This normalization is performed on observations (samples) using internal control features (genes). The internal control features, usually housekeeping genes, should not vary among samples[1]. The implementation details is as follows:
1. Compute geometric mean of all the control genes (features) e.g. (g1 to gm) in each sample S (f means feature, S means sample, 1-m are control features), represented by GS1 to GSn (n number of samples).
2. Compute geometric mean of across all samples (GS1 to GSn), represented by GS
3. Compute the scaling factor for each sample, S1=GS1/GS, S2=GS2/GS ... Sn=GSn/GS
4. Normalize all the gene expression by divided by its sample scaling factor
Note: The input data node must contain all positive values to compute geometric mean.
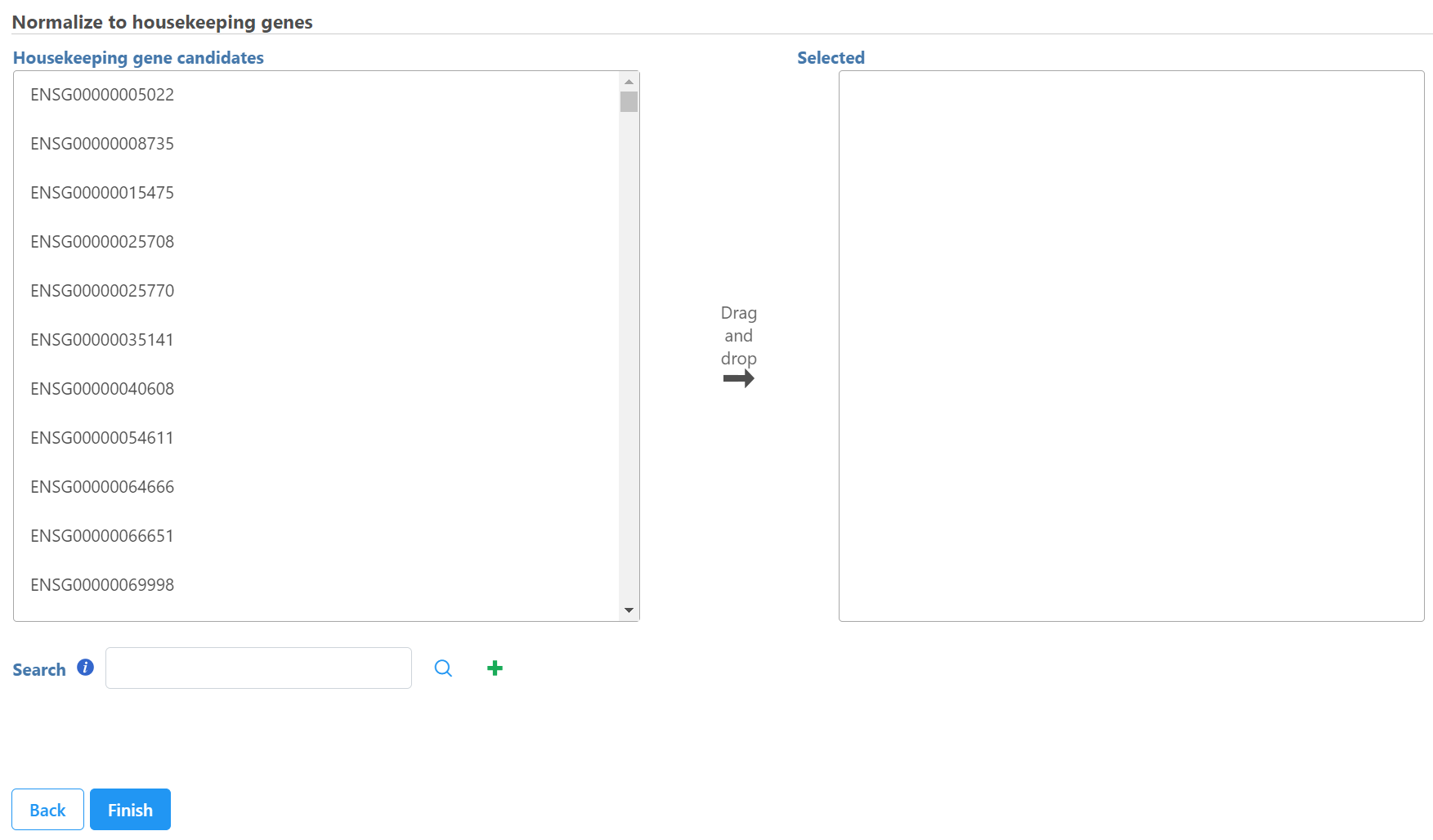
Select Normalize to housekeeping genes task in Normalization and scaling section in the pop-up menu when you select a count matrix data node, the dialog will list all the features included in the data node on the left panel
Select control genes on the left panel and move them to the right panel. You can also use search box to find the feature and click on the to add it to the right panel.
Click Finish
References
- Frank Speleman. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT_PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biology. 2002.
Additional Assistance
If you need additional assistance, please visit our support page to submit a help ticket or find phone numbers for regional support.


| Your Rating: |
    
|
Results: |
    
|
0 | rates |