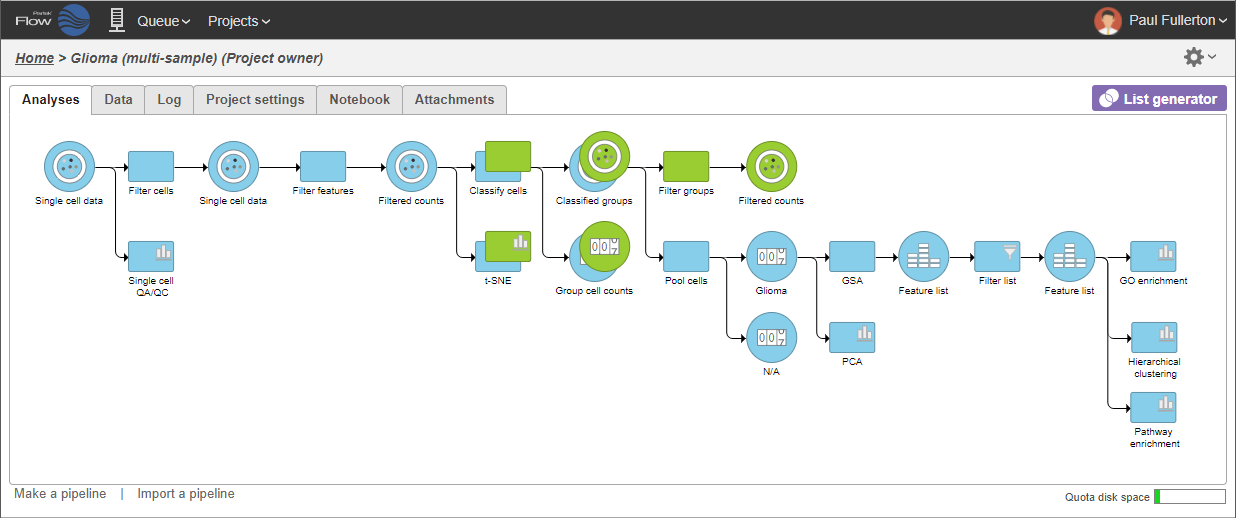
Page History
...
Differential expression analysis can be used to compare cell types. Here, we will compare glioma and oligodendrocyte cells to identify genes differentially regulated in glioma cells from the oligodendroglioma subtype. Glioma cells in oligodendroglioma are thought to originate from oligodendrocytes, thus ; directly comparing the two cell types will identify genes that distinguish them.
...
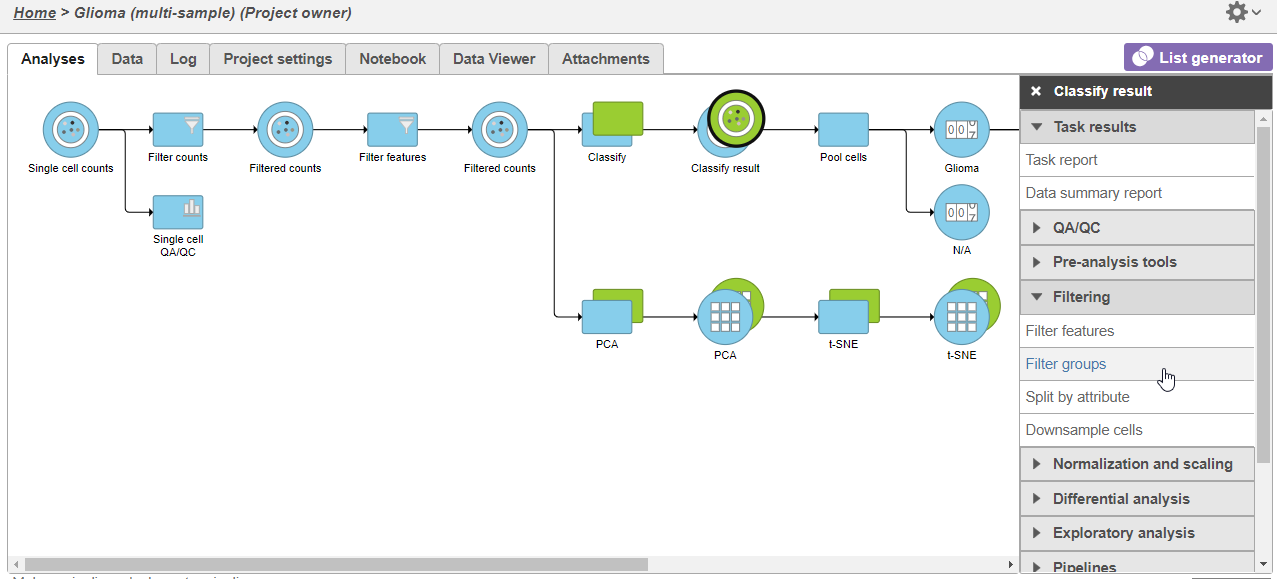
To analyze only the oligodendroglioma subtype, we can filter the samples.
