Page History
...
Hierarchical clustering groups similar objects into clusters. To To start, each row and/or column is considered a cluster. The two most similar clusters are then combined and this process is iterated until all objects are in the same cluster. Hierarchical clustering displays the resulting hierarchy of the clusters in a tree called a dendogramdendrogram. Hierarchical clustering is useful for exploratory analysis because it shows how samples group together based on similarity of features.
Hierarchical clustering is considered an unsupervised clustering method. Unsupervised clustering methods do not take the identity or attributes of samples into account when clustering. This means that experimental variables such as treatment, phenotype, tissue, number of expected groups, etc. do not guide or bias cluster building. Alternatively, supervised Supervised clustering methods do consider experimental variables when building clusters.
Partek Genomics Suite offers two alternatives to Hierarchical clustering - K-Means clustering and Self-Organizing Map. For a more in-depth description of how Partek Genomics Suite performs these different forms of clustering analysis, please see Chapter 8 Hierarchical & Partitioning Clustering of the Partek Manual. The Partek Manual can be accessed through Partek Genomics Suite under Help > On-Line Help.
Visualizing Hierarchical Clustering
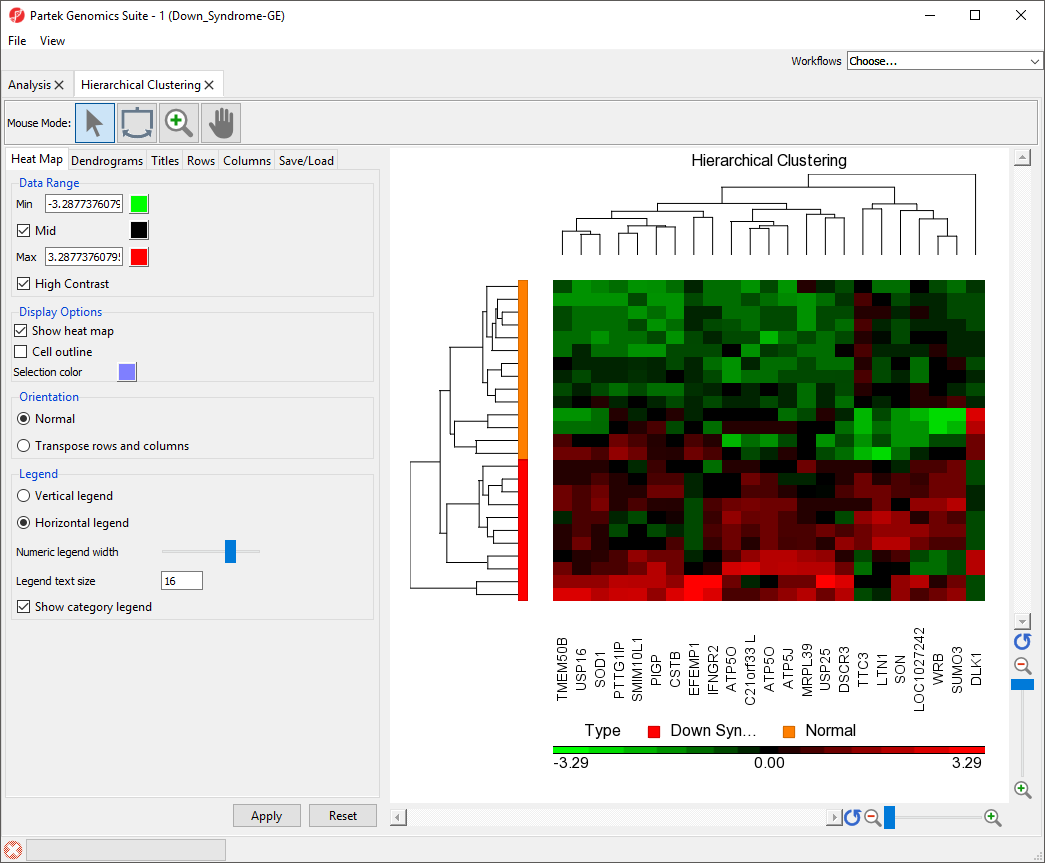
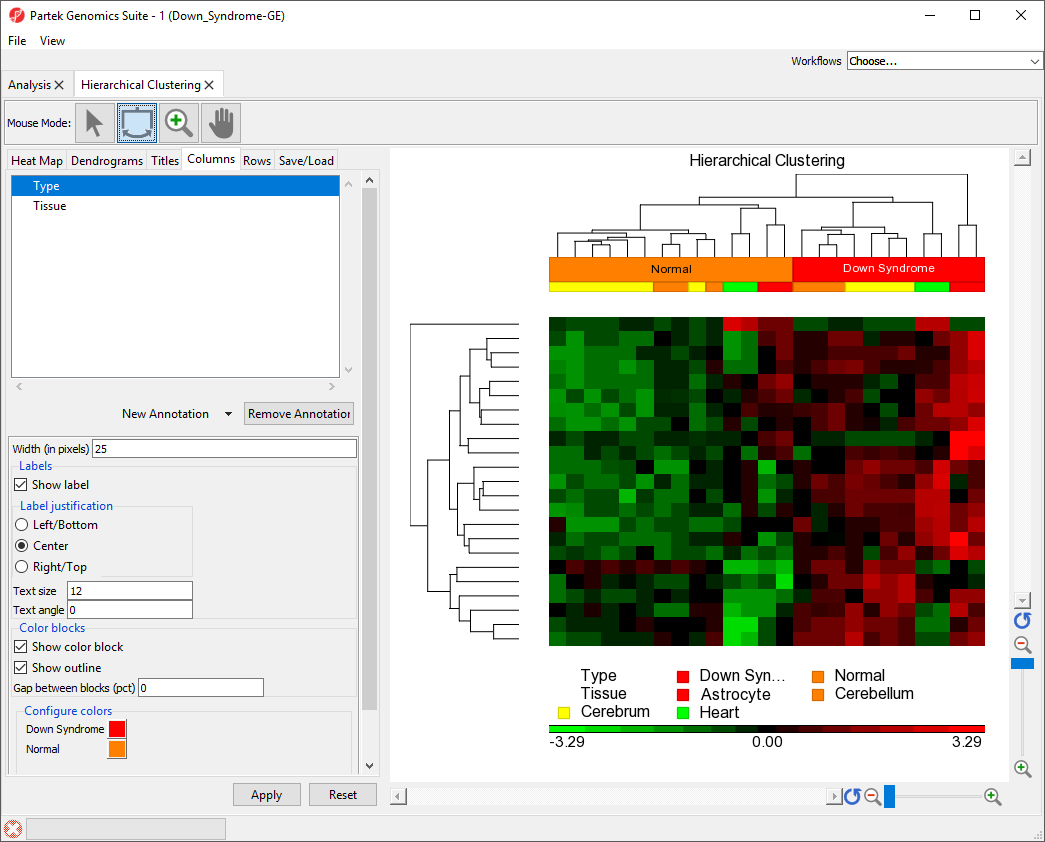
