Page History
...
We recommend uploading your FASTQ files (fastq.gz) to a folder on the Partek® Flow® server before importing them into a project. Data files can be transferred into Flow from the Home page by clicking the Transfer file button (Figure 1). Following the instruction In Figure 1 to complete the data transfer. Users have the option to change the Upload directory by clicking the Browse button and either select another existing directory or create a new directory.
To create a new project, from the Home page click the New Project Project button; enter a project name and then click Create project (Figure 1). Once a new project has been created, the user is automatically directed to the Data tab of the Project View.
...
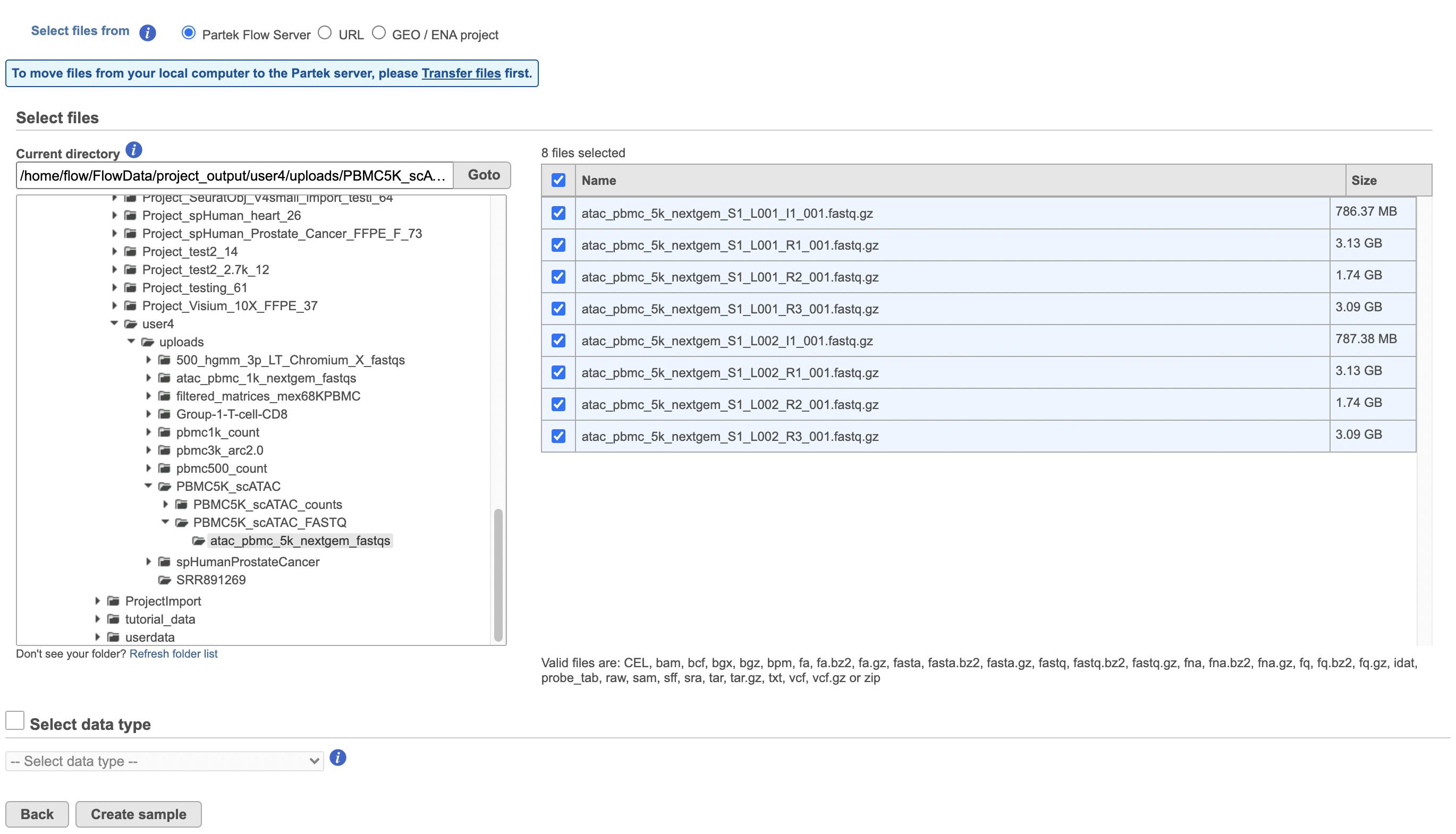
To proceed, click the Import button in the Data tab (Figure 2). Click the Automatically create samples from files button. The file browser interface will open (Figure 3). Select the FASTQ files using the file browser interface and push the Create sample button to complete the task. Paired end reads will be automatically detected and multiple lanes for the same sample will be automatically combined into a single sample. We encourage users to include all the FASTQ files including the index files although they are optional.
When the FASTQ files have finished importing, the Unaligned reads data node will turn from transparent to opaque.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Normalization
Because different cells will have a different number of total counts, it is important to normalize the data prior to downstream analysis. For droplet-based single cell isolation and library preparation methods that use a 3' counting strategy, where only the 3' end of each transcript is captured and sequenced, we recommend the following normalization - 1. CPM (counts per million), 2. Add 1, 3. Log2. This accounts for differences in total UMI counts per cell and log transforms the data, which makes the data easier to visualize.
