Page History
The Peak calling task is used to detect enriched genomic regions on reads generated from nucleic acid enrichment experiments such as ChIP-seq, DNase-seq, and MeDIP-seq etc. experiments. Partek® Flow® provides the widely used method of MACS2-model-based analysis1 (http://liulab.dfci.harvard.edu/MACS/) to find peaks. It can be performed with or without control sample.
...
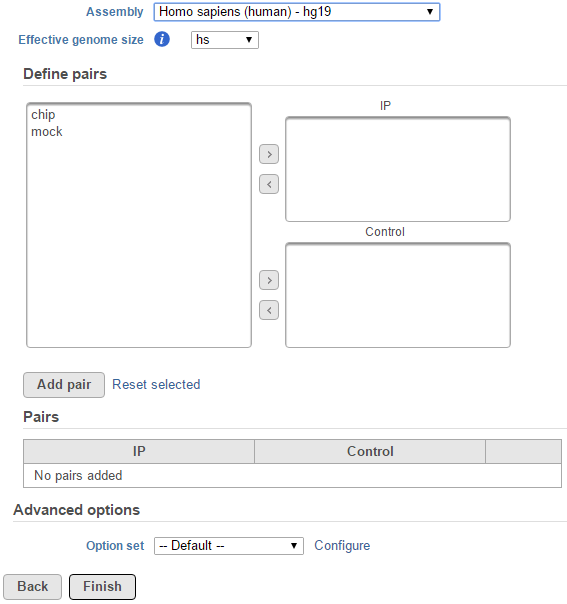
If the selected aligned data node was imported, the reference assembly used during data alignment needs to be specified. Choose the Assembly from the drop-down list within the MACS2 dialogue (Figure 1). If the selected aligned data node was generated by Partek Flow, this option will not appear.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
The Effective genome size is the genome must be configured prior to running the peak caller. It refers to the size of the genomic regions that can be sequenced. Because of the repetitive features on the chromosomes, the actual mappable genome size will be are actually mappable. This size is smaller than the original size, actual size of an organism's whole genome because of the presence of repetitive features. They are typically about 70%-90% of the whole genome size. There are presets of 4 species based on MACS2 recommendation1 for this parameter:
- hs – Homo sapiens, size is 2.7e9
- mm – Mus musculus, size is 1.87e9
- ce – Caenorhabditis elegans, size is 9e7
- dm – Drosophila melongaster, size is 1.2e8
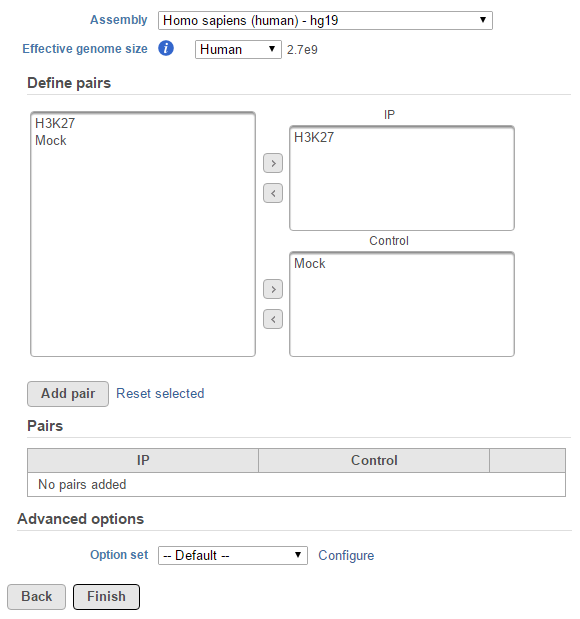
When Other... is selected, a specific value of the effective genome size needs to be specified with bps as unit (Figure 2).. The MACS2 authors1 have recommended presets available for four different species. Select from the drop-down menu the preset that best describes the genome you are working with. They are as follows:
- Human (Homo sapiens) – 2.7 x 109
- Mouse (Mus musculus) – 1.87 x 109
- C. elegans – 9 x107
- Fruitfly (Drosophila melongaster) – 1.2 x 108
If none of these presets match your genome of interest, select Other... Then enter the effective genome size (Figure 2). The values are in base pairs (bps). Consult the MACS documentation for guidance on selecting the best effective genome size for your experiment.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
For data where no sample attributes were are specified, the peak detection pairs needs need to be manually defined. In the example in Figure 1, there only two samples. For Under the Define pairs section, the left panel lists all the sample names uploaded to the project (chip H3K27 and mock Mock). Add one pair at a time by selecting dragging the chip sample to put in the IP corresponding samples to either the IP panel on the top-right , and selecting the mock sample in the Control panel or the Control panel on the bottom-right. If there is no control sample samples are present in the experiment, the Control panel can be blankleave the Control panel blank. If more than one ChIP or Control samples are added, the samples will be combined (or pooled) in during the analysis. After defining a pair, click the Add pair button.
For data where the sample attributes are defined (Figure 3), you will have an additional option to add pairing or grouping based on the sample attributes. Figure 3 shows an example data dataset with 4 samples, 2 time points, and there is one IP sample and one Input sample in each time point.
...
When running the MACS2 task, sample attributes will be used to define the multiple pairs (Figure 4). There is an IP-Input pair for each time point, so the Pair attribute is the Time attribute. The The Control attribute is the attribute that differentiates between the Input and IP groups, and in this example, it is the ChIP attribute. Finally, the Control term is labeled as Input in the example.
...