- Click the green Classified green Classified groups data node
- Expand Click Filtering in the task menu
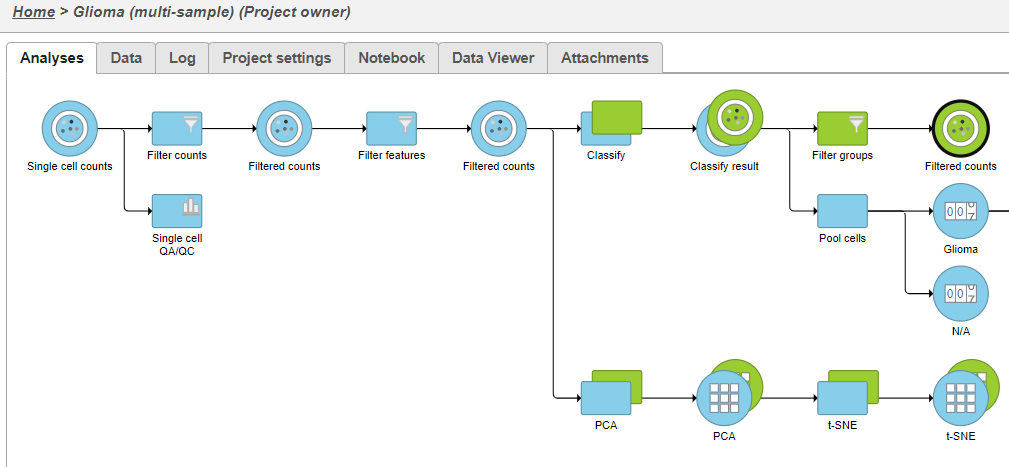
- Click Filter groups (Figure 1)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
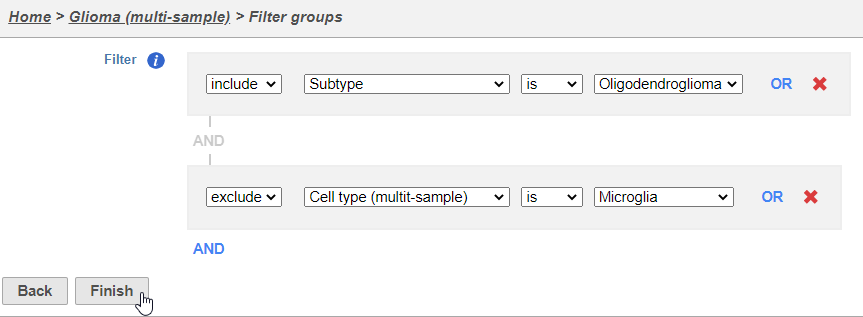
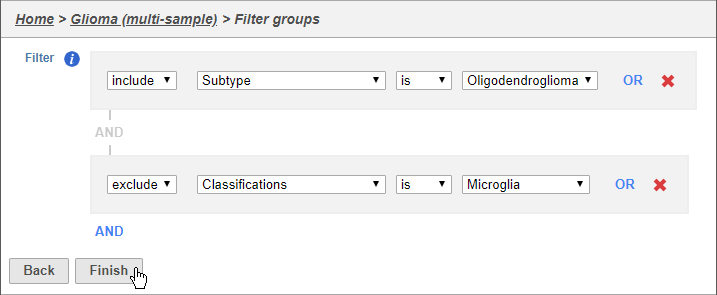
The filter lets us include or exclude samples based on sample ID and attribute.
- Set the filter to Include samples where Subtype is Oligodendroglioma
- Click AND
- Set the second filter to exclude Cell type (Multi-sample) Classifications is Microglia
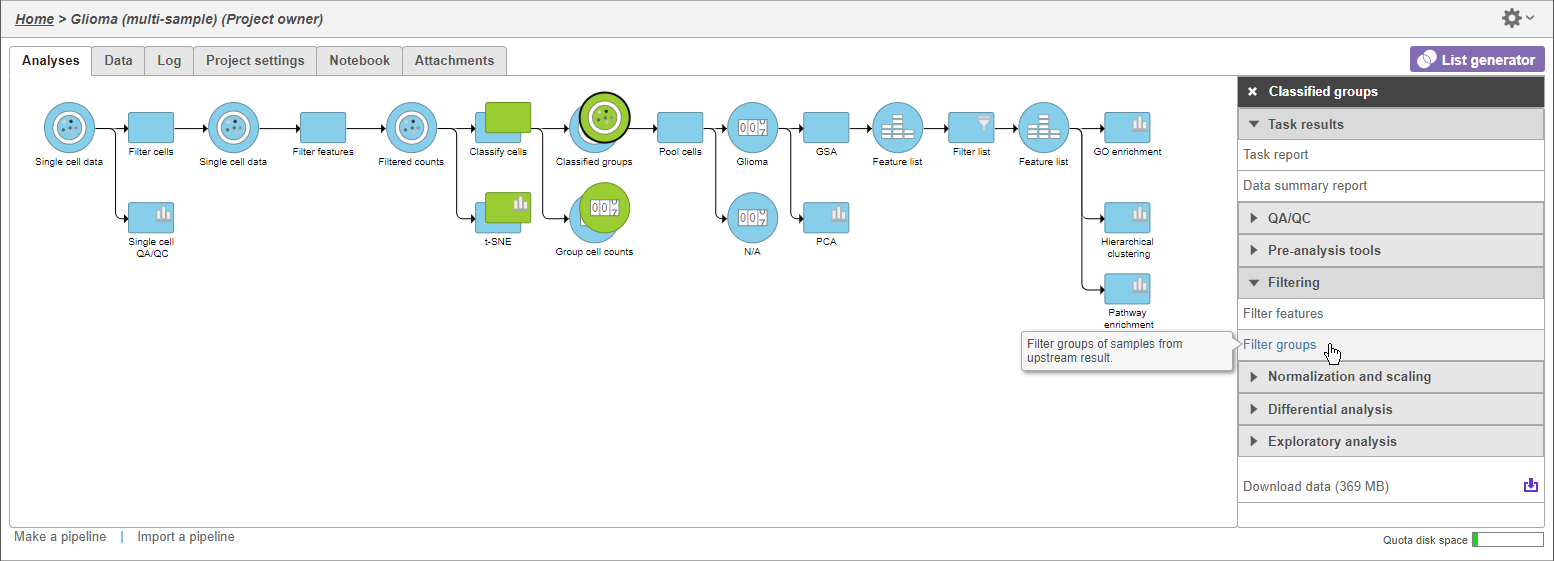
- Click Finish to apply the filter (Figure 2)
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
A Filtered counts data node will be created with only cells that are from oligodendroglioma samples (Figure 3).