To illustrate the capabilities and customization options of hierarchical clustering in Partek Genomics Suite, we will explore an example of hierarchical clustering drawn from the tutorial Gene Expression Analysis. The data set in this tutorial includes gene expression data from patients with or without Down syndrome. Using this data set, 23 highly differentially expressed genes between Down syndrome and normal patient tissues were identified. These 23 differentially regulated genes were then used to perform hierarchical clustering of the samples. Follow the steps outlined in Hierarchical Clustering and Adding Information to Gene Lists to Performing hierarchical clustering to perform hierarchical clustering and launch the Hierarchical Clustering tab (Figure 1).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The right-hand section of the Hierarchical Clustering tab is a heat map showing relative expression of the genes in the list used to perform clustering. The heat map can be configured using the properties panel on the left-hand side of the tab. By default, down-regulated genes will be shown in green, genes with no change in expression will be shown in black, and up-regulated genes will be shown in red.The dendograms In this example, the low expression value is colored in green, the high expression value is in red, and the mid-point value between min and max is colored in black.The dendrograms on the left-hand side and top of the heat map show clustering of samples as rows and features (probes/genes in this example) as columns. Columns are labeled with the gene symbol if there is enough space for every gene to be annotated. Rows are colored based on the groups of the first sample categorical attribute in the source spreadsheet. The sample legend below the heat map indicates which colors correspond to which attribute group. In this example, Down syndrome patient samples are red and normal patient samples are orange.
