Page History
...
In this section, you will learn how to find genomic features (genes) that are near the IP-enriched regions of the data. You will also learn how to classify the peak locations by gene section (5’ UTR, 3’ UTR, Promoter, CDSexon, intron).
Section Heading
Section headings should use level 2 heading, while the content of the section should use paragraph (which is the default). You can choose the style in the first dropdown in toolbar.
Finding the nearest genomic features
- Select p-value_filtered from the spreadsheet tree
- Select Find nearest genomic features from the Peak Analysis section of the ChIP-Seq workflow
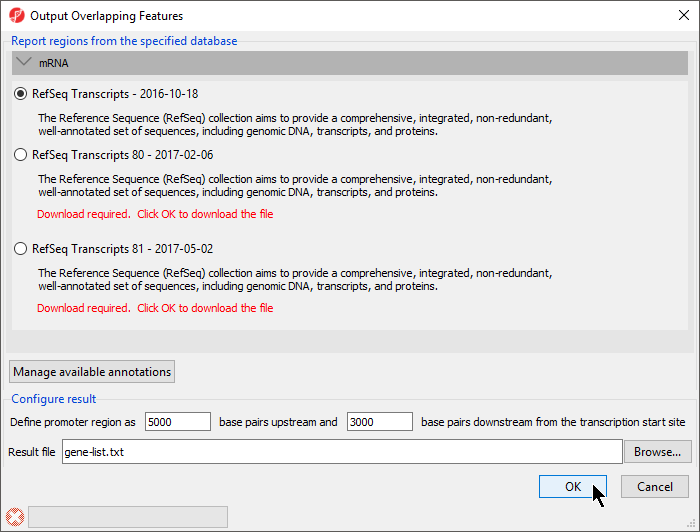
The Output Overlapping Features dialog will open (Figure 1).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
With this dialog, you can specify the reference database. Here RefSeq Transcripts - 2016-10-18 is selected. The promoter region can also be defined. The default settings are appropriate in this case.
- Select OK
The resulting spreadsheet, gene-list, is a child of the p-value_filtered spreadsheet (Figure 2). Each row represents a transcript.
Column 1. transcript chromosome gives the chromosome location of transcript
Column 2. transcript start gives the start of transcript (inclusive)
Column 3. transcript stop gives the end of transcript (exclusive)
Column 4. strand gives the strand of the transcript
Column 5. Transcript ID gives the identify of the transcript
Column 6. Gene Symbol gives the identity of the gene
Column 7. Distance to TSS gives the distance of each enriched region to the transcription start site in base pairs with positive indicates downstream and negative indicates upstream
Column 8. Percent overlap with gene gives the percent of the gene that overlaps with the region
Column 9. Percent overlap with region gives the percent of the region that overlaps with the gene
Column 10.-23. These columns are detailed in Detecting peaks and enriched regions in ChIP-Seq data
Percent overlap with gene is more likely to close to 1 in cases where one region covers several genes, in histone studies, for example. Percent overlap with region is likely to be close to 1 in cases where a region is relatively small and is found completely within a gene, in transcription factor binding studies, for example. If both columns are close to 1, then the gene and the region have nearly the same start and stop sites. If both columns are close to 0, then the region does not overlap with the gene directly and likely covers only the promoter region.
Classifying regions by gene section
Another way to interpret the genomic location of peaks is to use Classify regions by gene selection.
- Select p-value_filtered from the spreadsheet tree
- Select Classify regions by gene selection from the Peak Analysis section of the ChIP-Seq workflow
| Additional assistance |
|---|
|
| Rate Macro | ||
|---|---|---|
|