Join us for an event September 26!
How to Streamline RNA-Seq analysis and increase productivity—point, click, and done
Page History
A fusion gene is a hybrid gene that combines parts of two or more original genes. They can form as a result of chromosomal rearrangements (such as translocation, interstitial deletion, or chromosomal inversion) or abnormal transcription and have been shown to act as drivers of malignant transformation or/and progression in various neoplasms (1). The discovery and characterization of fusion genes hav have been greatly facilitated by the use of NGS (2) and several computational algorithms have been developed to detect them.
...
Clicking the Download data downloads a *.fusion file to the local computer. The file is human-readable and can be opened in a text editor (example in Figure 4). For details refer to TopHat-Fusion documentation.
...
The output is associated with the Chimeric resultsjunctions data node (Figure 12), which is a part of the STAR results in addition to Aligned reads node and, optionally, Unaligned reads node.
...
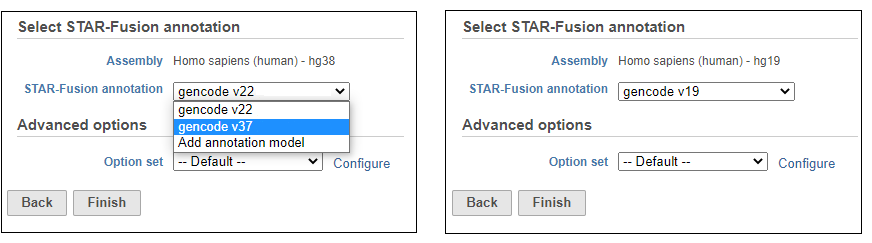
Choose the STAR-Fusion annotation from the drop-down list. We provide automatic downloads of the plug-n-play libraries distributed by Trinity Cancer Transcriptome Analysis Toolkit (CTAT) for Human hg38 (Gencode v22 and v37) and hg19 (Gencode v19) assemblies (Figure 1516).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
To change any of the advanced options, click the Configure link (Figure 1617). To run the task, click Finish.
...
The resulting Fusion predictions task node (Figure 1718) can be downloaded to your local machine by selecting the data node and clicking Download data from the toolbox. There will be one tab-separated (.tsv) file per sample. To view the full table, double-click the new data node to open the task report (Figure 1819). Each row of the table is a fusion event and the columns contain information about each detected fusion.
- FusionName: the name of the fusion event, given as LeftGene--RightGene. Multiple fusion events can be detected across the same pair of genes, so the FusionName of an event is not necessarily unique;
- JunctionReadCount: indicates the number of RNA-Seq fragments containing a read that aligns as a split read at the site of the putative fusion junction;
- SpanningFragCount: indicates the number of RNA-Seq fragments that encompass the fusion junction such that one read of the pair aligns to a different gene than the other paired-end read of that fragment;
- est_J: estimated junction read counts corrected for multiple mappings;
- est_S: estimated spanning fragment counts corrected for multiple mappings;
- SpliceType: indicates whether the proposed breakpoint occurs at reference exon junctions as provided by the reference transcript structure annotations (Gencode);
- LeftGene: name of the first (left) gene;
- LeftBreakpoint: genome coordinates for the breakpoint in left gene;
- RightGene: name of the second (right) gene;
- RightBreakpoint: genome coordinates for the breakpoint in right gene;
- JunctionReads: sequence identifiers for all junction reads;
- SpanningFrags: sequence identifiers for all spanning fragments;
- LargeAnchorSupport: indicates whether there are split reads that provide 'long' (set to 25bp) alignments on both sides of the putative breakpoint;
- FFPM: fusion fragments per million reads
- LeftBreakDinuc: dinucleotide base pairs at the left breakpoint
- LeftBreakEntropy: the Shannon entropy of the 15 exonic bases flanking the left breakpoint
- RightBreakDinuc: dinucleotide base pairs at the right breakpoint
- RightBreakEntropy: the Shannon entropy of the 15 exonic bases flanking the right breakpoint
- annots: provides a simplified annotation for fusion transcript
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
- Annala MJ, Parker BC, Zhang W, Nykter M. Fusion genes and their discovery using high throughput sequencing. Cancer Lett. 2013;340:192-200.
- Costa V, Aprile M, Esposito R, Ciccodicola A. RNA-Seq and human complex diseases: recent accomplishments and future perspectives. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013;21:134-142.
- Kim D, Salzberg SL. TopHat-Fusion: an algorithm for discovery of novel fusion transcripts. Genome Biology. 2011;12:R72
- TopHat-Fusion. An algorithm for discovery of novel fusion transcripts. http:// http://tophat.cbcb.umd.edu/fusion_index.html Accessed on April 25, 2014
- Dobin A, Davies CA, Schlesinger F et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:15-21.
- Haas B.J, Dobin A, Li B. et al. Accuracy assessment of fusion transcript detection via read-mapping and de novo fusion transcript assembly-based methods. Genome Biol. 2019;20:213 (2019)
| Additional assistance |
|---|
...