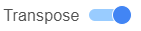Page History
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
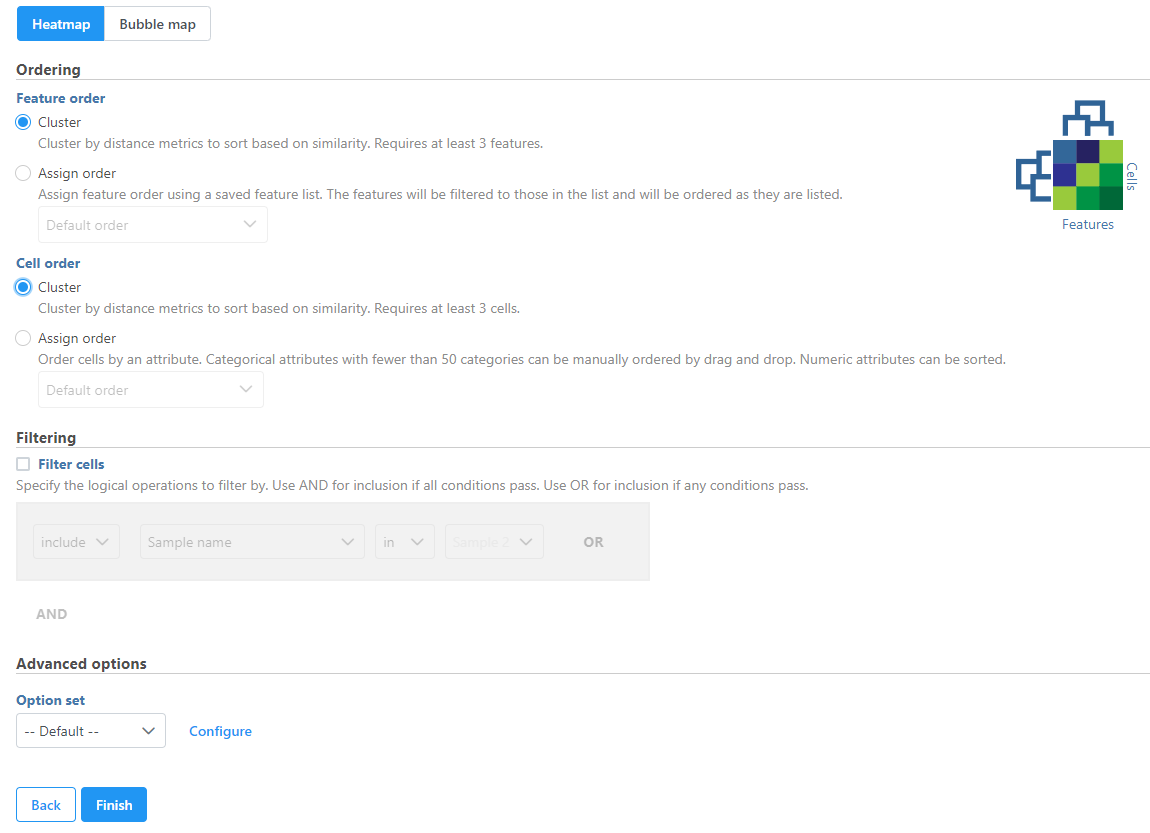
The hierarchical clustering setup dialog (Figure 2) enables you to control the clustering algorithm. Starting from the top, you can choose to plot a Heatmap or a Bubble map (clustering can be performed on both plot types). Next, perform Ordering by selecting Cluster for either feature order (genes/transcripts/proteins) or cell/sample/group order or both. Note the context-sensitive image that helps you decide to either perform hierarchical clustering (dendrogram) or assign order (arrow) for the columns and rows to help you orient yourself and make decisions (In Figure 2 below, Cluster is selected for both options so a dendrogram is shown in the image).
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
If you do not want to cluster all the samples, but select a subset based on a specific sample or cell attribute (i.e. group membership), check Filter cells under Filtering and set a filtering rule using the drop down lists (Figure 3). Notice the drop-down lists allow more than one factor (when available) to be selected at a time. When configuring the filtering rule, use AND to ensure all conditions pass for inclusion and use OR for any conditions to pass.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
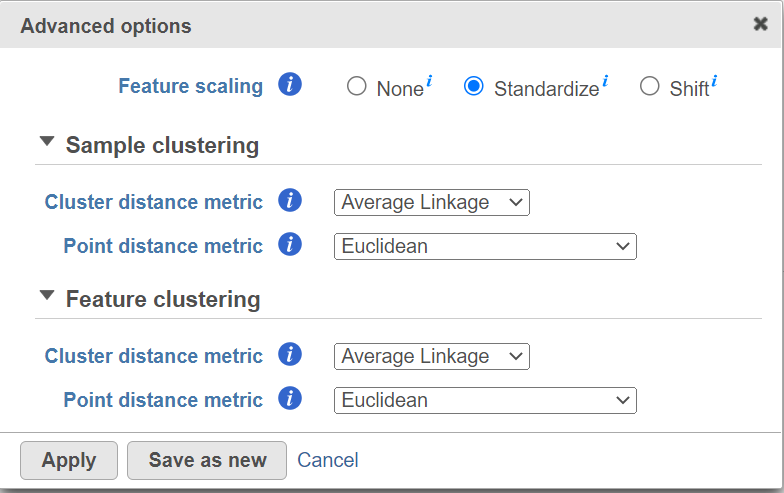
Hierarchical clustering uses distance metrics to sort based on similarity and is set to Average Linkage by default. This can be adjusted by clicking Configure under Advanced options (Figure 4).