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
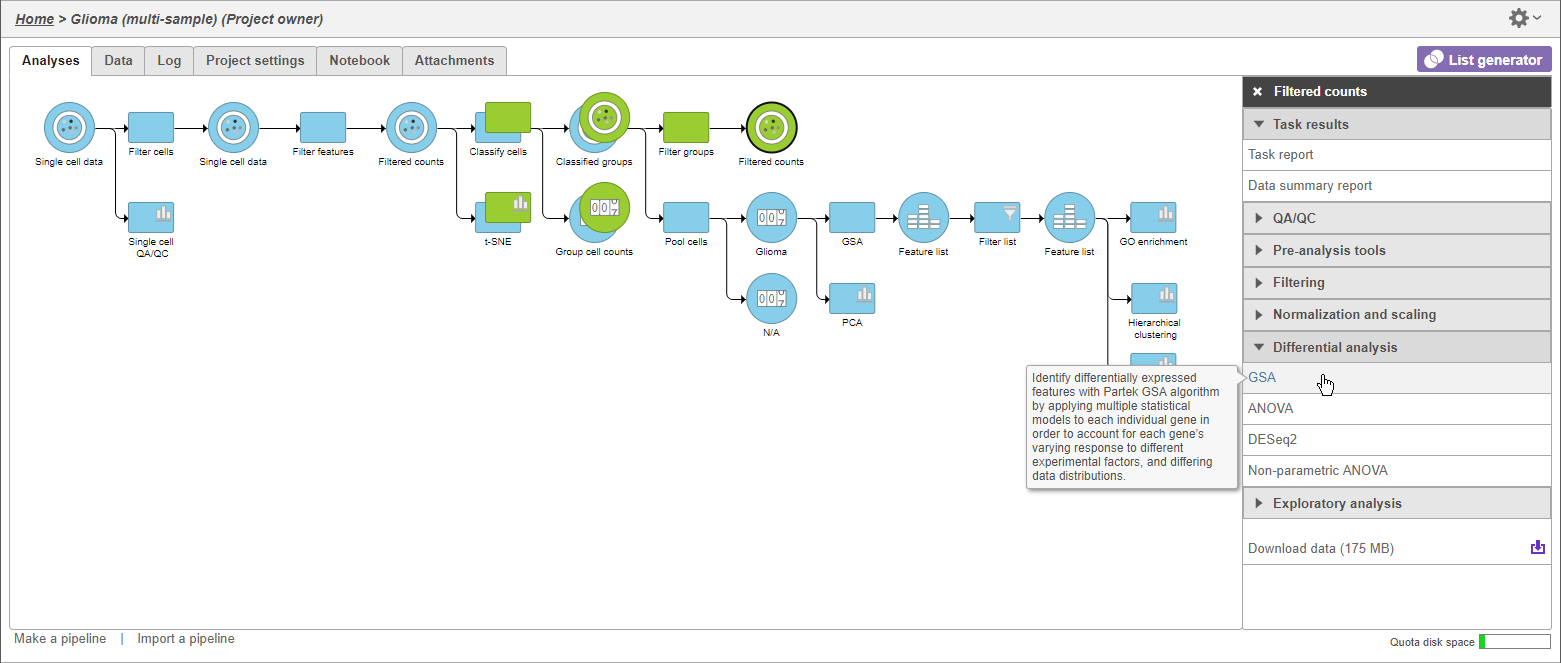
Identify differentially expressed genes
- Click the green Filtered green Filtered counts data node
- Click Differential analysis in the task menu
- Click GSA (Figure 5)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
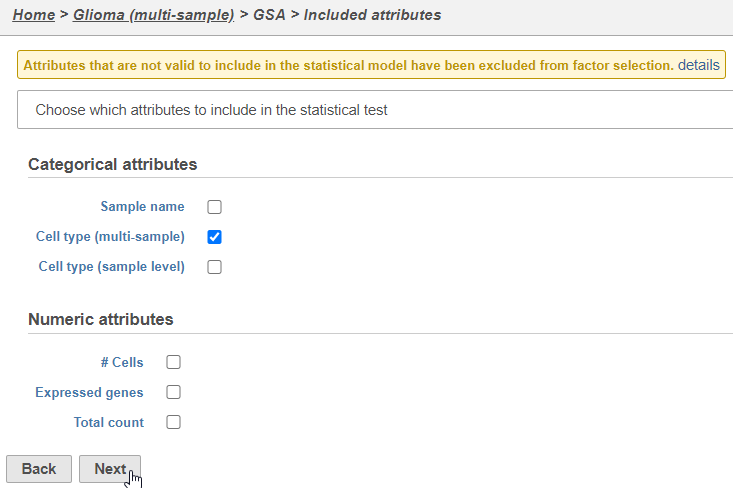
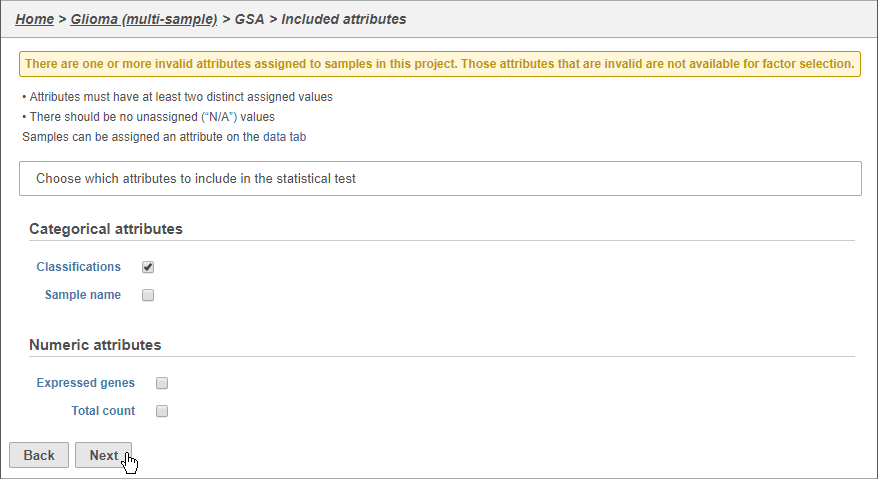
The configuration options (Figure 46) includes sample and cell-level attributes. Here, we want to compare different cell types so we will include Cell type (multi-sample) Classifications.
- Click Cell type (multi-sample)Classifications
