Page History
...
If the Require junction reads to match introns check button is selected, only junction reads that overlap with exonic regions and match the skipped bases of an intron in the transcript will be included in the calculation. Otherwise, as long as the reads overlap within the exonic region, they will be counted. Detailed information about read compatibility can be found in the Understanding Reads tutorial.
There are five options in Strand specificity drop-down selection. We recommend verifying with the data source how the NGS library was prepared to ensure correct option selection.
Some library preparations reverse transcribe the mRNA into double stranded cDNA, thus losing strand information. In this case, the total transcript count will include all the reads that map to a transcript location. Others will preserve the strand information of the original transcript by only synthesizing the first strand cDNA. Thus, only the reads that have sense compatibility with the transcripts will be included in the calculation. We recommend verifying with the data source how the NGS library was prepared to ensure correct option selection.
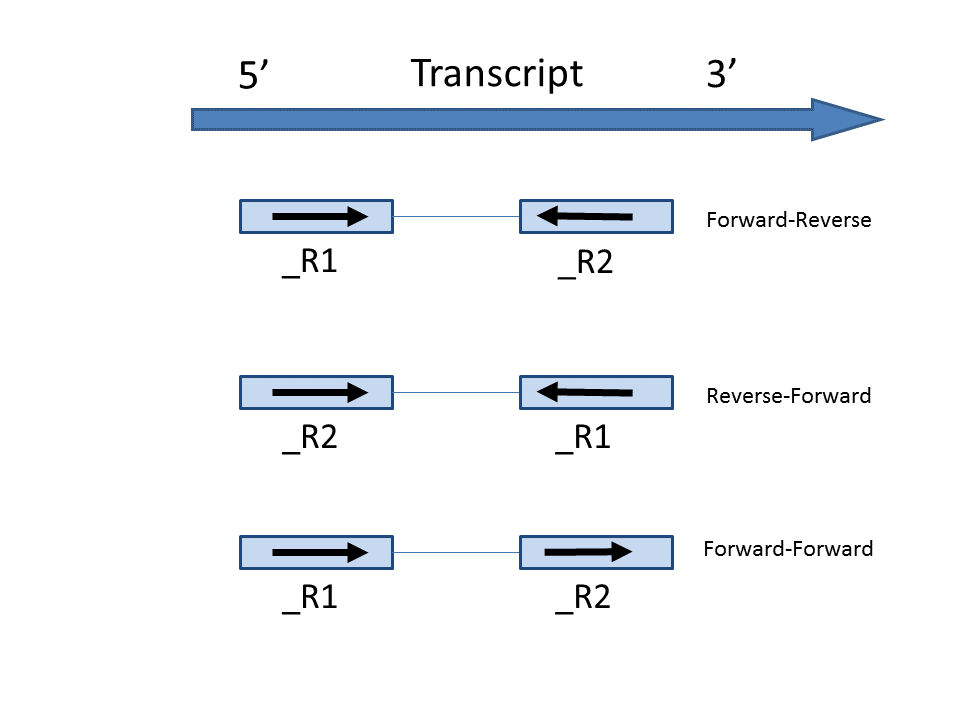
In the options, forward means the strand of the read must be the same as the strand of the transcript while reverse means the read must be the complementary strand to the transcript (Figure 3). The options in the drop-down list will be different for paired-end and single-end data. For paired-end reads, the dash separates first- and second-in-pair. For paired end reads, we determine these , determined by the flag information of the read in the BAM file. For single end reads, they are treated as the first read of paired end read. Briefly, the Briefly, the paired-end Strand specificity options are:
- No: Reads will be included in the calculation as long as they map to exonic regions, regardless of the direction.
- Auto-detect: The first 200,000 reads will be used to examine the strand compatibility with the transcripts. Two percentages are calculated: (1) the percentage of reads whose first-in-pair is the same strand as the transcript and second-in-pair is the opposite strand to transcript, (2) the percentage of reads whose first-in-pair is the opposite strand to transcript and second-in-pair is the same strand as the transcript. If the 1st percentage is higher than 75%, the Forward-Reverse option will be used. If the 2nd percentage is higher than 75%, the Reverse-Forward option will be used. If neither of the percentages exceed 75%, No option will be used.
- Forward - Reverse: this option is equivalent to the --fr-secondstrand option in Cufflinks [1]. First-in-pair is the same strand as the transcript, second-in-pair is the opposite strand to the transcript.
- Reserve Reverse - Forward: this option is equivalent to --fr-firststrand option in Cufflinks. First-in-pair is the opposite strand to the transcript, second-in-pair is the same strand as the transcript. The Illumina TruSeq Stranded library prep kit is an example of this configuration.
- Forward - Forward: Both ends of the read are matching the strand of the transcript. Generally colorspace data generated from SOLiD technology would follow this format
The single-end Strand specificity options are:
- No: same as for paired-end reads
- Auto-detect: same as for paired-end reads. All single-end reads are treated as first-in-pair reads
- Forward: this option is equivalent to the --fr-secondstrand option in Cufflinks. The single-end reads are the same strand as the transcript
- Reverse: this option is equivalent to --fr-firststrand option in Cufflinks. The single-end reads are the opposite strand to the transcript. The Illumina TruSeq Stranded library prep kit is an example of this configuration
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...