Cluster distance metric for cells/samples and features is used to determine how the distance between two clusters will be calculated:
- Single Linkage: the distance between two clusters is determined by the distance of the closest objects in the two clusters
- Complete Linkage: the distance between two clusters is equal to the distance between the two furthest members of those clusters
- Average Linkage: the average distance between all the pairs of objects in the two different clusters is used as the measure of distance between the two clusters
- Centroid method: the distance between two clusters is equal to the distance between the centroids of those clusters
- Ward's method: the distance between two clusters is designed to minimize the size of an error measure based on the sum of squares
Point distance metric is used to determine the distance between two rows or columns. For more detailed information about the equations, we refer you to the distance metrics chapter.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
If the Cluster option is unchecked for Cells/Sample/Group order or Feature order, the Ordering option will be Assign order (Figure 5).
...
When choose Assign order, the Default order of cells/samples/groups (rows) is based upon the labels as displayed in the Data tab and features (columns) are dependent on the input data of the data node.
...
Cell/Sample/Group order can also be assigned by choosing an attribute from the drop down list. Click and drag to rearrange categorical attributes; numeric attributes can be sorted in ascending or descending order (note the arrows in the image which are different from the dendrogram for Cluster) (Figure 3).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Another way to invoke a heatmap without performing clustering is via the data viewer. When you select the Heatmap icon in the available plots list, data nodes that contain two-dimensional matrices can be used to draw this type of plot. A bubble map can also be similarly plotted (use the arrow from the heatmap icon to select a Bubble map for descriptive statistics that have been generated in the data analysis pipeline.
If you do not want to cluster all the samples, but select a subset based on a specific sample or cell attribute (i.e. group membership), check Filter cells under Filtering and set a filtering rule using the drop down lists (Figure 4). Notice the drop-down lists allow more than one factor (when available) to be selected at a time. When configuring the filtering rule, use AND to ensure all conditions pass for inclusion and use OR for any conditions to pass.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Hierarchical clustering uses distance metrics to sort based on similarity and is set to Average Linkage by default. This can be adjusted by clicking Configure under Advanced options (Figure 5). You can choose how the data is scaled (sometimes referred to as normalized). Navigate to Advanced options → Configure → There are three Feature scaling options, Standardize (default for a heatmap) will make each column mean as zero and standard deviation as 1 in all features. This is the default scaling for a heatmap and it makes all of the features (e.g., genes or proteins) have equal weight; standardized values are also known as Z-scores. The scaling mode Shift will make each column mean as zero. Choose None to not scale and perform clustering on the values in the quantified input data node (this is the default for a bubble map). If a bubble map is scaled, scaling will be performed on the group summary method (color).
Another way to invoke a heatmap without performing clustering is via the data viewer. When you select the Heatmap icon in the available plots list, data nodes that contain two-dimensional matrices can be used to draw this type of plot. A bubble map can also be similarly plotted (use the arrow from the heatmap icon to select a Bubble map for descriptive statistics that have been generated in the data analysis pipeline.
Cluster distance metric for cells/samples and features is used to determine how the distance between two clusters will be calculated:
- Single Linkage: the distance between two clusters is determined by the distance of the closest objects in the two clusters
- Complete Linkage: the distance between two clusters is equal to the distance between the two furthest members of those clusters
- Average Linkage: the average distance between all the pairs of objects in the two different clusters is used as the measure of distance between the two clusters
- Centroid method: the distance between two clusters is equal to the distance between the centroids of those clusters
- Ward's method: the distance between two clusters is designed to minimize the size of an error measure based on the sum of squares
Point distance metric is used to determine the distance between two rows or columns. For more detailed information about the equations, we refer you to the distance metrics chapter.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Heatmap
The output of a Hierarchical clustering task can be a heatmap (Figure 6) or a bubble map with or without dendrograms depending on whether you performed clustering on cells/samples/groups or features. By default, samples are on rows (sample labels are displayed as seen in the Data tab) and features (depending on the input data) are on columns. Colors are based on standardized expression values (default selection; performed on the fly). Dendrograms show clustering of rows (samples) and columns (variables).
