Page History
...
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a very powerful technique for identifying differentially expressed genes in a multi-factor experiment. In this data set, ANOVA will be used to generate a list of genes that are significantly regulated by each treatment by two-fold.
Adding factors and interactions
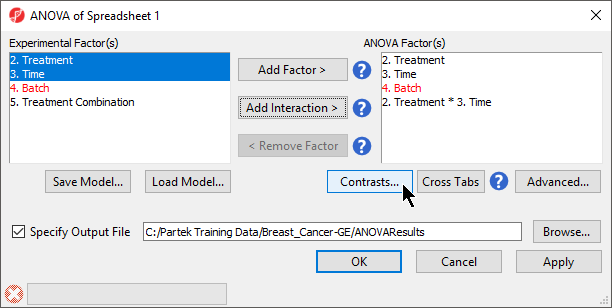
When setting up the ANOVA, the primary factors of interest, Treatment and Time, should be included. We will also include the interaction between Treatment and Time, Treatment * Time, because we are interested in whether different treatments behave differently over time. From our exploratory analysis using the PCA, we also know that Batch is a major source of variation and needs to be included. Including Batch as a random factor will allow us to account for the batch effect.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Adding linear contrasts
ANOVA will output a p-value and F ratio for each factor or interaction; to get the fold-change and ratio between the different levels of a factor or interaction, a linear contrasts, or comparisons, must be added.
...
- Select OK to perform the ANOVA
ANOVA results spreadsheet
The result of the 3-way mixed model ANOVA is displayed in a new spreadsheet, ANOVA-3way (ANOVAResults) that is a child of the Breast_Cancer.txt spreadsheet. In ANOVAResults, each row represents a probe(set)/gene with the columns containing the results of the ANOVA (Figure 5).
...
Each contrast in the ANOVA adds p-value, ratio, and fold-change columns. The p-value is calculated using log space. The ratio and fold change are calculated using linear space.
Viewing the sources of variation
Sources of variation captured in the ANOVA can be viewed for the entire data set or for individual probe(sets)/genes.
...