- Click Next
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
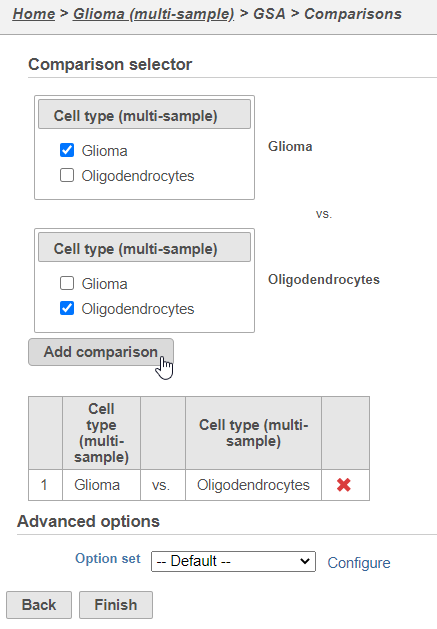
Next, we will set up a comparison between glioma and oligodendrocyte cellsoligodendrocytes.
- Click Glioma in the top panel
- Click Oligodendrocytes in the bottom panel
- Click Add comparison (Figure 57)
This will set up fold calculations with glioma as the numerator and oligodendrocytes as the denominator.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Click None in the Read count normalization section
- Click Finish to run the GSA
A green GSA data node Feature list node will be generated containing the results of the GSA.
