Page History
...
t-SNE (t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding) is a visualization method commonly used to analyze single-cell RNA-Seq data. Each cell is shown as a point on the plot and each cell is positioned so that it is close to cells with similar overall gene expression. When working with multiple samples, a t-SNE plot can be drawn for each sample or all samples can be combined into a single plot. Viewing samples individually is the default in Partek® Flow® because sample to sample variation and outlier samples can obscure cell type differences if all samples are plotted together. However, as you will see in this tutorial, in some data sets, cell type differences can be visualized even when samples are combined.
Using the t-SNE plot, cells can be classified based on clustering results or and differences in gene and pathway expressionexpression of key marker genes.
Multiple single-sample t-SNE plots
By default, each sample in a multi-sample data set is plotted on its own t-SNE.
...
Prior to performing t-SNE, it is a good idea to reduce the dimensionality of the data using principal components analysis (PCA).
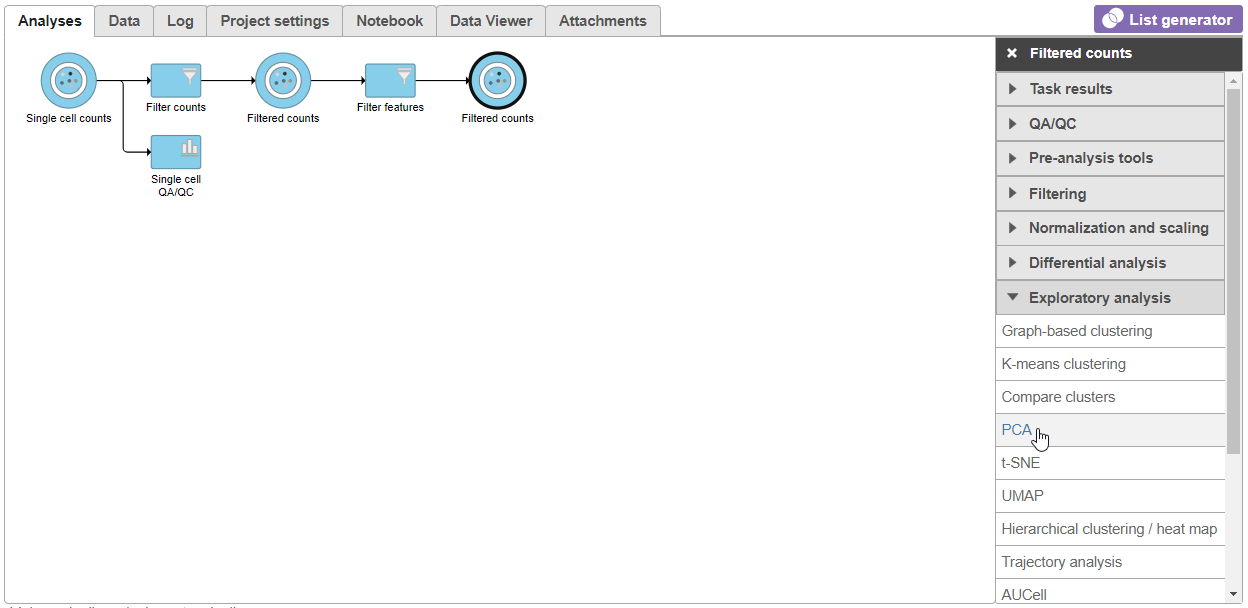
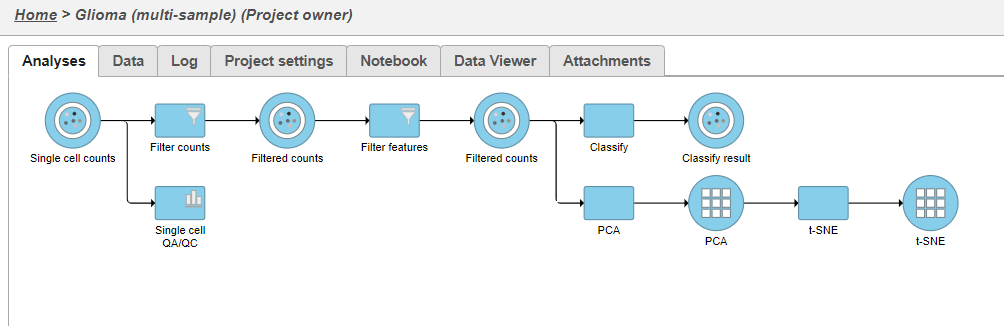
- Click the Filtered counts data node after the Filter features task
- Select PCA from the Exploratory analysis section of the task menu (Figure 1)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
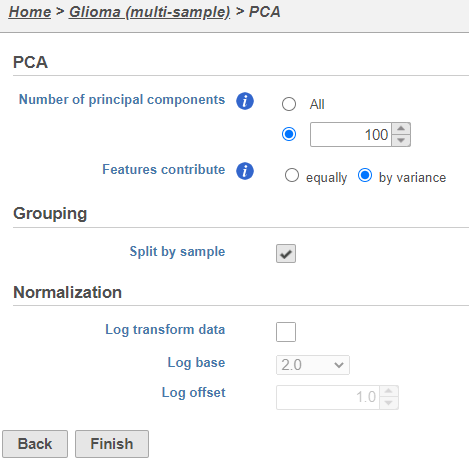
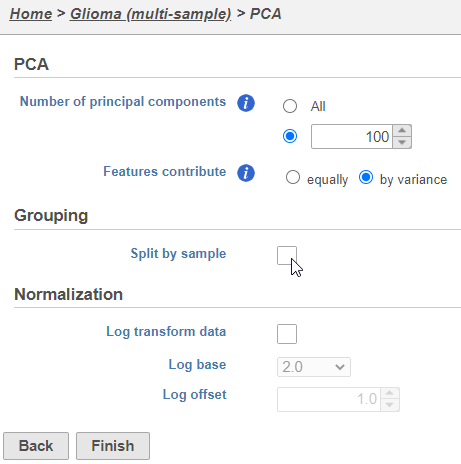
- Click Finish to run PCA with default settings (Figure 2)
Note, the default settings include the Split by sample checkbox being selected. This means that the dimensionality reduction will be performed on each sample separately.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
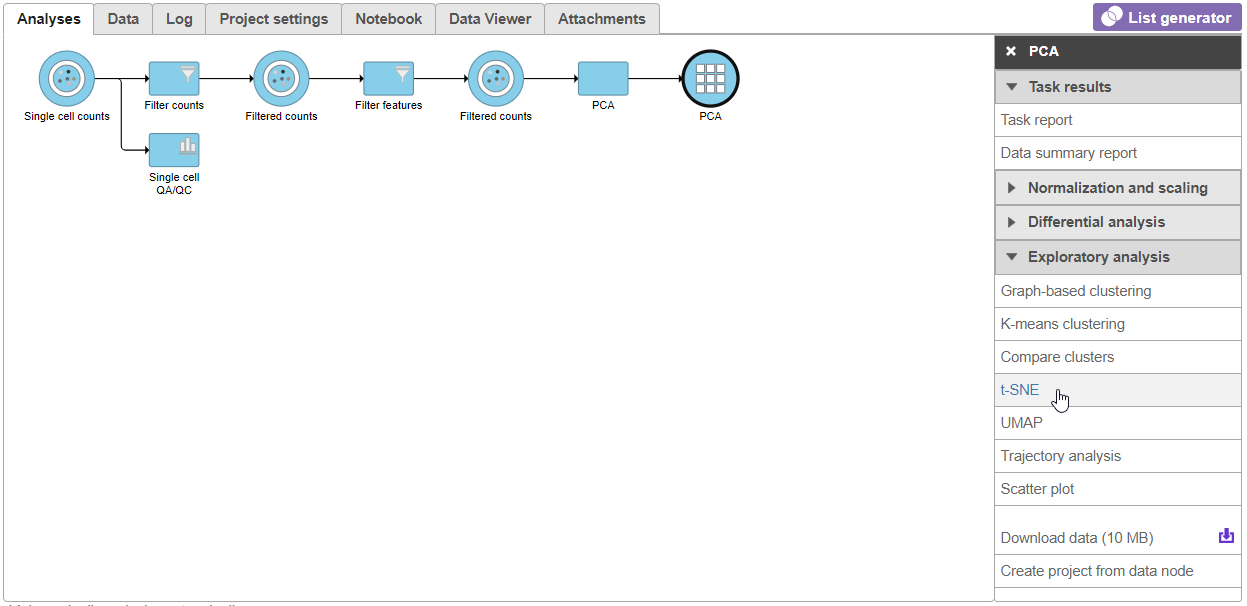
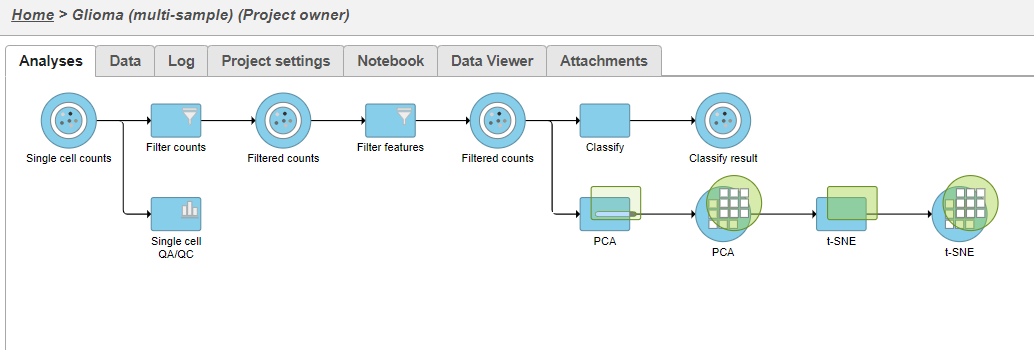
PCA task and data nodes will be generated.
