Page History
...
Starting with copy number estimates for each marker (either taken directly from the vendor’s input file or calculated previously), the goal is to derive a list of regions where adjacent markers share the same copy number.
Choosing a method for copy number detection
There are two algorithms available for copy number region detection: Genomic segmentation Segmentation and Hidden Markov Model (HMM). Both algorithms look for trends across multiple adjacent markers. The genomic segmentation algorithm identifies breakpoints in the data, i.e., changes in copy number between two neighboring regions. The HMM algorithm looks for discrete changes of whole number copy number states (e.g., 0, 1, 2 … with no upper limit) and will find regions with those numbers of copies. Therefore, the HMM model performs better in cases of homogeneous samples where copy numbers can be anticipated such as clinical syndromes with underlying copy number aberrations. Genomic segmentation is preferable for heterogeneous samples with unpredictable copy numbers such as cancer because tumor biopsies often contain “contaminating” healthy tissue and cancer cells can have heterogeneous copy number aberrations.
Detecting amplifications and deletions with Genomic Segmentation
The number of copies of each marker created in the previous step will be used to detect the genomic regions with copy number variation, i.e., to identify amplifications and deletions across the genome.
...
If desired, you can use the Merge Adjacent Regions under Tools in the main toolbar to combine similar regions.
To
...
Visualizing regions of interest
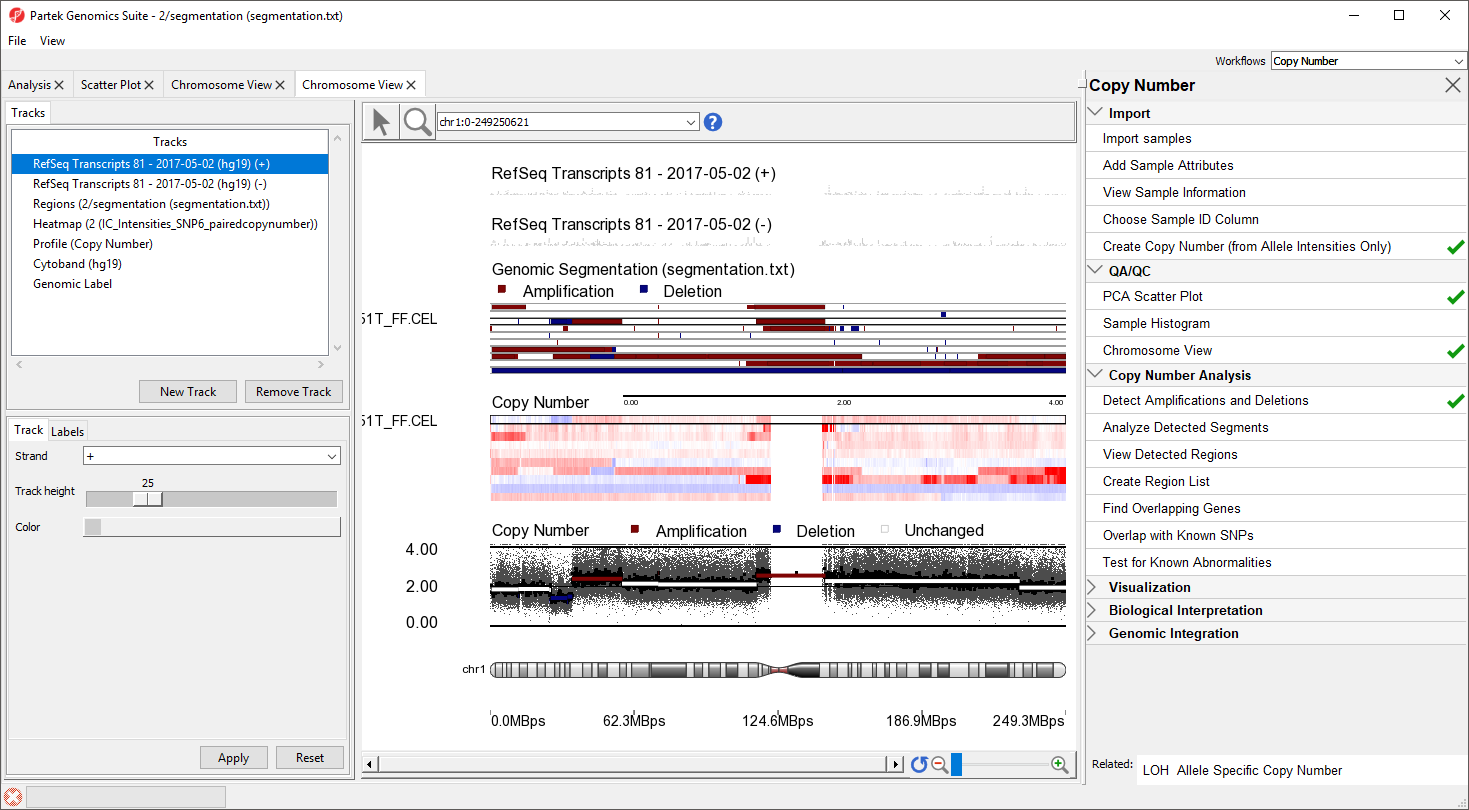
Individual regions of interest can be visualized using Chromosome View.
- Right-click a row header in the segmentation spreadsheet; here we have chosen row 5.
- Select Browse to location from the pop-up menu
Alternatively, you can visualize results at the whole chromosome level.
- Select the segementation spreadsheet