- Double-click the green GSA data node the green Feature list node to open the GSA report
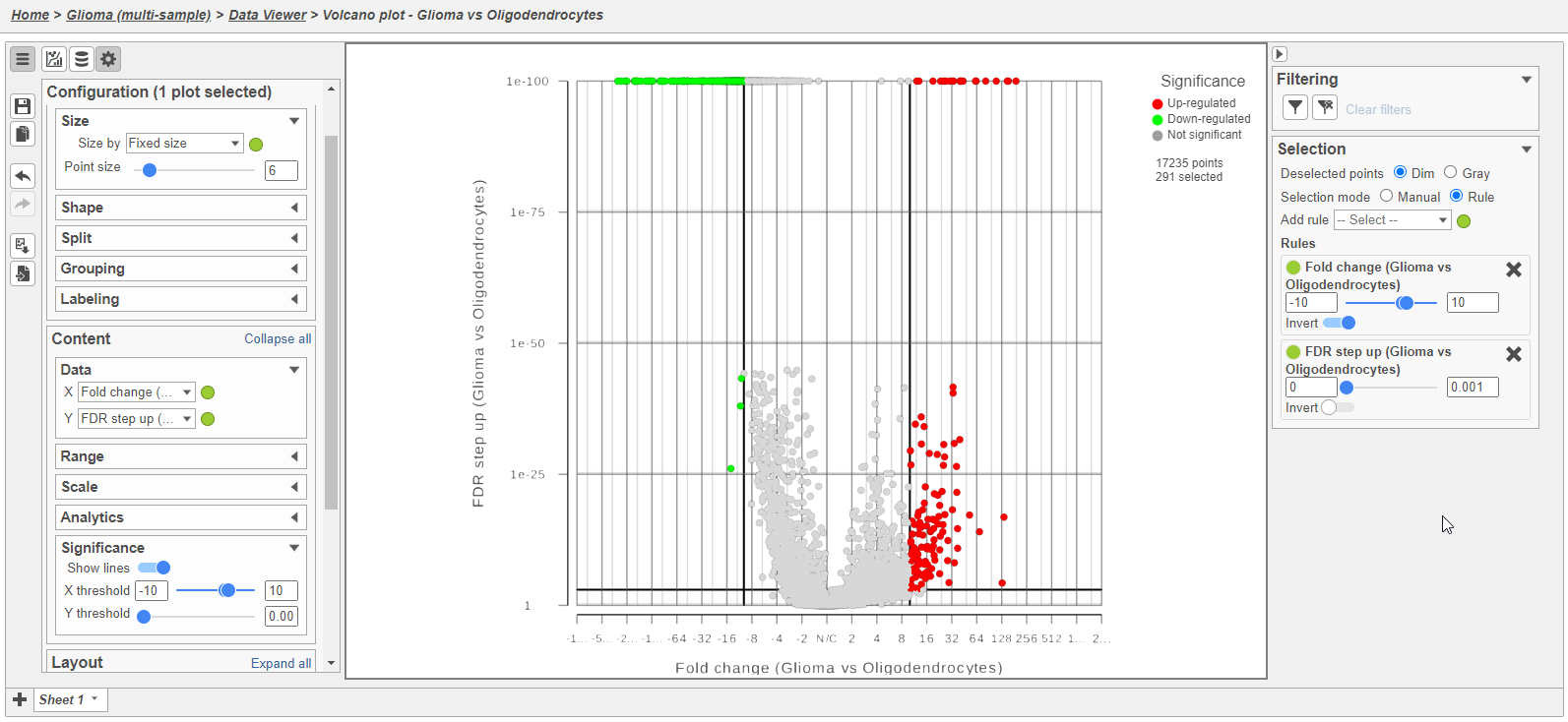
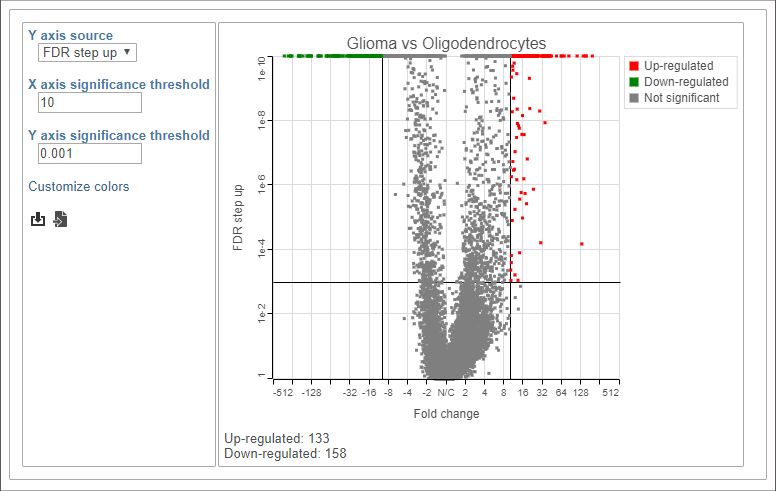
Because of the large number of cells and large differences between cell types, the p-values and FDR step up values are very low for highly significant genes. We can use the volcano plot to preview the effect of applying different significance thresholds.
- Click to view the Volcano plot
- In the Configuration card on the left, expand the Size card and increase the point size to 6
- In the Configuration card on the left, expand the Data card and change the Y-axis to FDR step up (Glioma vs Oligodendrocytes)
- In the Configuration card on the left, expand the Significance card and change X threshold to -10 and 10 and the Y threshold to 0.001
- In the Selection card on the right, set the Fold change thresholds to -10 and 10
- In the Selection card on the right, click to remove the P-value (Glioma vs Oligodendrocytes) selection rule. From the drop-down list, add FDR step up (Glioma vs Oligodendrocytes) as a selection rule and set the maximum to 0.001
...
- Choose FDR step up from the Y axis source drop-down menu
- Set the X axis significance threshold to 10
- Set the Y axis significance threshold to 0.001
This gives 133 up-regulated and 158 down-regulated genes (Figure 8).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
We can now recreate these conditions in the GSA report filter.
- Click GSA report tab in your web browser report at the top of the screen to return to the GSA report
- Click FDR step up
- Set the FDR step up filter to Less than or equal to 0.001
- Press Enter
- Click Fold change
- Set the Fold change filter to From -10 to 10
- Press Enter
The filter should include 291 genes.
- Click to apply the filter and generate a Filtered filtered Feature list node
Exploring differentially expressed genes
To visualize the results, we can generate a hierarchical clustering heat map.
