Page History
...
- Training set data–28 samples (11 disease samples and 15 normal samples) on 9953 genes
- Test set data – 8 samples on 9953 genes
- configuration of the model builder (.pcms file)
- 36 sample data set – total of training and test samples
- deployed model (.pbb file)
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
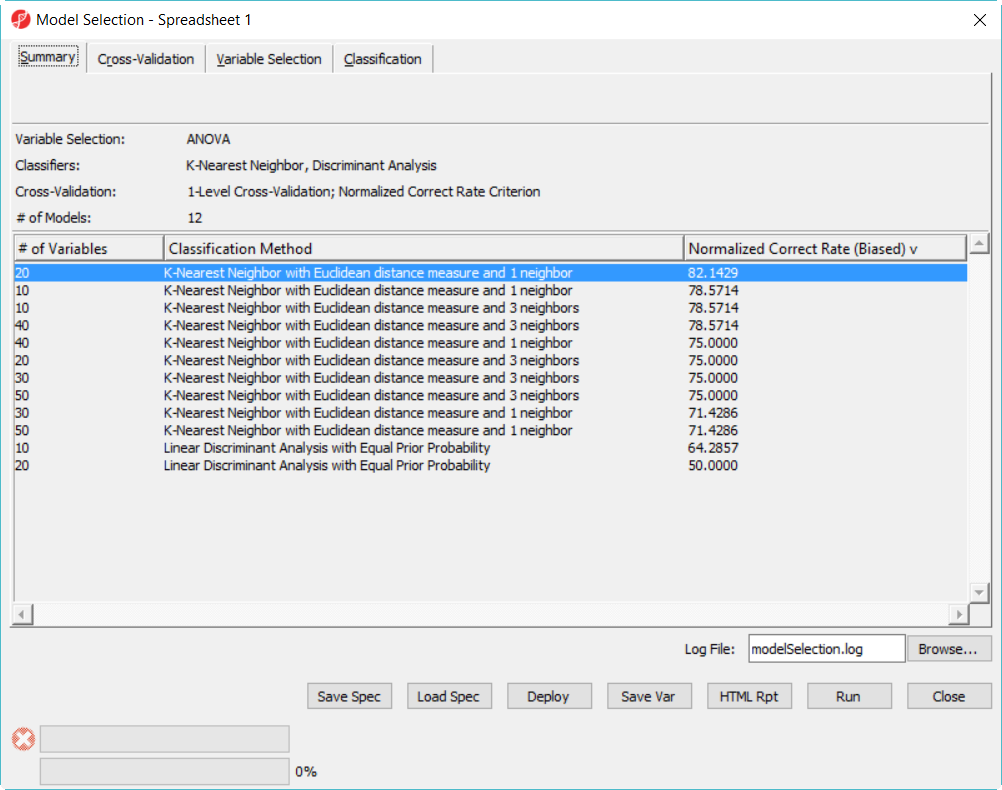
- Click on Deploy button to deploy the model using the whole dataset, save the file as 20var-1NN-Euclidean.ppb. It will run ANOVA on the 28 samples to generate the top 20 genes and build a model using 3 K-Nearest neighbor based on Euclidean distance measure.
- Since the deployed model was from the whole 28 samples, in order to know the correct rate, we need a test set to run the model on.
...
Hold-out validation have to split the whole data into two parts -- training set and test set. Increasing the size of training set will improve the efficiency of the fitted predicted models; increasing the size of test set will improve power of validation. When Typically genomic data (like Microarray or NGS data) doesn't have large number of sample size, using hold-out method, we have to make the training and test test even smaller, when the sample size is small (here the example data is just illustrate the function), the result is not precise. Some people believe that you should have at least 100 test samples to properly measure the correct rate with a useful precision. The bigger size of training set, the better efficiency of the fitted predicted models are; the bigger size of test set, the better power of validation.
Another method to get unbiased accuracy estimate in Partek Genomics Suite is to do 2-Level Cross validation utilize the 36 sample data, you don't have to split the data. The following steps is to show how to use all the 36 samples to select the best model and get the accuracy estimate using all the 36 samples. 36 sample data set --combining both training set and test set samples.
