Page History
...
You can choose how the data is normalized. Under the Normalization mode dropdown, Standardize (default) will make each column mean as zero and standard deviation as 1 in all features. This is the default normalization and it makes all the features (e.g., genes) have equal weight. Standardized values are also known as Z-scores. The normalization mode Shift will make each column mean as zero. Choose None to perform clustering on the values in the quantified data node. The data can also be Log2 transformed on the fly.
Another way to invoke a heatmap without performing clustering is in via the data viewer. When you select the Heatmap icon in the available plots list, data nodes that contains two dimension matrix dimensional matrices can be use used to draw this type of plot.
...
The output of a Hierarchical clustering task is a heat map (Figure 6) with or without dendrogram depends dendrograms depending on whether you perform cluster performed clustering on samples/cells or features. By default, samples are on rows (sample labels are displayed as seen in the Data tab) and features (genes or transcripts, depending on the input data) are on columns. Colors are based on standardized expression values (default selection; performed on the fly). Dendrograms show clustering of rows (samples) and columns (variables).
...
Depending on the resolution of your screen and the number of samples and variables that need to be displayed, some binning may be involved. If there are more than samples/genes than pixels, values of neighboring components will be averaged together. When you zoom in to certain level, you will see each cell represent one sample/gene. To zoom, use Use the mouse wheel to zoom in / out. To move the map around when zoomed in, press down the right left mouse button of the mouse and drag the map.
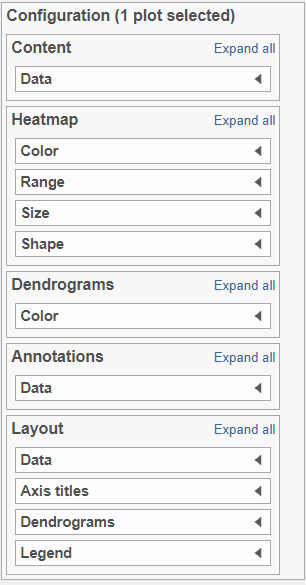
There are 5 sections in the Configuration panel (Figure 7): Content, Heatmap, Dendrograms, Annotations and Layout. Click on the section title or the triangle () to expand the a section to configure.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
This section controls the data source used to draw the values in the heatmap. The heatmap is a color representation of the values in the selected matrix selected. In addition to color, you can also use the Size drop-down list to size by a set of values. Most of the data nodes contain only one matrix, so the only options available in the Size drop down are None or Matrix (Figure 8).
...
However, if a data node contains multiple matrix informationmatrices, e.g. if you perform descriptive statistics on cluster groups for every gene like mean, std. dev, percent of detected cells, etc, each stats result will be in a separate matrix in the output data node. You might want to use the color of the component in the heatmap to represent one type of stats (like mean of the groups) and the size of the component to represent the information from a different statistic (like std. dev) (Figure 9).
...
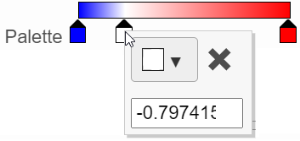
In the color palette horizontal bar, the left side color represents the lowest value and the right side color represents the highest value in the matrix data represented. By default, there are 3 color stops (): minimum, middle, and maximum color value of the default range calculated on the matrix. Left-click on the middle color stop and drag left/right can to change the middle the value this color stop represents. If you left-click on the middle color stop once, you can change the color and value this color stop represents (Figure 11). Click on the () to remove this color stop.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
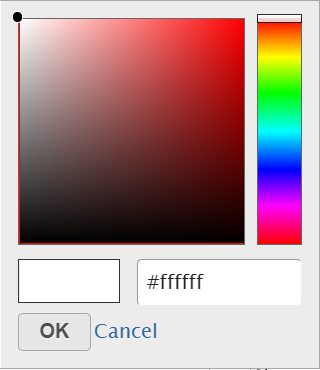
Click on the little triangle next to the color square or the adjacent triangle () to choose a color to represent the value. This will display a color picker dialog which allows selection of a color, either by clicking on a color or type in the RGB color of the color, click or by typing an RGB color code, then clicking OK (Figure 12).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
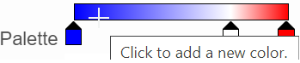
The min and max color stops cannot be dragged or removed. If you left-click on them, you can choose a different color. When you click on the Palette bar, you can add a new color stop between min and max (Figure 13). Adding a color stop can be useful when there is an outlier value in the data. You can use a different color to represent different value rangeranges.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
If cluster analysis is performed on samples and/or features, the result will be displayed in as dendrograms. By default, the dendrograms are all colored in black (Figure 6).
...
Click on the color square or its triangle () to choose a different color for the dendrogram.
When the By cluster in the Row/Column color drop-down list, the number of clusters needs to be specified (Figure 15). The top N number of clusters will be in N different colors.
...
This section allows you to add sample or cell level annotation annotations to the viewer. First, make sure to choose the correct data node which contains the annotation information you would like to use by clicking the circle (). All project level annotation annotations will be available on all data nodes in the pipeline (Figure 16). Choose an attribute from the Row annot drop-down list. Multiple attributes can be chosen from the drop-down list and can be reordered by clicking and dragging the groups below the drop-down list.
...
To change the orientation of the plot, click on the toggle switch of Data the () toggle switch in the Data sub-section of the Layout section (Figure 17).
...
Axis titles, dendrograms, and the legend can be turned on or off by clicking the relevant toggle switches. The axes axis label font size can be changed by specifying the number of pixels.
In-plot controls
In the mode bar of the viewer (in the top The heatmap has several different mouse modes which modify the way the plot responds to the mouse buttons. The mode buttons are in the upper right corner of the heatmap), there is a Flip mode button (). . Clicking one of these buttons puts the heatmap into that mode.
In flip mode (), you can click on a line in the dendrogram (which represents a cluster branch) and the location of the two legs of the branch will be swapped.
In move mode (), you can left-click and drag to move around the heatmap (if you are not fully zoomed inout). Left-clicking once on the heatmap or on a dendrogram branch will select that the associated rows/columncolumns.
In selection mode (), you can click and drag to select a range of rows, columns, or components.
...