...
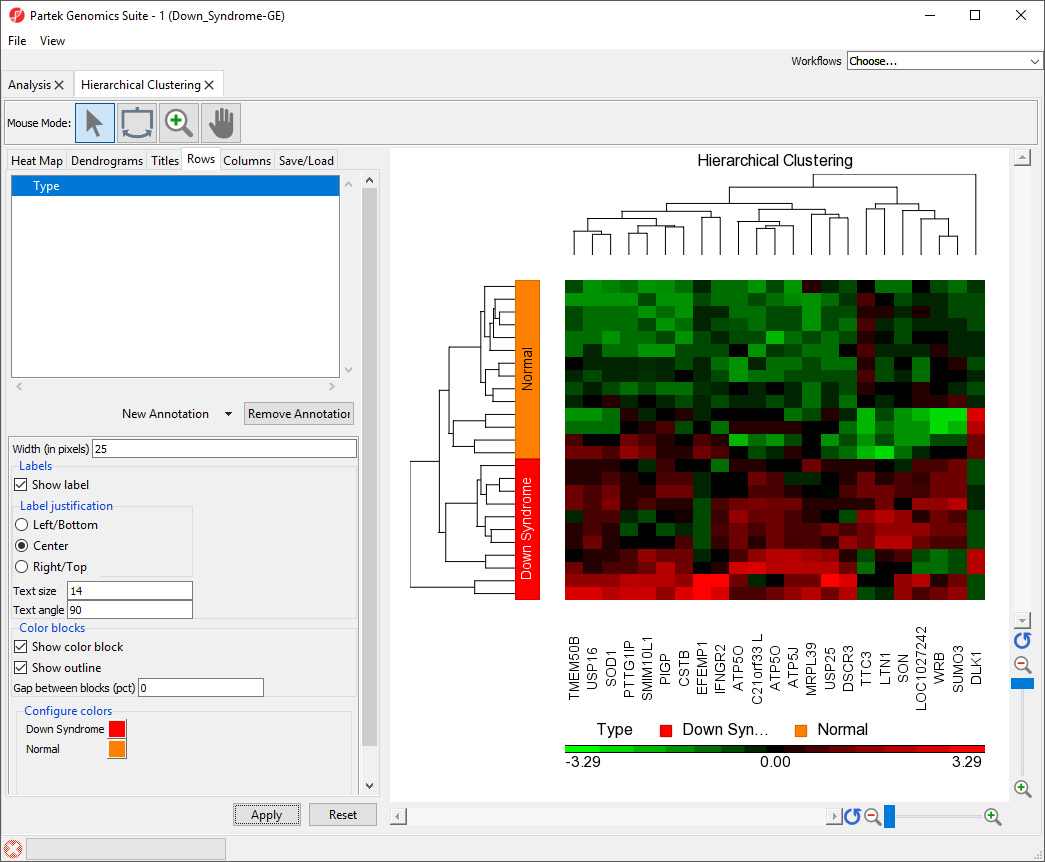
The sample attributes are now labeled with group titles (Figure 2).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Adding a Sample Attribute to the Heat Map
...