- Click the PCA data node
- Select t-SNE from the Exploratory analysis section of the task menu (Figure 1Figure 3)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
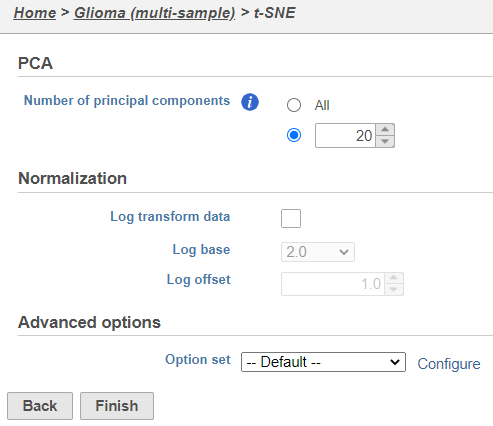
- Click Finish from the t-SNE dialog to run t-SNE with the default settings
...
- (Figure 4)
| Numbered figure captions | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
| |||
Because the upstream PCA task was performed separately for each sample, the t-SNE task will also be performed separately for each sample. t-SNE task and data nodes will be generated (Figure 5).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Once the t-SNE task has completed, we can view the t-SNE plot.plots
- Click the t-SNE node
- Click Task report from the task menu or double click the t-SNE node
The t-SNE plot will open to in a new data viewer session. The t-SNE plot for the first sample in the data set, MGH36 (Figure 3)Figure 6), will open on the canvas. Please note that the appearance of the t-SNE plot will may differ each time it is drawn so your t-SNE plots will may look different than those shown in this tutorial; however. However, the cell-to-cell relationships indicated will be the same.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The t-SNE plot is in 3D by default. To change the default, click your avatar in the top right > Settings > My Preferences and edit your graphics preferences and change the default scatter plot format from 3D to 2D.
You can rotate the 3D plot by left-clicking and dragging your mouse. You can zoom in and out using your mouse wheel. The 2D t-SNE is also calculated and you can switch between the 2D and 3D plots using the Plot style radio buttons. on the canvas. We will do this later on in the tutorial.
Each sample has its own plot. We can switch between samples using the Back and Next buttons .
- Scroll down on the Configuration card on the
...