- Choose File>Open... to open to browse and open 36samples.fmt
- Choose Tools>Predict>Model Selection... from the menu
- Click on Load Spec to select tutorial.pcms
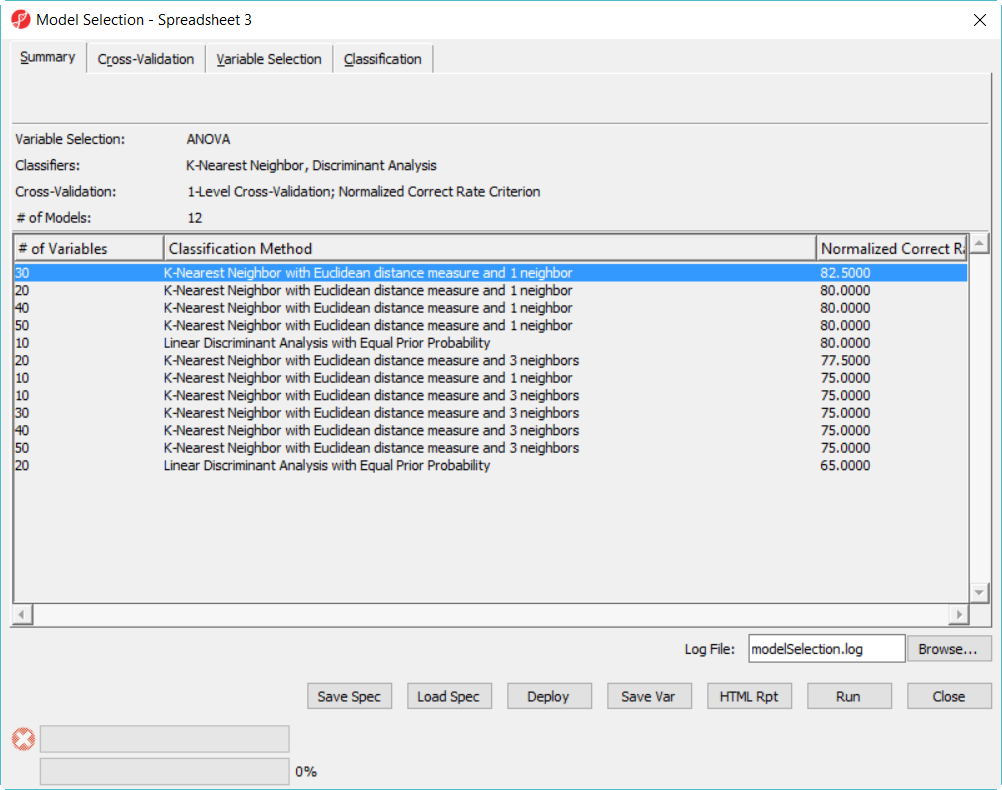
- Click Run on 1-level cross validation to select the best model using 36 samples
The best model is 30 variables using 1-Nearest Neighbor with Euclidean distance measure (Figure 8)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Click on the model with best correct rate and deploy the model
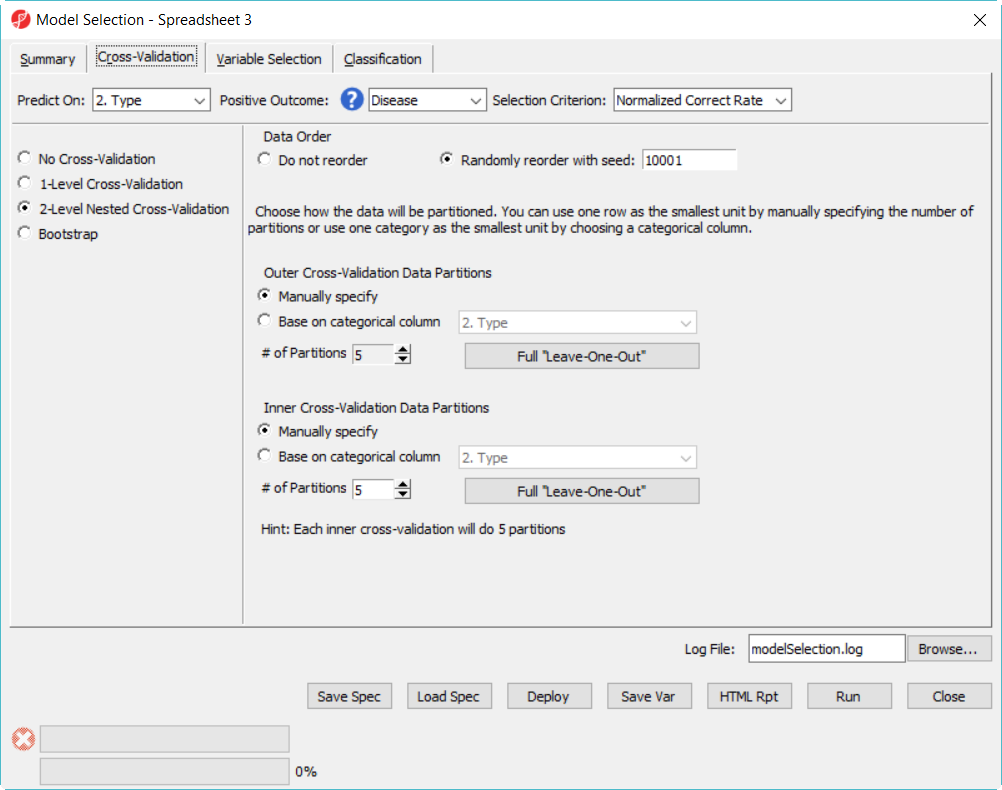
Since there is no separate data to test the correct rate of the best model in the 12 model space, we will do a 2-level cross-validation to get the accuracy estimate.
- Click on Cross-Validation tab, choose 2-Level nested Cross-Validation, specify the number of partition as 5 for both, level everything else the same and click Run (Figure 9)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Cross validation
Common mistakes
| Additional assistance |
|---|
|
| Rate Macro | ||
|---|---|---|
|