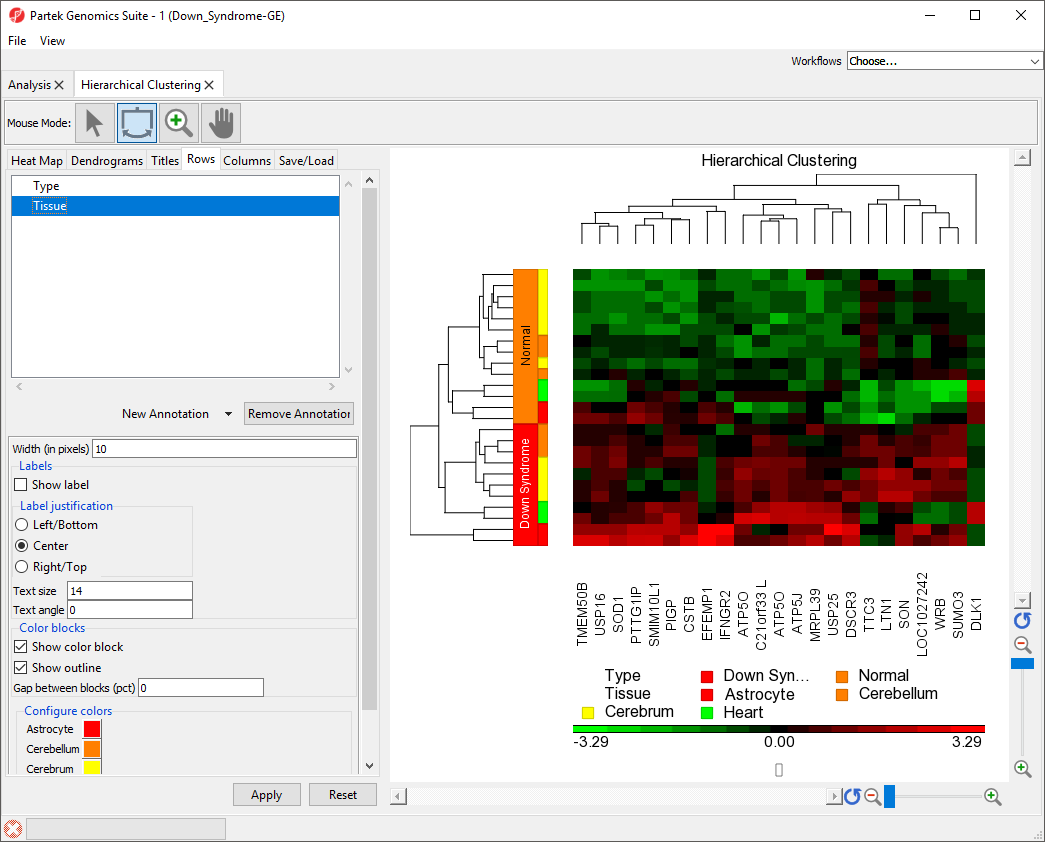
Color blocks indicating the tissue of each sample have been added to the row labels and sample legend (Figure 3).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
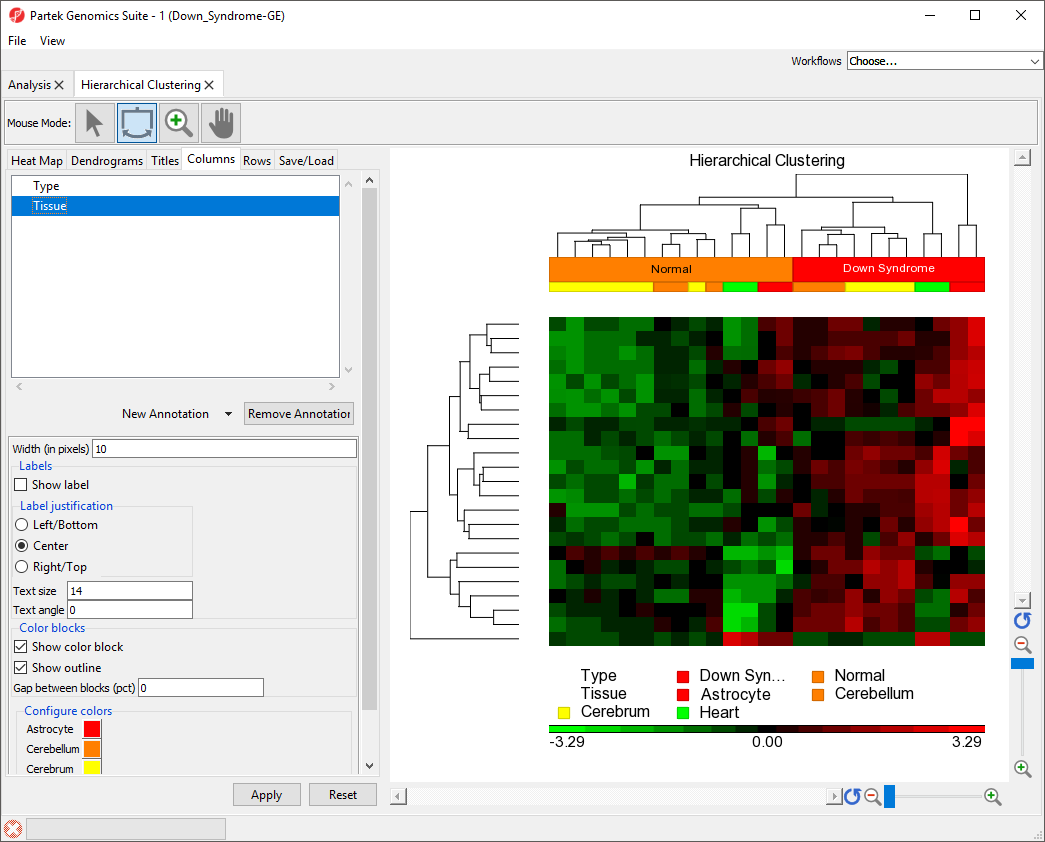
Flipping Columns or Rows
Any of the denograms legs can be flipped to reorient Each cluster node has two sub-cluster branches (legs) except for the bottom level in the dendrogram, the order of the two branches (or legs) is arbitrary, so the two sub-clusters position can be flipped within the cluster. This does not change the clustering, only the position of the clusters on the plot.