- Select Nextleft and expand the Data card (Figure 7)
- Select the icon below the sample name to go to the next sample
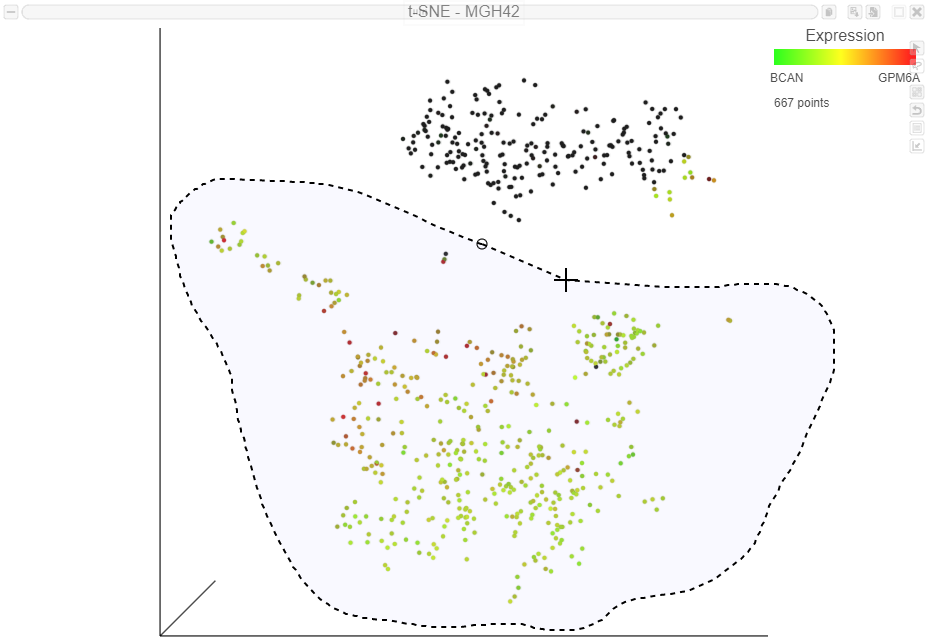
The t-SNE plot has switched to show the next sample, MGH42 (Figure 47).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The goal of this analysis is to compare malignant cells from two different glioma subtypes, astrocytoma and oligodendroglioma. To do this, we need to identify which cells are the malignant cells we want to include and which cells are the normal cells we want to exclude.
The t-SNE plot in Partek Flow offers several options for identifying, selecting, and classifying cells. In this tutorial, we will use the expression of known marker genes to identify cell types.
To visualize the expression of a marker gene, we can color cells on the t-SNE plot by their expression level.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The cells will turn black and a text box Gene ID will open below the drop-down box.
- Type BCAN in the Gene ID text box
- Select BCAN from the list of genes in the data set (Figure 6)Select any of the count data nodes from the Data card on the left (Single cell counts, or any of the Filtered counts, Figure 8)
- Search for the BCAN gene
- Click and drag the BCAN gene onto the plot and drop it over the Green (feature) option
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
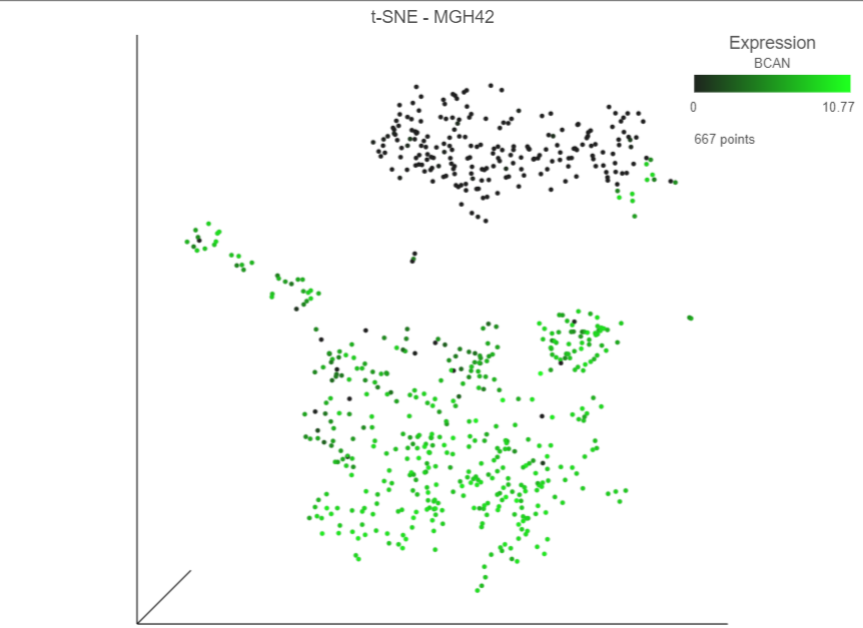
The cells will be colored from black to green based on their expression level of BCAN, with cells expressing higher levels more green (Figure 7Figure 9). BCAN is highly expressed in glioma cells.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
In Partek Flow, we can color cells by more than one gene. We will now add a second glioma marker gene, GPM6A.