- Click the green Filtered feature green Feature list produced by the Differential analysis filter the Filter list task
- Click Exploratory analysis in the task menu
- Click Hierarchical clustering/heat mapclustering
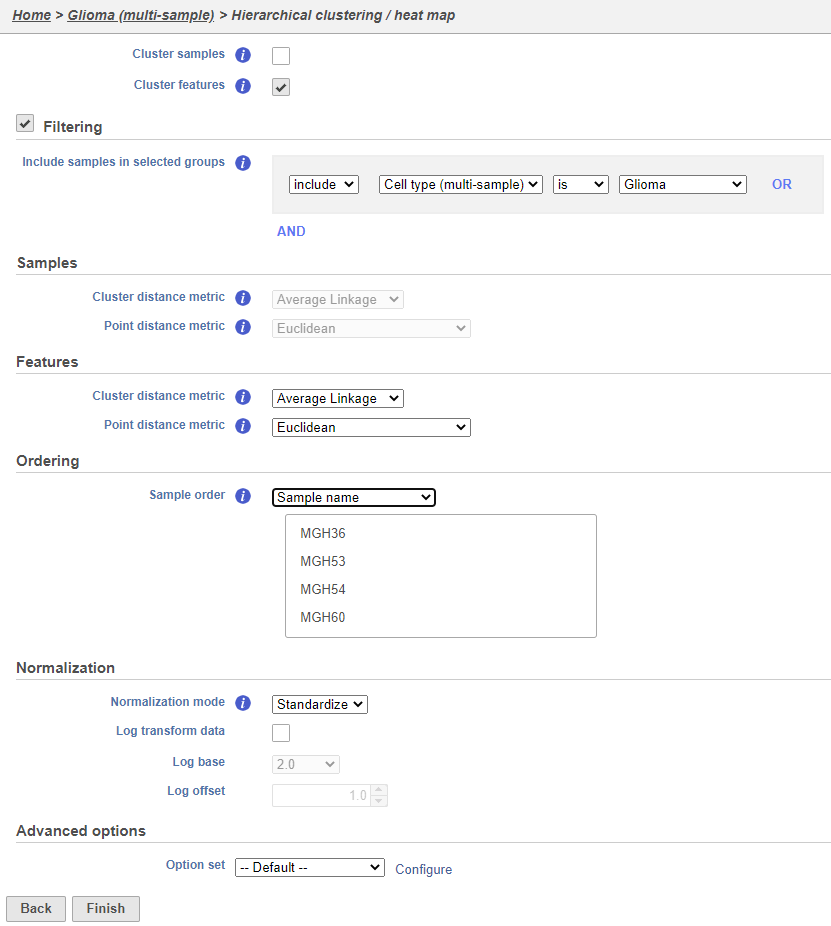
Using the hierarchical clustering options we can choose to include only cells from certain samples. We can also choose the order of cells on the heat map instead of clustering. Here, we will include only glioma cells and order the samples by sample name (Figure 79).
- Make sure Cluster samples is uncheckedUncheck Cluster samples
- Click Filtering and set the filter to include Cell type (multi-sample) Classifications is Glioma
- Choose Sample name from the Sample order drop-down menu in the Ordering section
- Click Finish
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Double click the green Hierarchical clustering node to open the heat map
