Page History
...
In survival analysis, the event should be well-defined with two levels and occur at a specific time. Because the primary outcome of the event is typically unfavorable (e.g., death, metastasis, relapse, etc.), the event is called a “hazard.” The hazard ratio is used to assess the likelihood of the event occurring while controlling for other co-predictors (co-variables/co-factors) if added to the model. In other words the hazard ratio is how rapidly an event is experienced by comparing the hazard between groups. A hazard ratio greater than 1 indicates a shorter time-to-event, a hazard ratio less than 1 is associated with a greater time-to-event, and a hazard ratio of 1 indicates no effect on time-to-event. For example, if the hazard ratio is 2 then there is twice a chance of occurrence compared to the other group. More Click here for more information on hazard ratios.
...
Cox regression (Cox proportional-hazards model) tests the effects of factors (predictors) on survival time. Predictors that lower the probability of survival at a given time are called risk factors; predictors that increase the probability of survival at a given time are called protective factors. The Cox proportional-hazards model are similar to a multiple logistic regression that considers time-to-event rather than simply whether an event occurred or not. Cox regression should not be used for a small sample size (n < 40) because the events could accidently concentrate into one of the cohorts leading to an infinite hazard ratio which will not produce meaningful results (Xu R, Shaw PA, Mehrotra DV. Hazard ratio estimation in small samples. Stat Biopharm Res. https://shawstat.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Hazard-ratio-estimation-in-small-samples.pdf) Click here to read more about hazard ratio estimation in small samples.
Configuring the Cox Regression Dialogue
...
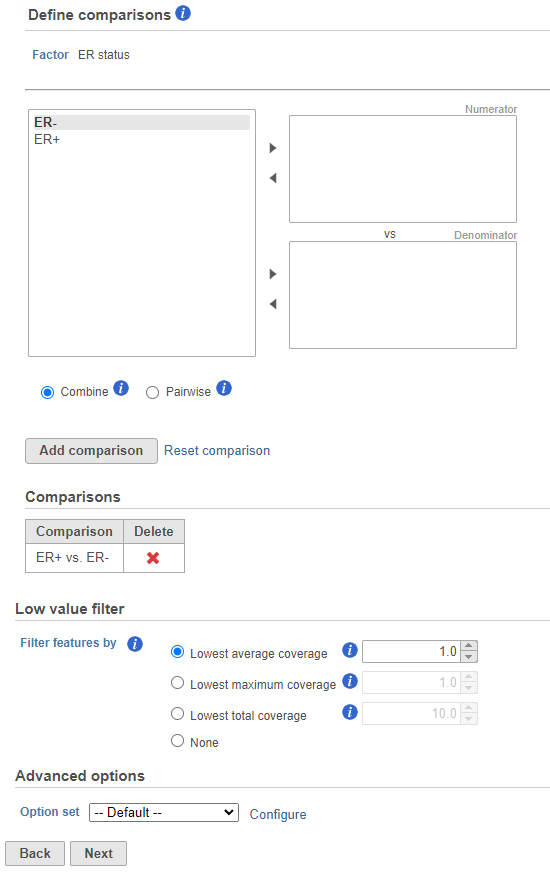
- Next, the user can define comparisons for the co-predictors if they have been added. Configure contrasts by moving factors into the numerator (e.g. experimental factor) or denominator (e.g. control factor / reference), choose Combine or Pairwise, and add the comparison which will be displayed below. Combine all numerator levels and combine all denominator levels in a single comparison or choose Pairwise to split all numerator levels and split all denominator levels into a factorial set of comparisons meaning every numerator will be paired with every denominator. Multiple comparisons from different factors can be added with Add comparison. Low value filter can be used to filter by excluding features; choose a filter or select none. Click Next to proceed with the task.
- Select The user can select categorical factors to perform stratification if needed. Stratification is used when proportional hazard assumptions are violated or not constant over time with co-predictors. Stratified Cox regression accounts for non-proportional hazards over time by optimizing hazard strata then fitting the stratified Cox regression model. In other words, the data is split into subgroups based on the categorical variable and the model is re-estimated. This accounts for the effect of a co-predictor that varies over time. Click Finish to complete the task.
- The results of Cox regression analysis provide key information to interpret, including:
- Hazard ratio (HR): if the HR = 0.5 then half as many patients are experiencing the event compared to the control group, if the HR = 1 the event rates are the same in both groups, and if the HR = 2 then twice as many are experiencing an event compared to the control group.
- HR limit:
- P-value: the lower the p-value, the greater the significance of the observation.
Kaplan-Meier Survival Curve
staircase pattern (instead of straight lines connecting each point). Each drop in this staircase represents the occurrence of on (or more) events of interest for this plotted group.
...