- Select the icon next to BCAN
- Type GPM6A in the new Gene ID box
- Select GPM6A from the list of genes in the data setany of the count data nodes from the Data card on the left (Single cell counts, or any of the Filtered counts)
- Search for the GPM6A gene
- Click and drag the GPM6A gene onto the plot and drop it over the Red (feature) option
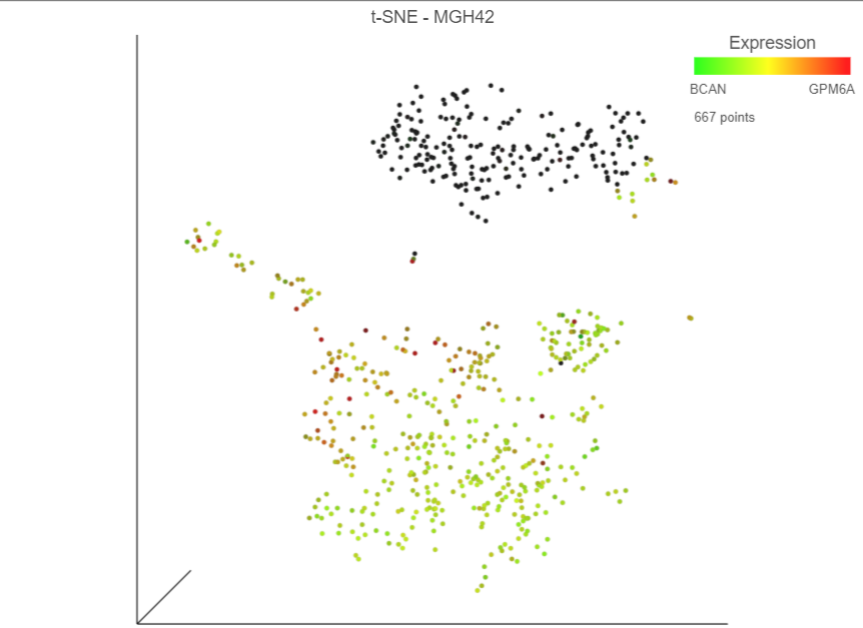
Cells expressing GPM6A are now colored red and cells expressing BCAN are colored green. Cells expressing both genes are colored yellow, while cells expressing neither are colored black (Figure 8Figure 10).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Relative expression of the two genes for selected cells can be visualized on the legend.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Selected cells are shown in bold and unselected cells are dimmed.
The relative expression of the two genes for the selected cells will be shown on the legend as dots (Figure 10).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
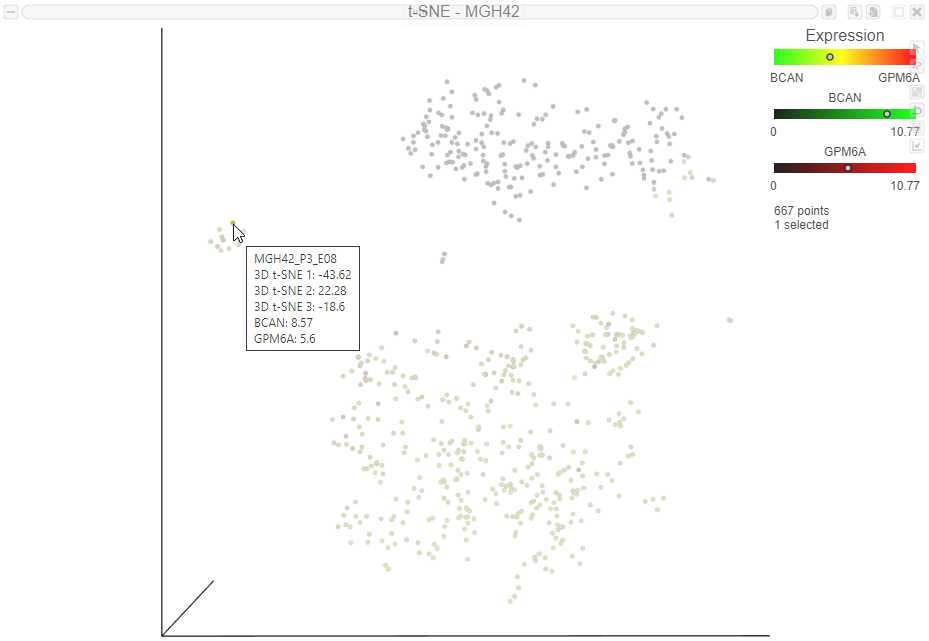
Numerical expression levels for each gene can be viewed for individual cells.
- Switch modes to pointer mode by clicking in the top right corner of the plot
- Select a cell by pointing and clicking
The expression level for that cell is displayed on the legend for each gene (Figure 11. Expression values can also be viewed by mousing over a cell (Figure 11).
- Deselect the cell by clicking on any black blank space on the plot
Expression values can also be viewing by selecting Gene Expression from the Label by drop-down menu and mousing over a cell.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
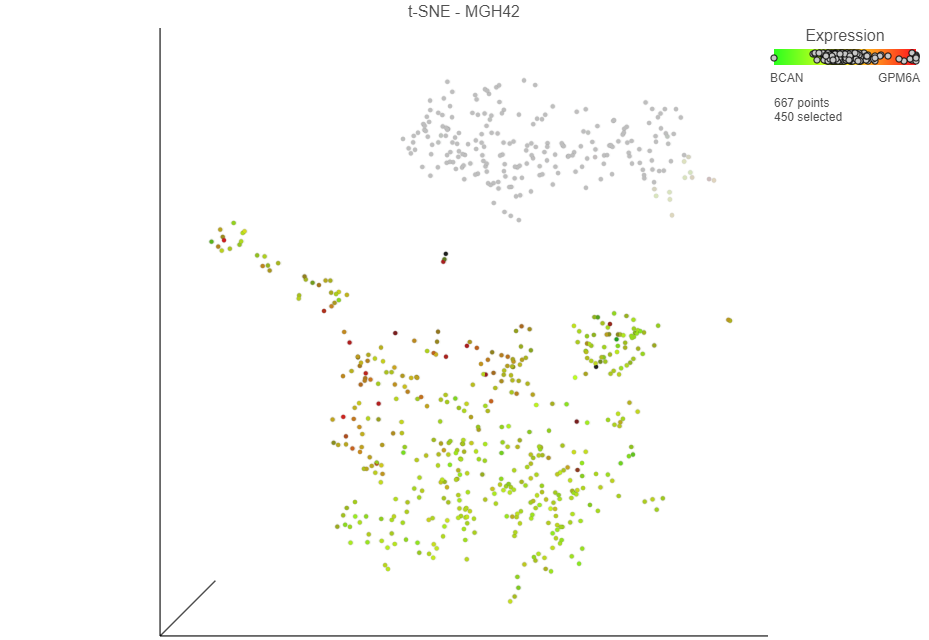
Now that cells are colored by the expression of two glioma cell markers, we can classify any cell that expresses these genes as glioma cells. Because t-SNE groups cells that are similar across the high-dimensional gene expression data, we will consider cells that form a group with BCAN where the majority of cells express BCAN and/or GPM6A -expressing cells as the same cell type, even if they do not express the either marker gene.
