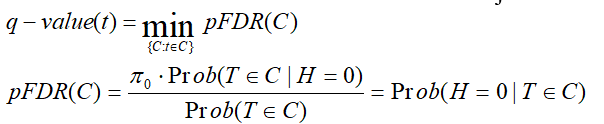Page History
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
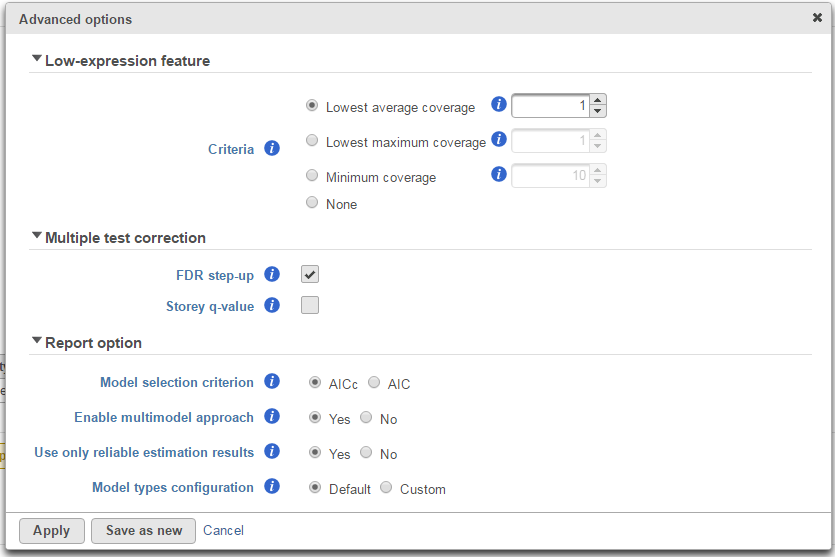
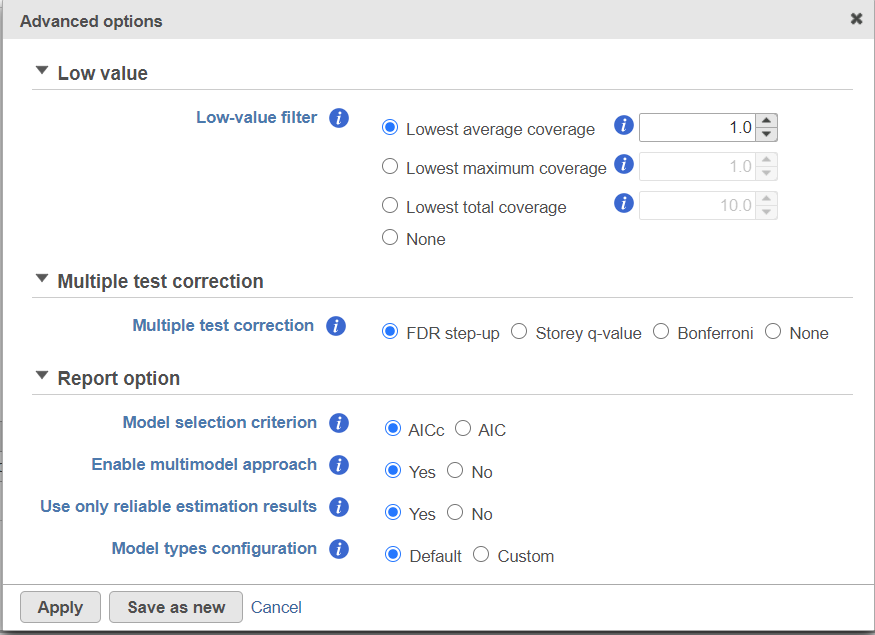
Low-expression feature
...
Multiple test correction can be performed on the p-values of each comparison, with FDR step-up being the default (1). If you check the Other options like Storey q-value (2), an extra column with q-values will be added to the report.In the step up method, and Bonferroni are provided, select one method at a time; None means no multiple test correct will be performed.
FDR step-up:
Suppose there are n p-values (n is the number of features). The p-values are sorted by ascending order and m represents the rank of a p-value. The calculation compares p-value*(n/m) with the specified alpha level, and the cut-off p-value is the one that generates the last product that is less than the alpha level. The goal of step up method is to find:
...
In order to find K* , start with Sn* and then go up the list until you find the first step up value that is less or equal to alpha.