- Select () from the Mouse Mode icon set to activate Flip Mode
- Click on the dendogram leg associated with the bottom row
...
- Clicking on a line (or drawing a bounding box on a line using left mouse button) that represents a sub-cluster branch (or dendrogram leg) will flip the selected leg with the other one leg within the same parent cluster. In this example, clicking on the bottom line will move it to the top of the heat map (Figure 5).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
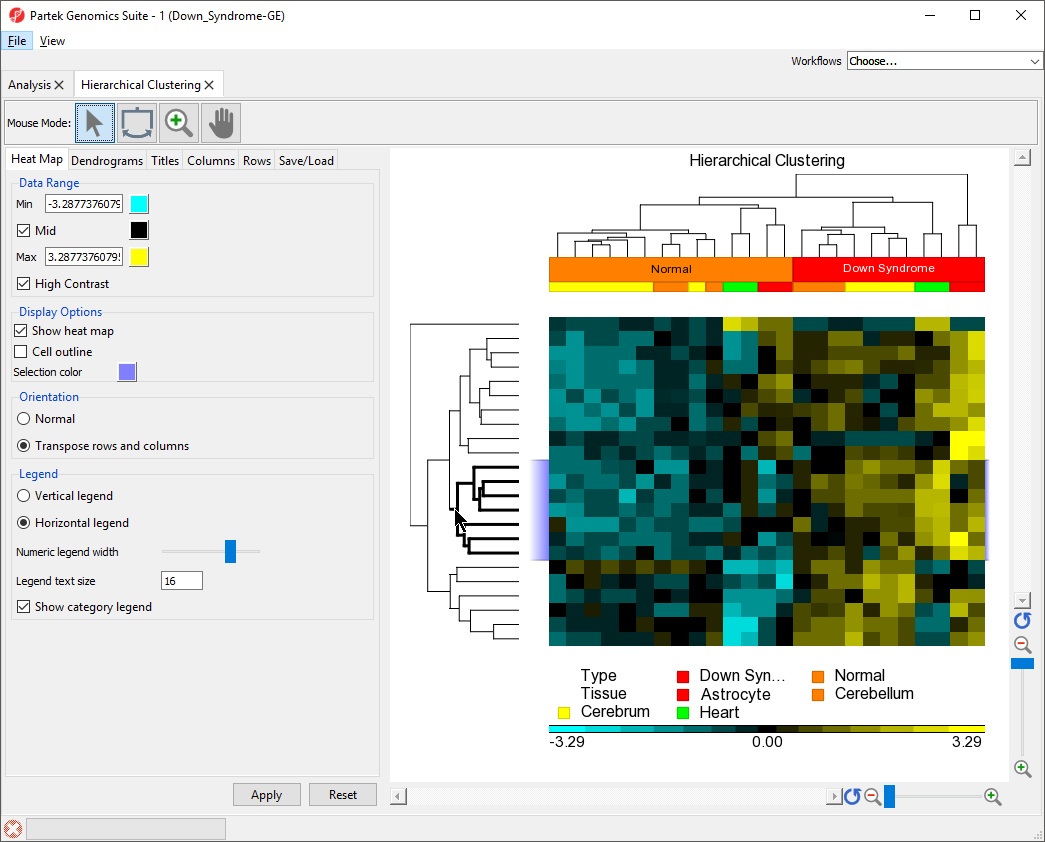
Changing Heat Map Colors
The minimum, maximum, and midpoint colors of the heart map intensity plot can be customized.