- Click anywhere on the t-SNE plot without a cell to clear the selection
- Activate the 3D lasso tool Switch to lasso mode by clicking in the top right of the plot
- Draw the lasso around the cluster of green, red, and yellow cells and click the circle to close the lasso . You may need to switch to selection mode and rotate the 3D plot to select only cells from the yellow cluster(Figure 12)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Selected cells are shown in bold and unselected cells are dimmed. The number of selected cells is indicated in the Selection section of the menu.
...
figure legend. The cells are plotted on the color scale depending on their relative expression levels of the two marker genes (Figure 13)
| Numbered figure captions | |
|---|---|
|
...
|
...
|
...
- Click Classify selection in the Classification card on the right
A dialog to give the classification a name will appear.
- Name the classification Glioma
- Click Save (Figure 13Figure 14)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Once cells have been classified, the classification is added to the Classifications section of card on the panelright. The number of cells belonging to the classification is listed; in . In MGH42, there are 462 450 glioma cells (Figure 14Figure 15).
| Numbered figure captions | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
|
...
Classifications made on the t-SNE plot are retained as a draft after you exit the t-SNE task report. The Apply classifications button runs a task, Classify cells, which generates a new Classified cells data nodeas part of the data viewer session. In this tutorial, we will classify malignant cells for each sample before we save and apply the classifications, but if necessary, you can exit the t-SNE task report and continue classifying the next sample later.
...
save the data viewer session by clicking the save icon on the left to retain all of the formatting and draft classifications. The data viewer session will be stored under the Data viewer tab and can be re-opened to continue making classifications at a later time.
- Switch to pointer mode by clicking in the top right corner of the plot
- Deselect the cells by clicking on any blank space on the plot
- Scroll down on the Configuration card on the left and expand the Data card
- Select the icon below the sample name to go to the next sample, MGH45
- Rotate the 3D t-SNE plot to allow you to select only get a better view of cells from the green, red, and yellow cluster
- Activate the 3D lasso tool Switch to lasso mode by selecting in the top right corner of the plot
- Draw the lasso around the cluster of black colored cells and click the circle to close the lasso (Figure 14Figure 16).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Select Classify selection selection in the Selection card on the right
- Type Glioma or select Glioma from the prompt (Figure 15drop-down list (Figure 17)
- Click Save
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Repeat these steps for each of the 6 remaining samples
...
- . Remember to go back to the first sample (MGH36) to classify the glioma cells in that samples too.
There should be 5,348 glioma cells in total across all 8 samples. With the malignant cells in every sample classified, it is useful time to check the number of cells in each sample assigned to each classification.
...
save the classifications.
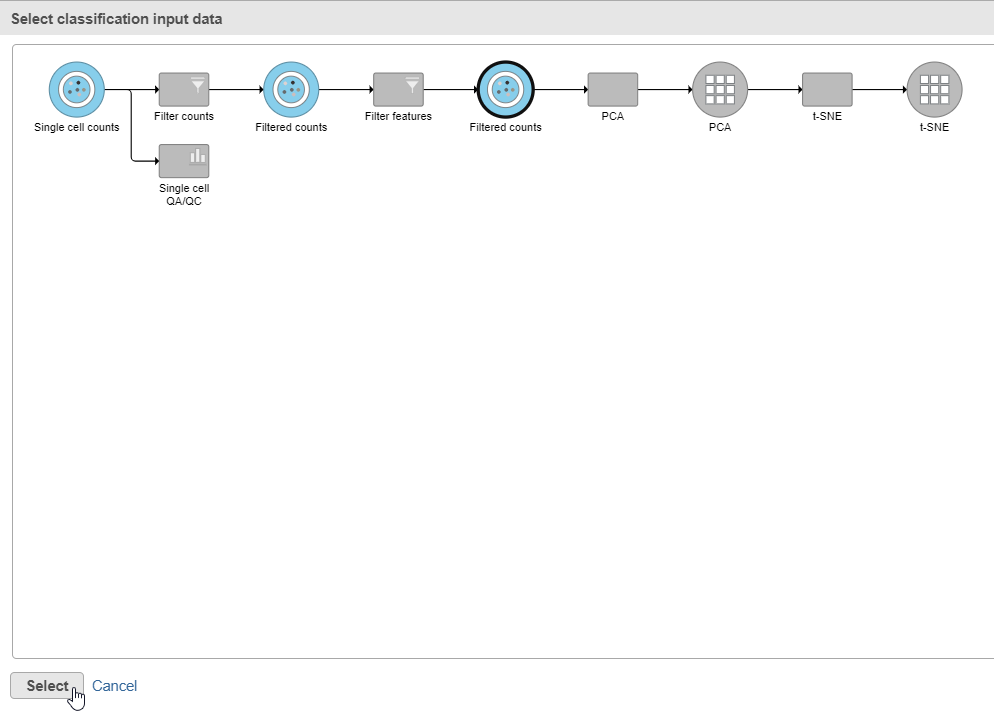
- Click Apply classifications in the Classification card on the right
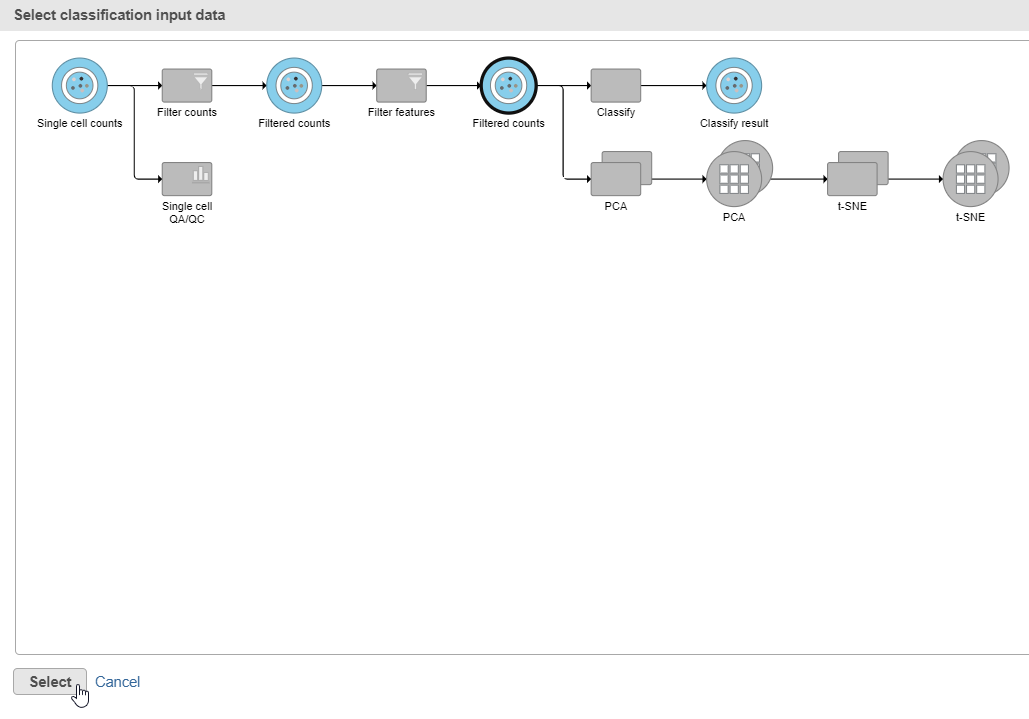
- Click the Filtered counts data node as input data for the classification task (Figure 18)
- Click Select
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The classifications summary lists every sample, the number of cells in the sample, the number of cells in each classification, and the percentage of cells in each sample that belong to each classification (Figure 17).