- Click the Filtered cells results node produced by the Filtered counts task
- Click Normalization and scaling in the context-sensitive task menu on the right
- Click Normalization
- Click to add the recommended normalization scheme
This adds CPM (counts per million), Add 1, and Log2 to the Normalization order panel. Normalization steps are performed in descending order.
...
Convert FASTQ to count
To deal with the single cell ATAC-seq FASTQ data, Flow® has wrapped the 'cellranger-atac count' pipeline from Cell Ranger ATAC v2.0[1]. It takes FASTQ files and performs multiple analysis simultaneously including reads filtering and alignment, barcode counting, identification of transposase cut sites, peak and cell calling, and generates the count matrix.
To run Cell Ranger - ATAC task:
- Click the Unaligned reads data node
- Select Cell Ranger - ATAC in the 10x Genomics section in the task menu on the right
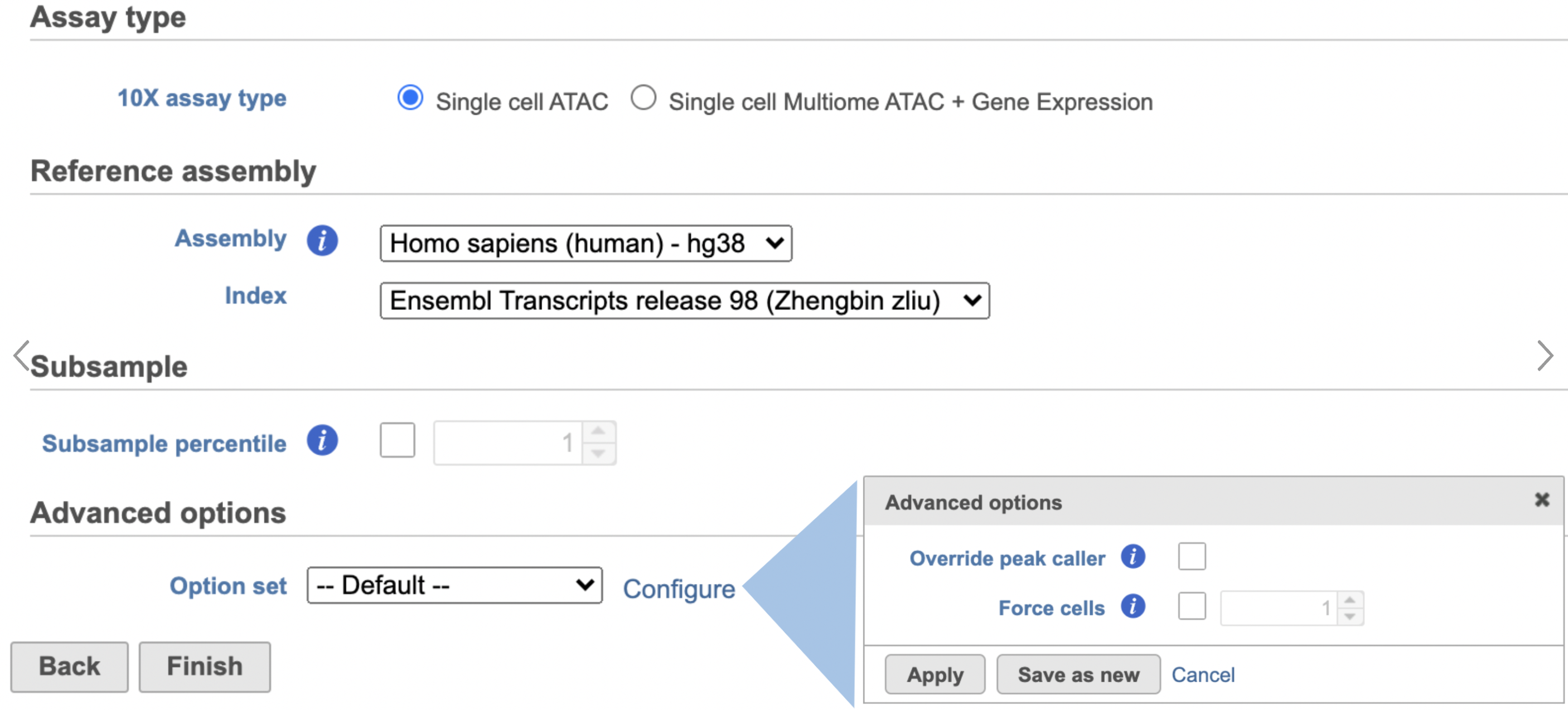
- Select Single cell ATAC in Assay type for ATAC-Seq data only
- Choose the proper Reference assembly for the data
- Press the Finish button to run the task with default settings (Figure 4)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
A new Normalized counts data node will be produced. You can choose to change the color of this node by right-clicking on the task node then clicking Change color and/or rename the result node by right-clicking and selecting Rename data node.
In the example below, I have changed the color to dark blue and renamed the results node based on the scheme.
...
| |
To learn more about how to Flow Cell Ranger - ATAC task, please refer to our online documentation.
The output of the count matrix then becomes the starting point for downstream analysis for scATAC-seq data in Flow (Figure 5).
Filter features
A common task in bulk and single-cell RNA-Seq analysis is to filter the data to include only informative genes (features). Because there is no gold standard for what makes a gene informative or not and ideal gene filtering criteria depend on your experimental design and research question, Partek Flow has a wide variety of flexible filtering options. The Filter features step can also be performed before normalization.
...