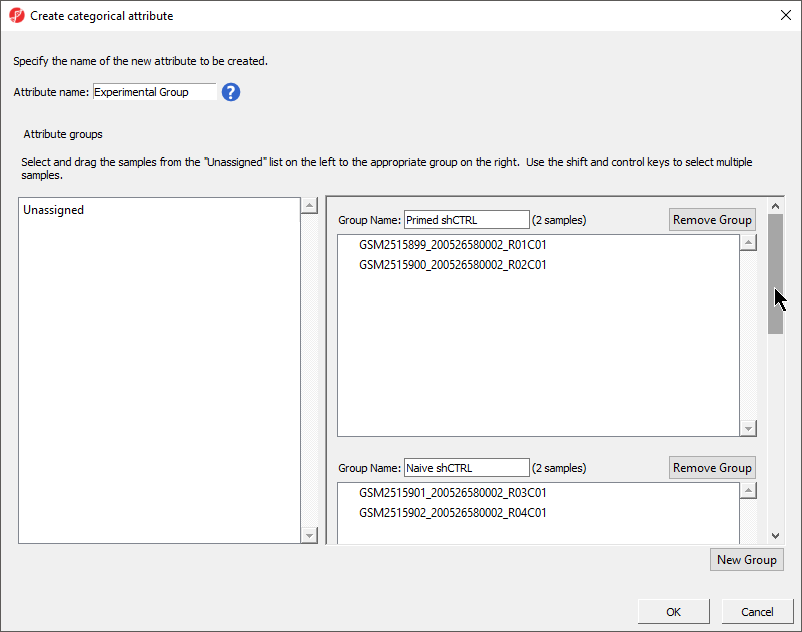
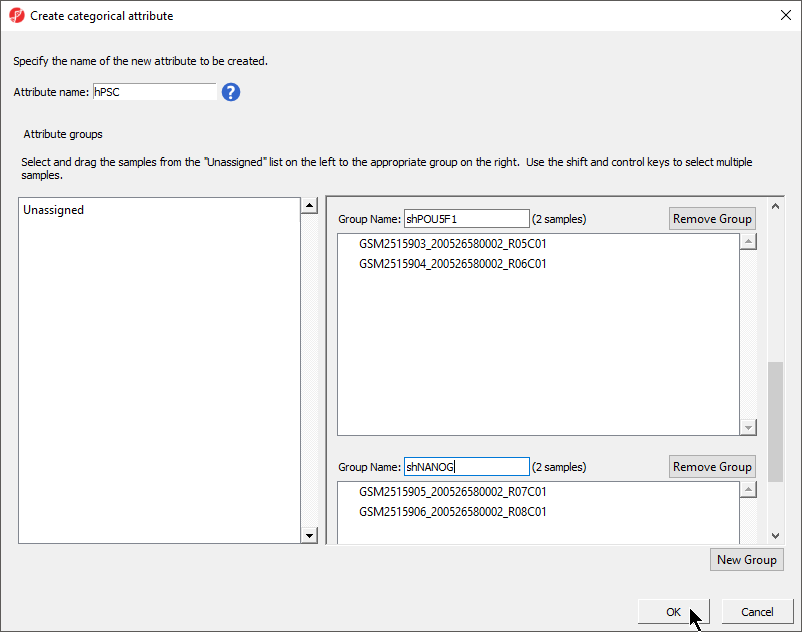
For this analysis, specify Attribute name as HPSC and then create the groups and add samples to them using the table below.
- Select New Group twice to add two additional groups
- Set Attribute name: to hPSC
- Rename the four groups Primed, Naive, shPOU5F1, and shNANOG
- Drag and drop the samples from the Unassigned list to their groups as listed in the table below
| Sample ID | Group Name |
|---|---|
GSM2515899_200526580002_R01C01 | Primed |
GSM2515900_200526580002_R02C01 | Primed |
GSM2515901_200526580002_R03C01 | Naive |
GSM2515902_200526580002_R04C01 | Naive |
GSM2515903_200526580002_R05C01 | shPOU5F1 |
GSM2515904_200526580002_R06C01 | shPOU5F1 |
GSM2515905_200526580002_R07C01 | shNANOG |
GSM2515906_200526580002_R08C01 | shNANOG |
Push OK. When asked to add another categorical attribute, say No, and the confirm that you would like to save the spreadsheet (Yes).
Section Heading
Section headings should use level 2 heading, while the content of the section should use paragraph (which is the default). You can choose the style in the first dropdown in toolbar.
There should now be four groups with two samples in each group (Figure 4).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Select OK
- Select No from the Add another categorical attribute dialog
- Select Yes to save the spreadsheet
A new column as been added to spreadsheet 1 (Differential Methylation Analysis) with the experimental group of each sample.
| Page Turner | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Additional assistance |
|---|
|
| Rate Macro | ||
|---|---|---|
|