- Select Chromosome View from the QA/QC section of the workflow
The Genomic Segementation track displays the segmentation results (Figure 5). Each line in the track represents a smaple. Amplified, deleted, and unchanged regions are shown in red, blue, and white, respectively. The Profile track now also includes information from the segmentation spreadsheet ffor the selected sample.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Analyzing shared regions of copy number variation
Once regions with amplification and deletion in each sample have been detected, we can compare the regions across multiple samples to detect copy number changes that are shared by multiple samples.
- Select Analyze detected segments from the Copy Number Analysis section of theworkflow
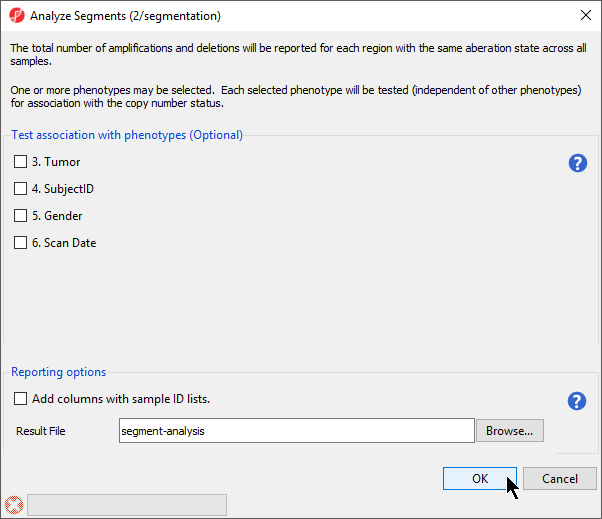
The Analyze Segments task (Figure 6) can test for associations between copy number variations and sample categories using the χ2 test. In this tutorial, all pairs share the sample phenotype, so we will not test for associations.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Leave all boxes unchecked
- Select OK to run the Analyze Segements task
The task generates a new spreadsheet, summary (segment-analysis) (Figure 7), shows one region per row. The columns provide the following information:
1-4. Genomic locations of the regions
5. Total number of samples
6-7. Number of samples with amplifications and the average amplified copy number, respectively
8-9. Number of samples with deletions and the average deleted copy number, respectively
10. Total number of samples with copy number abberations
11-12. Number of samples with no change in copy number and the average copy number in those samples, respectively
13. Number of markers in the region
14. Length of the region (in base pairs)
15+. Two columns per sample - the average copy number in each sample as well as the copy number change status of the sample sample (e.g., amplified,
| Additional assistance |
|---|
|
| Rate Macro | ||
|---|---|---|
|