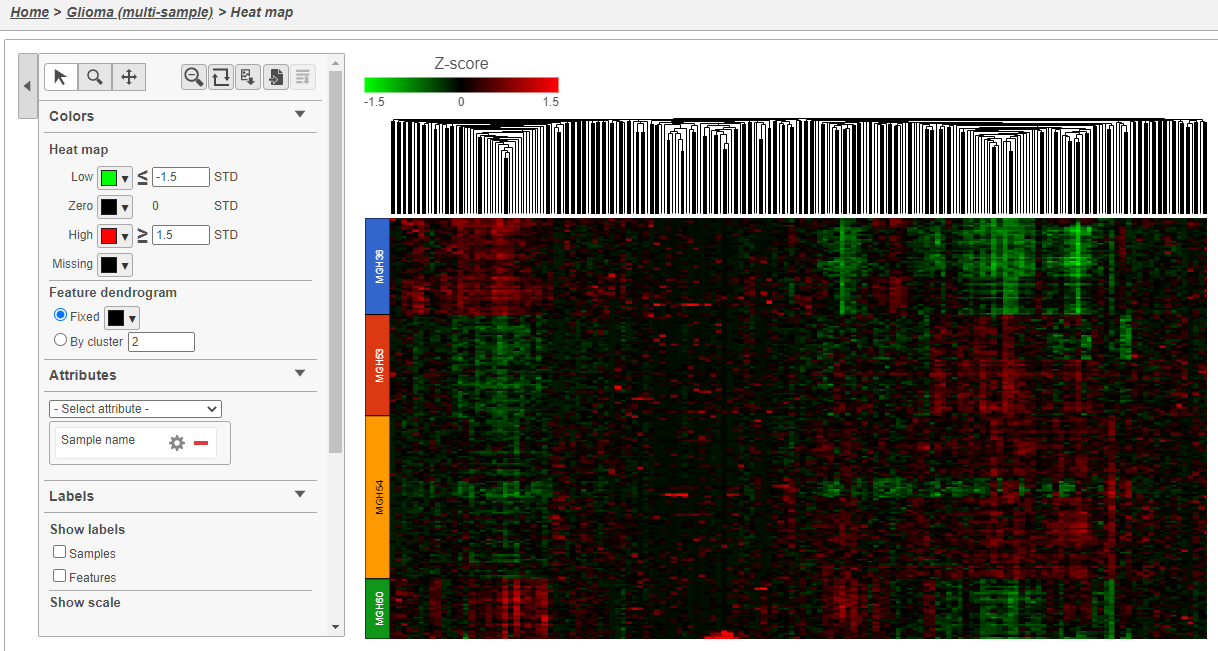
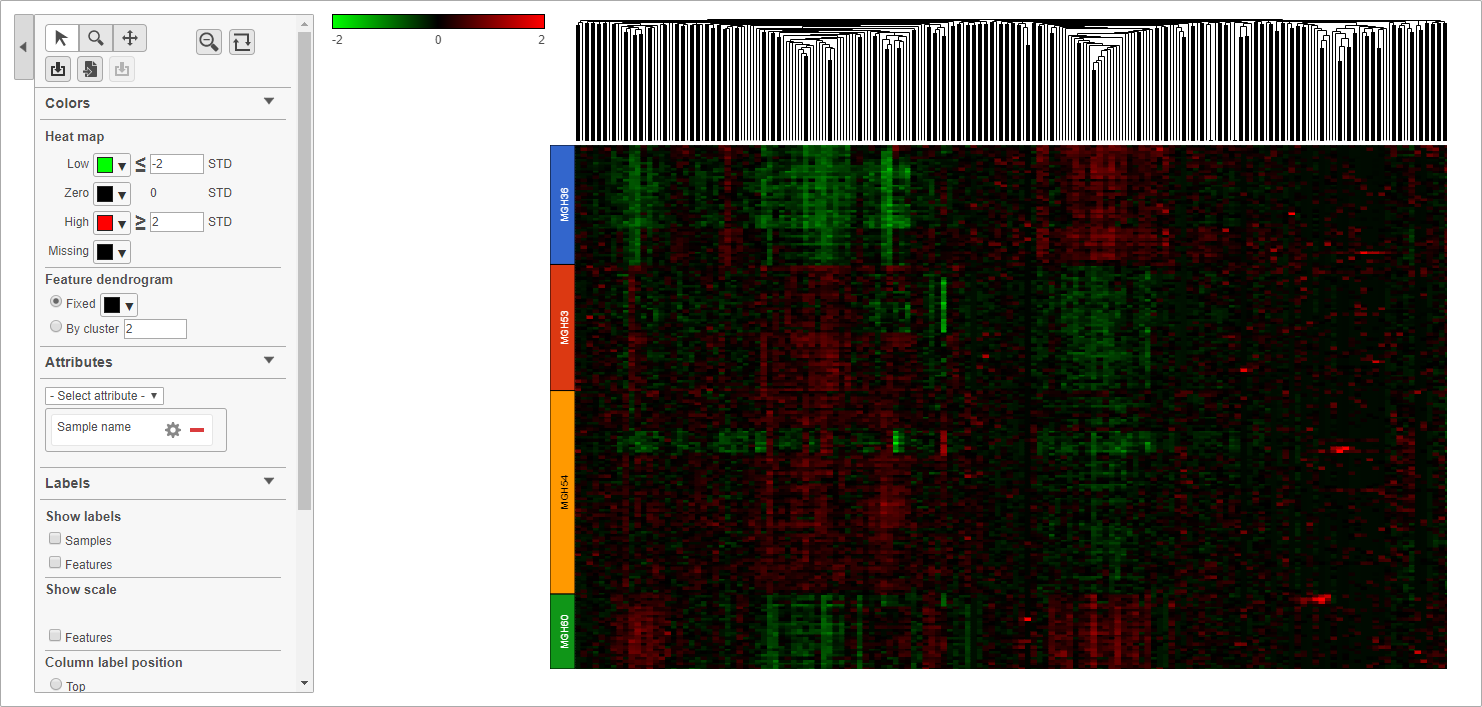
The heat map will appear black at first; the range from red to green with a black midpoint is set very wide because of a few outlier cells. We can adjust the range to make more subtle differences visible.
- Set Set Low to -1.5
- Press Enter
- Set High to 1.5
- Press Enter
- 2
- Set High to 2
The heat map now shows clear patterns of red and green.
...
Cells are now labeled with their sample name. Interestingly, samples show characteristic patterns of expression for these genes (Figure 810).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Click Glioma (multi-sample) to return to the Analyses tab.pipeline view
We can use gene set GO enrichment to further characterize the differences between glioma and oligodendrocyte cells.
