Page History
...
If the Log Odds are undefined because of machine numeric representation limitations, then the log odds are capped at 106.
Partek Genotype Likelihood Dialog
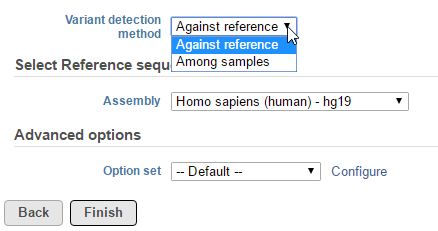
Selecting Partek Genotype Likelihood from the context sensitive menu will bring up the task dialog, which contains three default sections: Variant detection method, Select Reference sequence, and Advanced options.
In the Variant detection method drop-down list, Against reference will compare base composition for each sample against the reference sequence assembly, independently (Figure 1).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
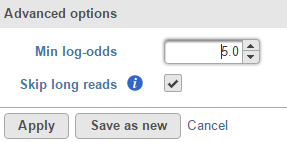
The detection method produce log-odds score, a high log-odds score for a reported SNV indicates a strong chance that the nucleotide is different from the reference sequence at that particular position in the detected sample. By default minimum log-odds on the reported SVN is 5. To change the value, click on Configure the Advanced options (Figure 2):
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Variant detection among sample option is to compare base composition across all the samples in the input data node, but not to compare the reference sequence. A high log-odds score indicates a strong chance that at least one of the samples has a different base call at the position. This is useful in detection somatic mutations if there are 1 pair (two samples) in the input data.
| Additional assistance |
|---|
|
Overview
Content Tools