...
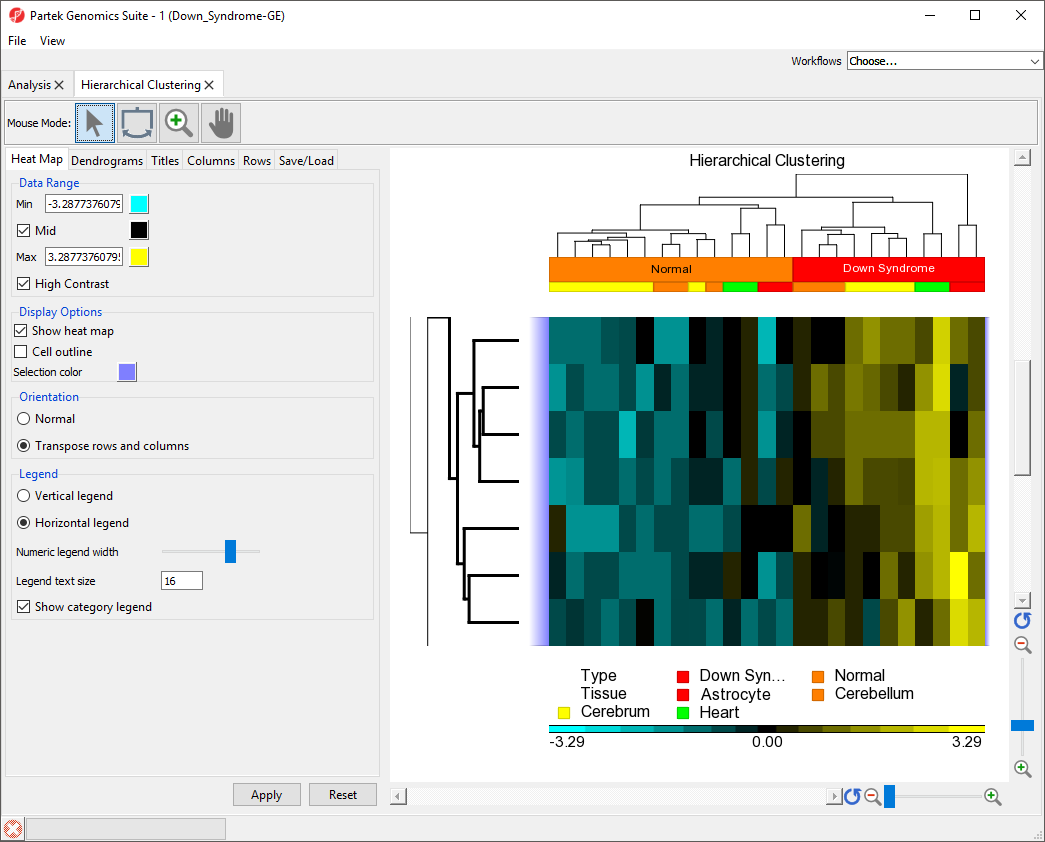
We can use the hierarchical clustering heat map to examine groups of genes that exhibit similar expression patterns. For example, genes that are up-regulated in Downs Down syndrome samples and down-regulated in normal samples.
- Select () from the Mouse Mode icon set to activate Selection Mode
- Select on the middle cluster of the rows denodgram dendrogram as shown (Figure 7) to select it
...
- by clicking on the line or drawing a bounding box around the line
The lines within the selected cluster will be bold and the corresponding columns (or rows) on the spreadsheet in the analysis tab will be highlighted.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Right-click on anywhere in the dendogramviewer
- Select Zoom to Fit Selected Rows
The same steps can be used to zoom into columns or rows. Here, we have zoomed in on the rows, but not columns to show the expression levels of the selected genes for all samples (Figure 8).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
To reset zoom select () on the xy-axis to show all columns rows and the yx-axis to show all rowscolumns.
- Select () on the y-axis to show all rows
- Click Left click anywhere in the hierarchical clustering plot to deselect the dendogram dendrogram
Exporting a List of Genes From a Selected Cluster
...