- Click the green Filtered feature second green Feature list node
- Click Biological interpretation in the task menu
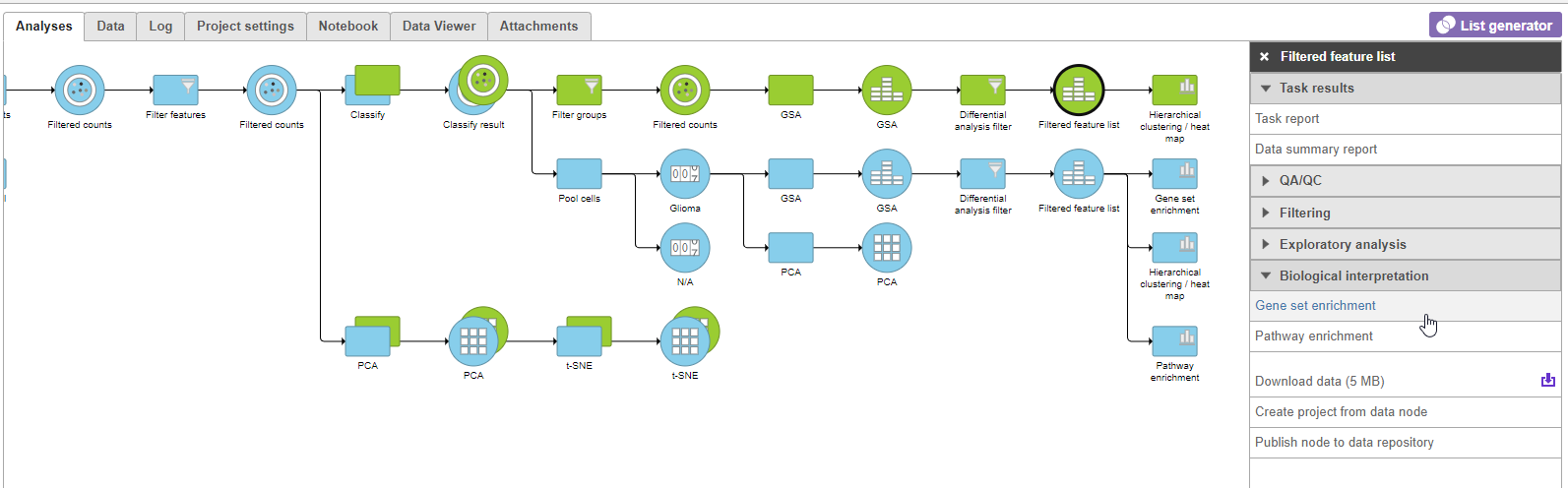
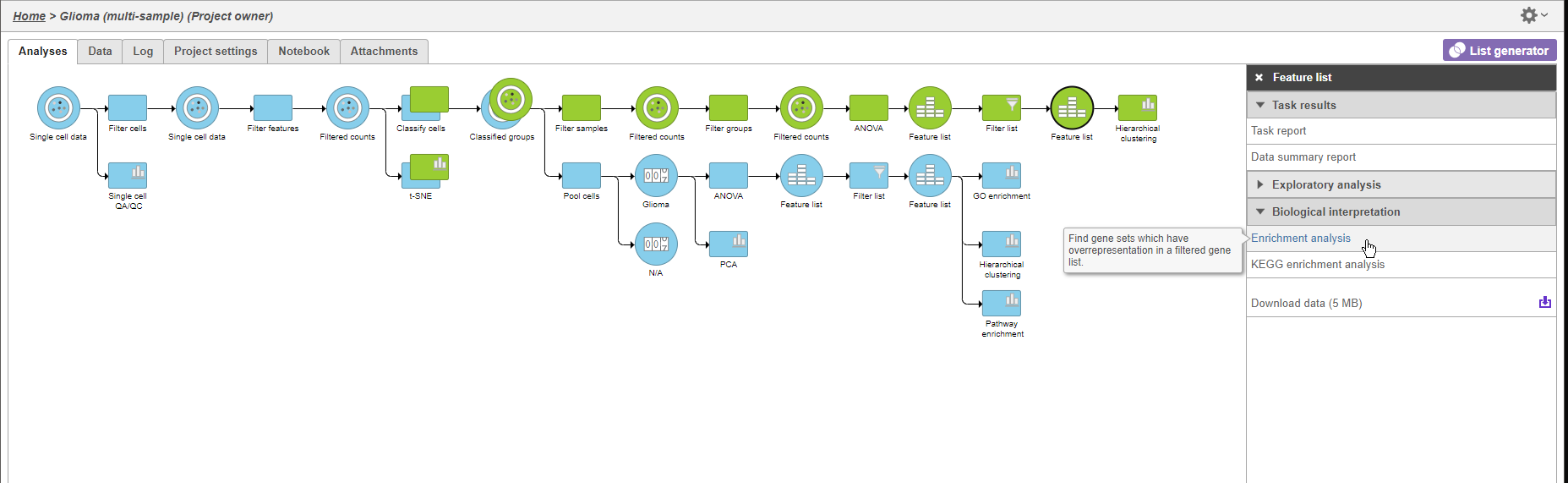
- Click Gene set enrichment Click Enrichment analysis (Figure 911)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Select Finish to continue with the most recent gene set
A Gene set A GO enrichment node will be added to the pipeline view (Figure 12).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Double-click the green Gene set green GO enrichment task node to open the task report
Top GO terms in the enrichment report include "ensheathment of neurons" and "axon ensheathment" (Figure 1013), which corresponds well with the role of oligodendrocytes in creating the myelin sheath that supports and protect axons in the central nervous system.
...