| |||
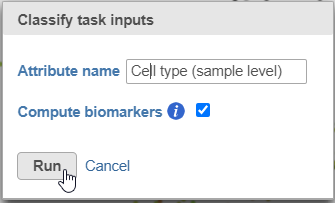
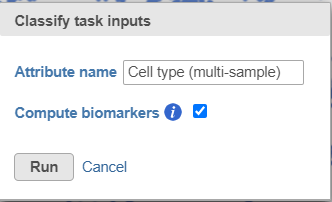
- Name the classification attribute Cell type (sample level) (Figure 19)
- Click Run
- Click OK on the information box that says a classification task has been enqueued
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
With the malignant cells in every sample classified, it is time to save the classifications.
- Click Apply classifications
- Click Apply when asked to confirm
The pipeline view will open and the Classify cells tasks will run, generating a Classified groups data node and a Group cell counts data node (Figure 18).
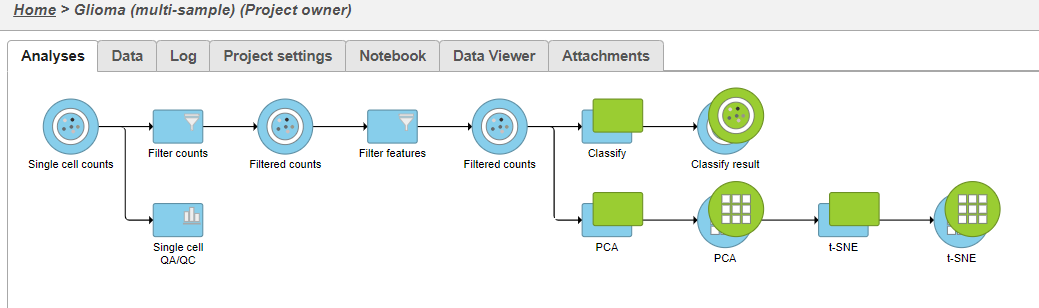
A new task, Classify, is added to the Analyses tab. This task produces a new Classify result data node (Figure 20).
- Click on the Glioma (multi-sample) project name at the top to go back to the Analyses tab
- Your browser may warn you that any unsaved changes to the data viewer session will be lost. Ignore this message and proceed to the Analyses tab
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
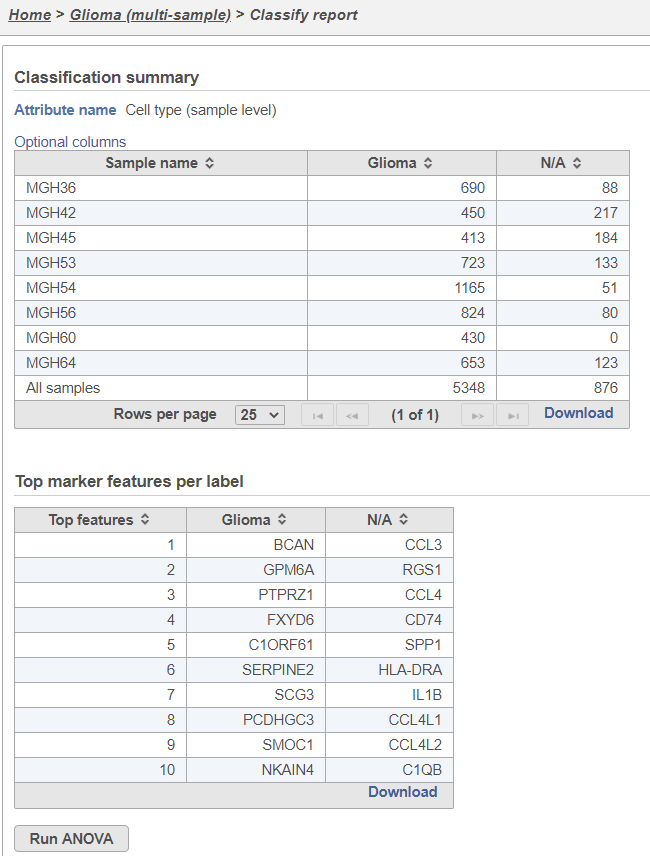
- Double-click the new Classify result data node to open the task report (Figure 21)
The Classification summary table shows a breakdown of the number of glioma cells that were classified per sample. The cells that were not classified are labeled N/A.
The Top marker features per label table shows the top 10 upregulated genes in each cell type. In this case, the glioma cells are compared to the N/A cells using ANOVA and the genes are filtered for fold-change >1.5 and sorted by descending fold-change values. To obtain the full list of biomarker genes with p-values and fold-changes, click the Download link in the bottom right of the table.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
One multi-sample t-SNE plot
For some data sets, cell types can be distinguished when all samples can be visualized together on one t-SNE plot. We will use a t-SNE plot of all samples to classify glioma, microglia, and oligodendrocyte cell types.