In the Storey q-value method, :
q-value is the minimum "positive false discovery rate" (pFDR) that can occur when rejecting a statistic.
For an observed statistic T=t and nested set of rejection area {C},
Bonferroni:
Suppose there are n p-values (n is the number of features), the expected number of Type I errors would be given by , thus the significance level of each individual test should be adjusted to . Alternatively the p-values should be adjusted as pB=p*n, pB is Bonferroni corrected p-value. If pB is greater than 1, it is set to 1
Report option
This section configures how to select the best model for a feature. There are two options for Model selection criterion: AICc (Akaike Information Criterion corrected) and AIC (Akaike Information Criterion). AICc is recommended for small sample size, while AIC is recommended for medium and large sample size What about large samples?(3). Note that when sample size grows from small to medium, AICc converges to AIC. Taking the AICc/AIC value into account, GSA considers the model with the lowest information criterion as the best choice.
...
The design pool can also be restricted by Min error degrees of freedom. The minimal When "Model types configuration" is set to Default , this is automated as follows: it is desirable to keep the error degrees of freedom is at or above six. Therefore, we automatically set to the largest k (k represents the error degree of freedom of the model) in the design model pool, with 0 <= k <=6 for which admissible models exist. Admissible model is one that can be estimated given the specified contrasts. In the above example, when we compare A vs B in Cell type, there are three possible design models. The error degree of freedom of model Cell type is largest and the error degree of freedom of model Cell type, Time, Cell type * Time is the smallest:
...
If the sample size is big, k >=6 in all three models, all the models will be evaluated and the best model will be selected for each feature. However, if the sample size is too small, none of the models will have k >=6, then only the model with maximal k will be used in the calculation. If the maximal k happens to be zero, we are forced to use Poisson response distribution only.
There are two types of p-value, F and Wald., Poisson, negative binomial and normal models can generate p-value using either Wald or F statistics. Lognormal models always employ the F statistics; the more replicates in the study, the less the difference between the two options. When there are no replicates, only Poisson can be used to generate p-value using Wald.
Note: Partek Flow keeps tracking the log status of the data, and no matter whether GSA is performed on logged data or not, the LSMeans, ratio and fold change calculation is are always in linear scale. Ratio is the ratio of the two LSMeans from the two groups in the comparison (left is the numerator, right is the denominator); Fold change is converted from ratio: when ratio is greater than 1, fold change is same as ratio; when ratio is less than one, fold change is -1/ratio. In other words - fold change value is always >=1 or <=-1, there is no fold change value between -1 and 1. When the LSmean of numerator group is greater than that of denominator group, fold change is greater than 1; when LSmean of numerator group is less than denominator group, fold change is less than 1; when the group groups are the same, fold change is 1. Logratio is ratio is log2 transformed, which is equivalent to logfoldchange is some other software.
GSA report
If there are multiple design models and multiple distribution types included in the calculation, the fraction of genes using each model and type will be displayed as pie charts in the task result (Figure 9).
...
- Feature ID information: if transcript level analysis was performed, and the annotation file has both transcript and gene level information, both gene ID and transcript ID are displayed. Otherwise, the table shows only the available information.
- Total readscounts: total number of read counts across all the samples observations from the input data in linear space. If the input data is quantification output, then the total reads is the sum of reads of raw counts; if the input data is normalized, then the total reads is the sum of normalized reads; if the input data is logged, then the total reads is the sum of anti-logged value.
- Each contrast outputs p-value, FDR step up p-value, ratio and fold change in linear scale, LSmean of each group comparison in linear scale
When you click on the Optional columns link on the top-left corner of the table, extra information will be displayed in the table when select:
- Maximum count: maximum number of reads counts across all the observations from the input data.
- Geometric mean: geometric mean value of the input counts across all observations.
- Arithmetic mean: arithmetic mean value of input counts across all observations.
Click on View extra details report () icon under View section to get more statistical information about the feature. In a case that the task doesn't fail, but certain statistical information is not generated, e.g. p-value and/or fold change of a certain comparison are not generated for some or all feature, click on this icon to get more information by mousing over the read exclamation icon
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Feature list filter panel is on the left of the table (Figure 12). Click on the black triangle ( ) to collapse and expand the panel.
...
The filtered result can be saved into a filtered data node by selecting the Generate list button at the lower-left corner of the table ( ). Selecting the Download button at the lower-right corner of the table downloads the table as a text file to the local computer.
...