Page History
...
Compatible reads with junction are reported in a separate block of columns in the transcripts spreadsheet (“junction RPKM”).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
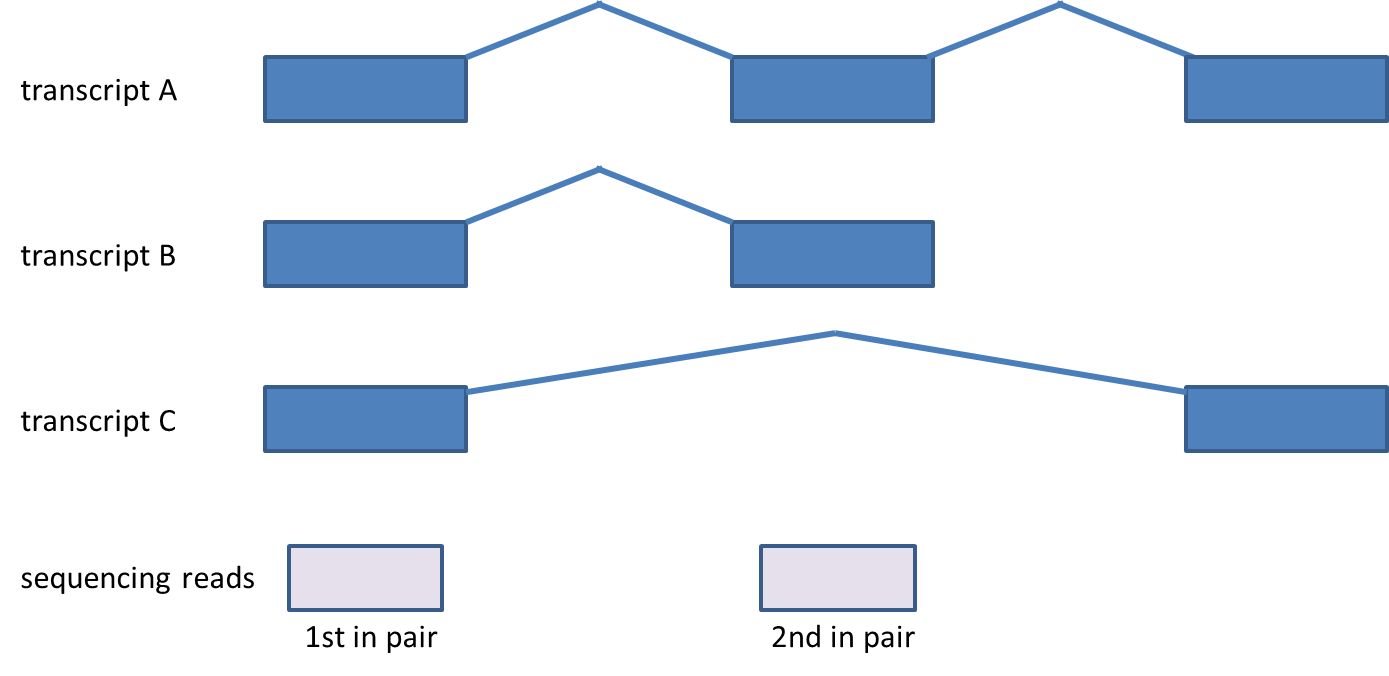
Considering genes with multiple transcripts, a read can be both counted as compatible for some transcripts, as well as counted incompatible for other transcripts of the same gene (Figure 4). Please note that this concept holds for single-end reads as well.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
With respect to the gene-level summarization, user can decide whether or not to consider intronic reads (both single- and paired-end) as compatible with the gene (Figure 5). In the latter case, the entire gene is basically treated as one giant exon. In the case that one end of a paired-end read falls within a gene, and the other end does not, the read will not be included in the gene-level summarization.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
When interpreting the unexplained reads, you should have in mind that these are actually the reads not compatible with the applied transcript model. By changing the model, some reads will become compatible and thus will not be labeled “unexplained” any more. Figure 6 shows such an example. The depicted regions map just downstream of the human LONP2 gene as defined by RefSeq and are hence flagged as unexplained. However, by overlaying the AceView transcripts, it is apparent that mapping to AceView would yield a different result.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...