- Click on the Glioma (multi-sample) project name at the top to go back to the Analyses tab
- Click the Filtered counts data node after the Filter features task
- Click t-SNE PCA in the Exploratory analysis section of the task menu
- Click Uncheck the Split cells by sample option under Misc to uncheck it checkbox (Figure 1922)
- Click Finish
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
The PCA task will run as a new green layer.
- Click the new PCA data node
- Select t-SNE from the Exploratory analysis section of the task menu
- Click Finish to run the t-SNE task with default settings
The t-SNE task will be added as a to the green layer in the analysis tab (Figure 21(Figure 23). Layers are created in Partek Flow when the same task is run on the same data node.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Once the task has completed, we can view the plot.
- Double-click the green t-SNE plot data node to open the t-SNE scatter plot
...
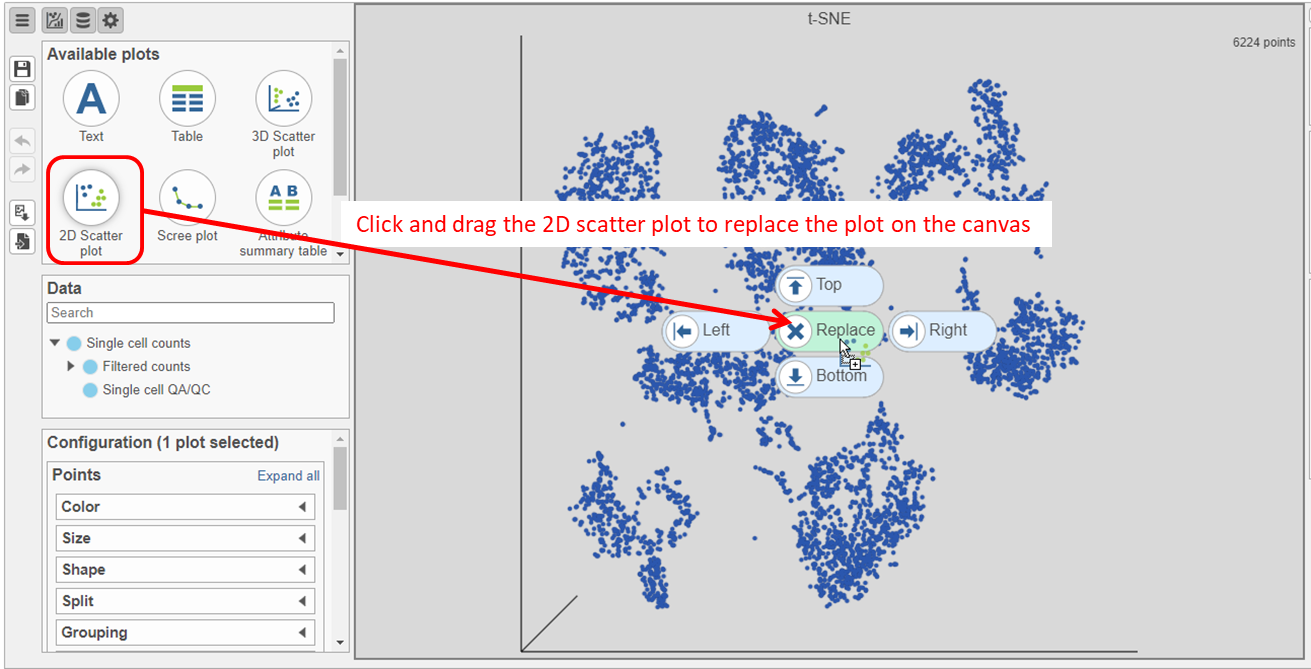
- Click and drag the 2D scatter plot icon onto the canvas and replace the 3D scatter plot (Figure 24)
| Numbered figure captions | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
| |||
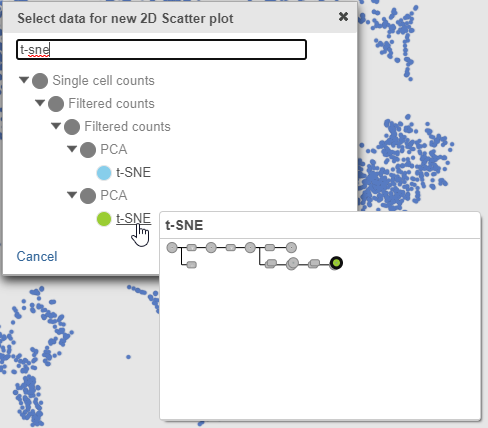
- Search for and select green t-SNE data node (Figure 25)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
- In the Configuration card, expand the Color card and choose Sample name from the Color by drop-down list
Viewing the 2D t-SNE plot, while most cells cluster by sample, there are a few clusters with cells from multiple samples (Figure 23Figure 26).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
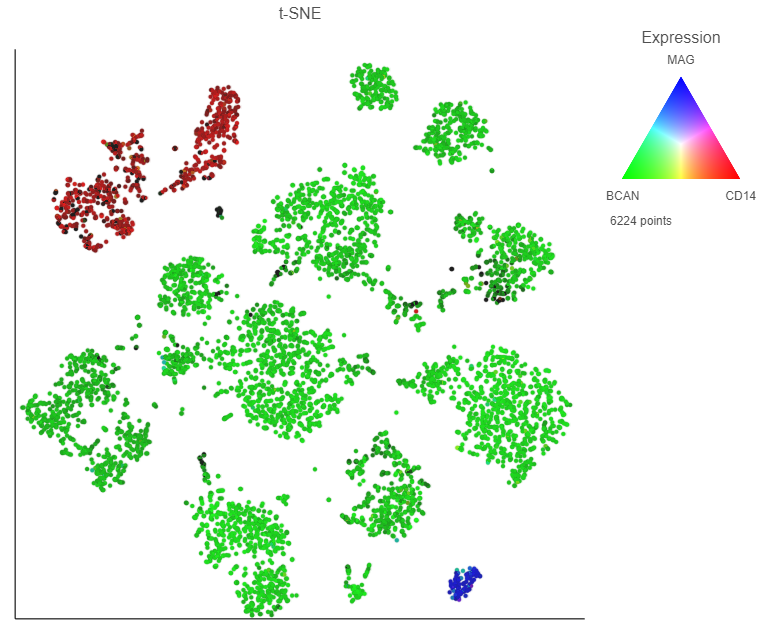
Using maker marker genes, BCAN (glioma), CD14 (microglia), and MAG (oligodendrocytes), we can assess whether these multi-sample clusters belong to our known cell types.