- Select () from the Mouse Mode icon set to activate Selection Mode
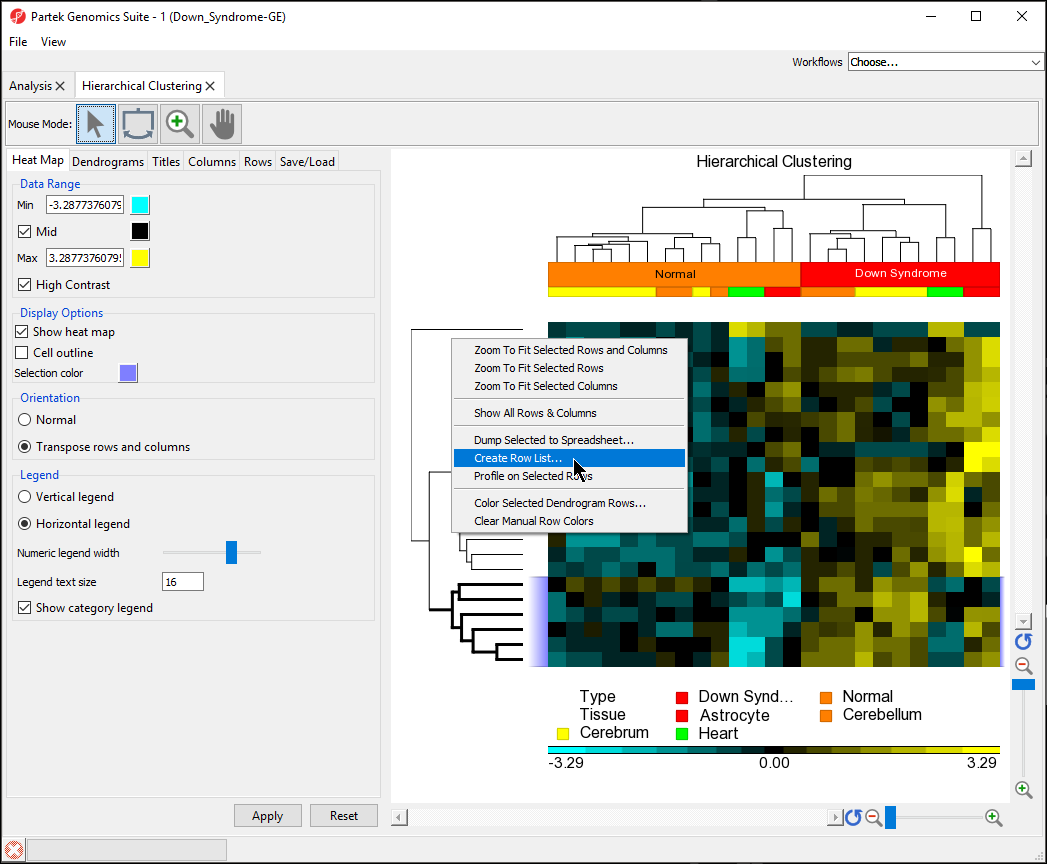
- Select the bottom cluster of the rows dendogram (Figure 9dendrogram
- Right-click to open the pop-up menu
- Select Create Row List... (Figure 9)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Name the gene set Down down in normal
- Select OK
- Save the list as down in normal
In the Analysis tab, there is now a spreadsheet row_list (down in normal.txt) containing the 6 genes that were in the selected cluster. The same steps can be used to create a list of samples form from the hierarchical clustering by selecting clusters on the sample dendogram. dendrogram.
Saving Plot Properties
Once you have created a customized plot, you can save the plot properties as a template for future hierarchical clustering analyses.
- Select the Save/Load tab
- Select Save current...
- Name the current plot properties template; we selected Transposed Blue and Yellow
The new template now appears in the Save/Load panel as an option. To load a template, select it in the Load/Save panel and select Load selected. Note that all properties, including Min and Max values and sample groups (based on the column number of the attribute in the source spreadsheet) that may not be appropriate for a different data set, will be applied.
Exporting the Hierarchical Clustering Plot Image
Like very visualization in Partek Genomics Suite, the The hierarchical clustering image plot can be exported as a publication quality image.
...