Page History
...
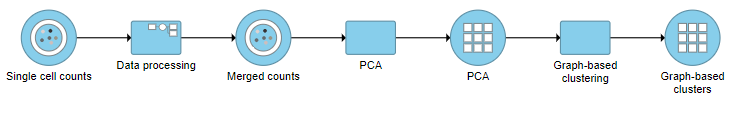
A Graph-based clustering task node will be added to the pipeline under the Analyses tab and a circular Graph-based clusters output data node will be produced (Figure ?10)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
- Click the circular Graph-based clusters data node
- Click Exploratory analysis in the toolbox
- Click UMAP
- Set the number of principal components to 15 (Figure ?11)
- Click Finish to run the task
...
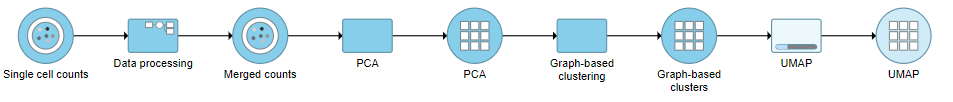
A UMAP task node will be added to the pipeline under the Analyses tab and a circular UMAP output data node will be produced (Figure ?12)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
Performing exploratory analysis with gene expression data is the same as for the merged counts. Because there are a large number of genes, you will need to reduce the dimensionality with PCA, choose an optimal number of PCs and perform downstream clustering and visualization (e.g. graph-based clustering and UMAP/t-SNE). Performing exploratory analysis with protein data is different. There is no need to reduce the dimensionality as there are only a handful of features (17 proteins in this case), so you can proceed straight to downstream clustering and visualization. Figure ? 13 shows an example of how the pipeline might look if the data is split and analyzed separately.
...
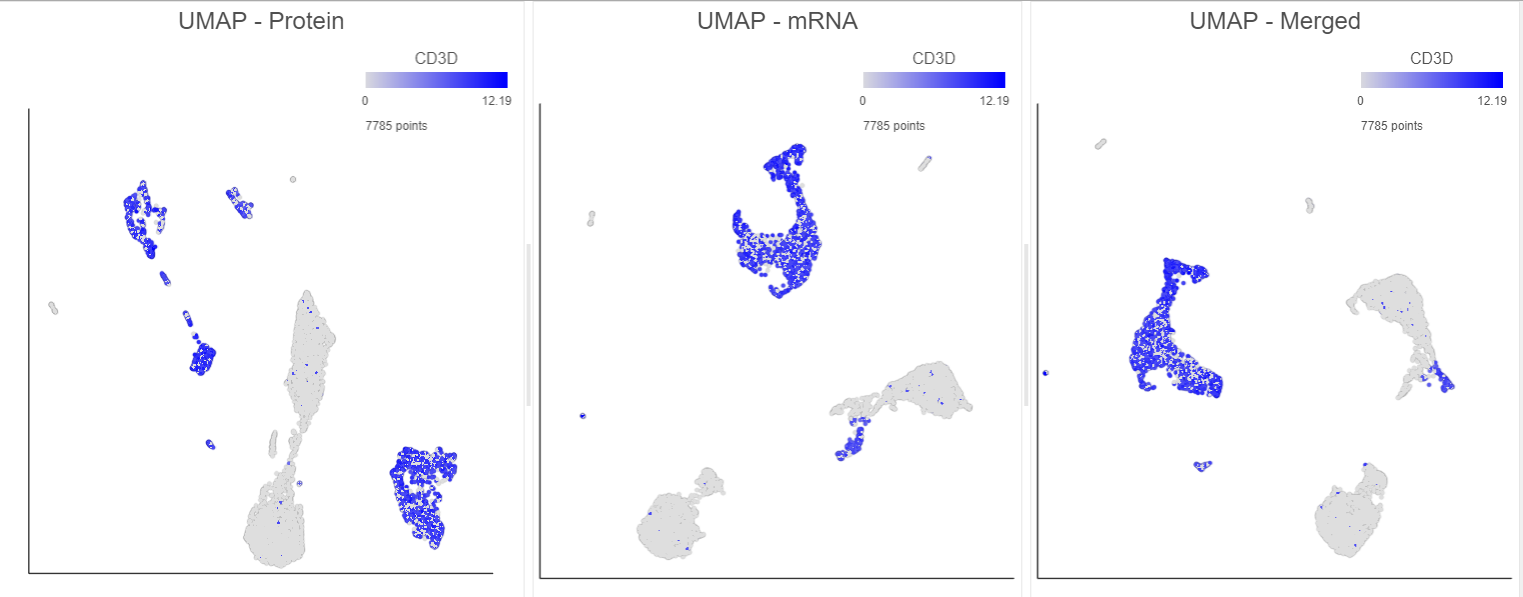
You can then use the Data viewer to bring together multiple plots for comparison (Figure ?14).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...