- Choose Gene expression from the Color by drop-down menu
- Type BCAN in the new Gene ID box
- Choose BCAN from the list of genes in the data set
- Click the icon next to BCAN
- Type CD14 in the new Gene ID box
- Choose CD14 from the list of genes in the data set
- Click the icon next to CD14
- Type MAG in the new Gene ID box
- Choose MAG from the list of genes in the data setSelect any of the count data nodes from the Data card on the left (Single cell counts, or any of the Filtered counts)
- Search for the BCAN gene
- Click and drag the BCAN gene onto the plot and drop it over the Green (feature) option
- Search for the CD14 gene
- Click and drag the CD14 gene onto the plot and drop it over the Red (feature) option
- Search for the MAG gene
- Click and drag the MAG gene onto the plot and drop it over the Blue (feature) option
After coloring by these marker genes, three cell populations are clearly visible (Figure 24Figure 27).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
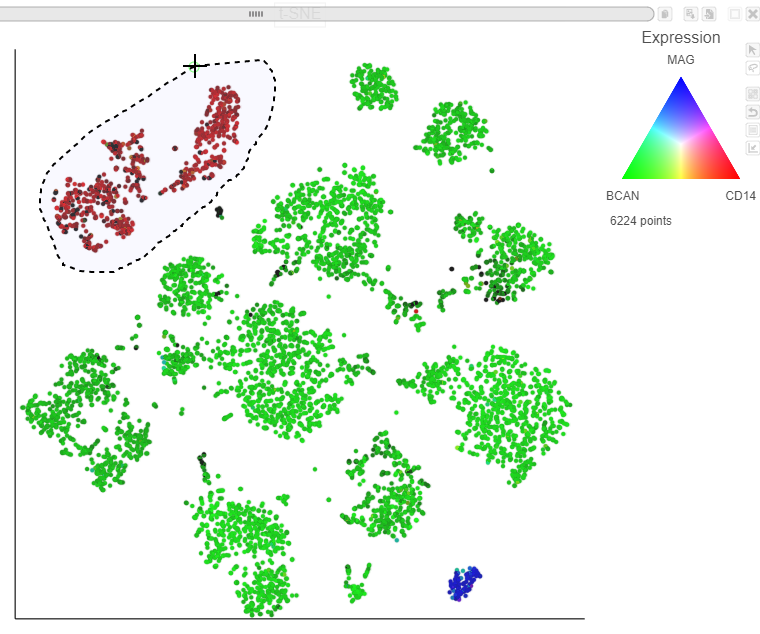
The red cells are CD14 positive, indicating that they are the microglia from every sample.
- Switch to lasso mode by clicking the icon in the top right of the plot
- Draw the lasso around the cluster of red cells and click the circle to close the lasso (Figure 25Figure 28)
- Click Classify selection
- Name the classification Microglia
- Click Save
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Click Classify selection
...
The blue cells are CD14 MAG positive, indicating that they are the microglia oligodendrocytes from every sample.
- Name the classification Microglia
- Click Save
To clearly see the MAG expressing population, clear the current selection.
- Deselect by double clicking on any black Switch to pointer mode by clicking in the top right corner of the plot
- Deselect the cells by clicking on any blank space on the plot
...
- Switch to lasso mode again by clicking the icon in the top right of the plot
- Draw the lasso around the cluster of blue cells and click the circle to close the lasso (Figure 26)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Click
- Click Classify selection
- Name the classification Oligodendrocytes
- Click Save
- Deselect by double clicking on any black space on the plot
Finally, we will classify the BCAN expressing cells on the plot as glioma cells from every sample.
- Switch to pointer mode by clicking in the top right corner of the plot
- Deselect the cells by clicking on any blank space on the plot
- Switch to lasso mode again by clicking the icon in the top right of the plot
- Draw the lasso around the cluster of green cells and click the circle to close the lasso (Figure 27
- Click Classify selection
- Name the classification Glioma
- Click Save
- Switch to pointer mode by clicking in the top right corner of the plot
- Deselect the cells by clicking on any blank space on the plot
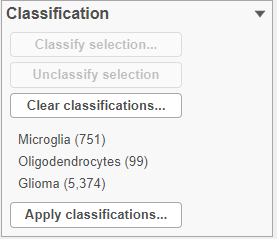
The number of cells classified as microglia, oligodendrocytes, and glioma are shown in the Classification card on the right (Figure 29)
| Numbered figure captions | |
|---|---|
|
...
|
...
|
...
- Click Classify selection
- Name the classification Glioma
- Click Save
With every cell from every sample classified, we can view the number of cells classified into each cell type for each sample on the classification summary page.
- Click Summary
The fraction of cells of each cell type in each sample is highly heterogeneous (Figure 28).
- Apply classifications in the Classification card on the right
- Click the Filtered counts data node as input data for the classification task (Figure 30)
- Click Select
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Name the classification attribute Cell type (multi-sample) (Figure 31)
- Click Run
- Click OK on the information box that says a classification task has been enqueued
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Click Apply classifications
- Click Apply to confirm classification
The pipeline view will open and the Classify cells task will run, generating a new green-layer Classified groups and Group cell counts data nodes (Figure 29).
| |
A new task, Classify, is added to the Analyses tab. This task produces a new Classify result data node in a green layer (Figure 32).
- Click on the Glioma (multi-sample) project name at the top to go back to the Analyses tab
- Your browser may warn you that any unsaved changes to the data viewer session will be lost. Ignore this message and proceed to the Analyses tab
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Page Turner | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Additional assistance |
|---|
| Rate Macro | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...