...
There are plot Configuration/Action options for the Hierarchical clustering / heat mapheatmap task which apply to both the heatmap and bubble map in the Data viewer (below): Axes, Heatmap, Dendrograms, Annotations, and DescriptionsDescription. Click on the icon to open these configuration options.
Axes
- This section controls the Content or data source used to draw the values in the heatmap or bubble map and also the ability to transpose the axes. The plot is a color representation of the values in the selected matrix. Most of the data nodes contain only one matrix, so it will just say Matrix for the chosen data node. However, if a data node contains multiple matrices (e.g. descriptive statistics were performed on cluster groups for every gene like mean, standard deviation, percent of cells, etc) each statistic will be in a separate matrix in the output data node. In this case, you can choose which statistic/matrix to display using the drop-down list (this would be the case in a bubble map).
- To change the orientation (switch the columns and rows) of the plot, click on the () toggle switch.
- Row labels and Column labels can be turned on or off by clicking the relevant toggle switches.
- The label size can be changed by specifying the number of pixels using Max size and Font. If an Ensembl annotation model has been associated with the data, you can choose to display the gene name or the Ensembl ID using the Content option.
...
- To change the min and max threshold values represented by the color palette, click on the toggle switch () in the under Range card, and specify the values in the text boxes.
- In addition to color, you can also use the Size drop-down list to size by a set of values from another matrix stored in the same data node. Most of the data nodes contain only one matrix, so the only options available in the Size drop down will be None or Matrix. In cases where you have multiple matrices, you might want to use the color of the component in the heatmap to represent one type of statistic (like mean of the groups) and the size of the component to represent the information from a different statistic (like std. dev).
...
- The shape of the heatmap cell (component) can be configured either as a rectangle or circle by selecting the radio button in the under Shape card.
Dendrograms
If cluster analysis is performed on samples and/or features, the result will be displayed as dendrograms. By default, the dendrograms are all colored in black.
...
The heatmap has several different mouse modes which modify the way the plot responds to the mouse buttons. The mode buttons are in the upper right corner of the heatmap. Clicking one of these buttons puts the heatmap into that mode.
- In point mode (), you can left-click and drag to move around the heatmap (if you are not fully zoomed out). Left-clicking once on the heatmap or on a dendrogram branch will select the associated rows/columns.
- In selection mode (), you can click and drag to select a range of rows, columns, or components.
- In flip mode (), you can click on a line in the dendrogram (which represents a cluster branch) and the location of the two legs of the branch will be swapped. If no clustering is performed (no dendrogram is generated), in this mode, you can click on the label of an item (observation or feature), drag and drop to manually switch orders of the row or column on the heatmap.
- Click on
...
- reset view () to
...
- reset to the default
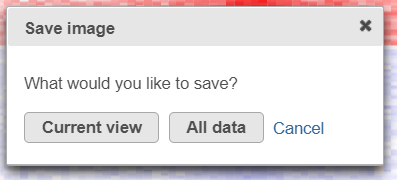
- Save Image icon () enables you to download the heat map to your local computer. If the heat map contains up to 2.5M cells (features * observations), you can choose between saving the current appearance of the heat map window (Current view) and saving the entire heat map (All data)
...
- . Depending on the number of features / observations, Partek Flow may not be able to fit all the labels on the screen, due to the limit imposed by the screen resolution. All Data option provides an image file of sufficient size so that all the labels are readable (in turn, that image may not fit the compute screen and the image file may be quite large). If the heat map exceeds 2.5M cells, the Current view option will not be shown, and you will see only a dialog like the one
...
| SubtitleText | Save Image tool dialog downloads an image file to the local computer: Current view - only the visible part of the heat map will be saved; All data - entire heat map will be saved |
|---|---|
| AnchorName | save_image_heat_map |
- below.
- After selecting either Current view (if applicable) or All data button, the next dialog (
...
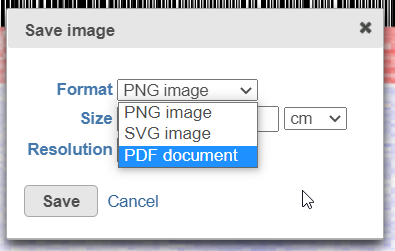
- below) will allow you to specify the image format, size, and resolution.
...
| SubtitleText | Save image dialog: specifying image type (.png is supported for Current view only), size, and resolution |
|---|---|
| AnchorName | save_image_type |
| Additional assistance |
|---|
| Rate Macro | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...