Page History
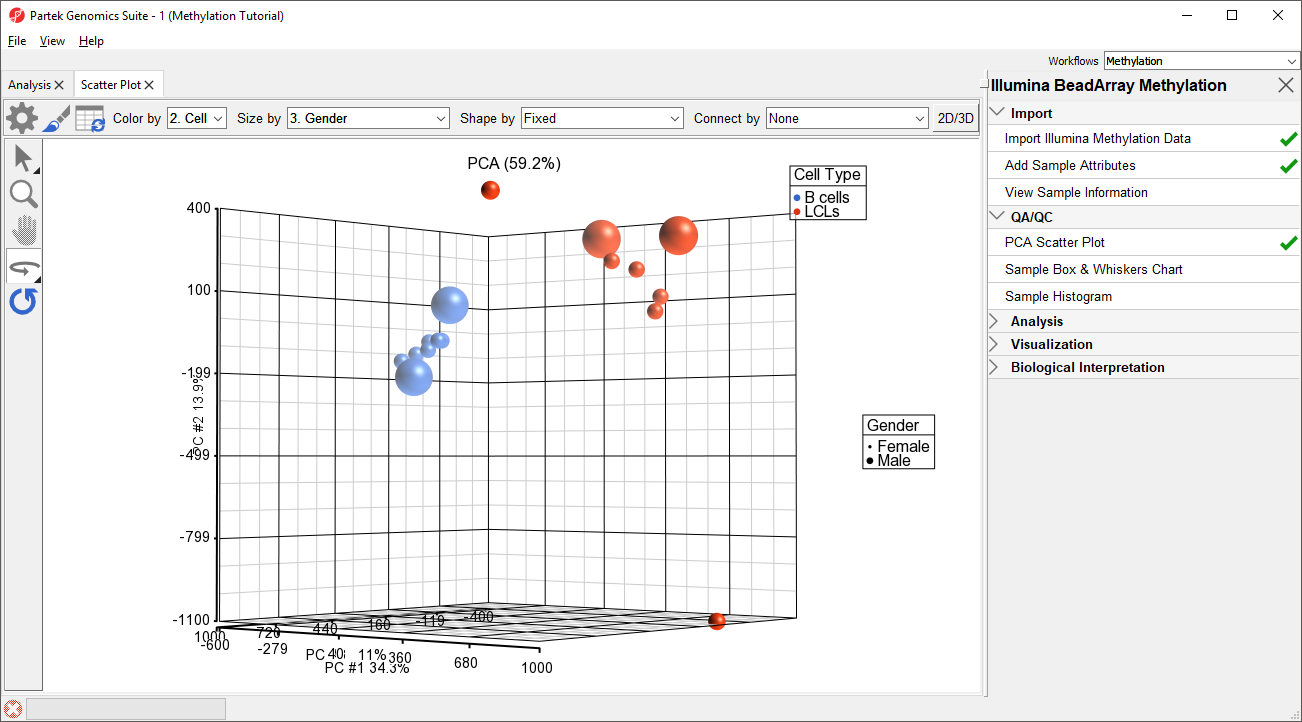
Principal component analysis (PCA) can be invoked on performed to visualize clusters in the methylation data to reveal clustering of the samples, but also serves as a quality control procedure (detection of outliers could point to possible low quality or mislabeled samples). To obtain the PCA plot, switch to the Scatter Plot tab, push Recompute ( ) and from the Color by drop down list select HPSC. Use the Rotate Mode ( )to explore the plot from different angles, as seen in Figure 1. Each ; outliers within a group could suggest poor data quality, batch effects, mislabeled samples, or uninformative groupings.
- Select PCA Scatter Plot from the QA/QC section of the Illumina BeadArray Methylation workflow to bring up a Scatter Plot tab
- Select 2. Cell Type for Color by
- Select 3. Gender for Size by
- Select () to enable Rotate Mode
- Left click and drag to rotate the plot and view different angles (Figure 1)
Each dot of the plot is a single sample and represents the average methylation status across all CpG loci. The result is shown in the demonstrating clear separation of naive and primed HPSC from the cells transduced with short hairpin (sh) RNA lentiviruses (shNANOG and shPOU5F1).Two of the LCLs samples do not cluster with the others, but we will not exclude them for this tutorial.
| Numbered figure captions | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
|
...
|
...
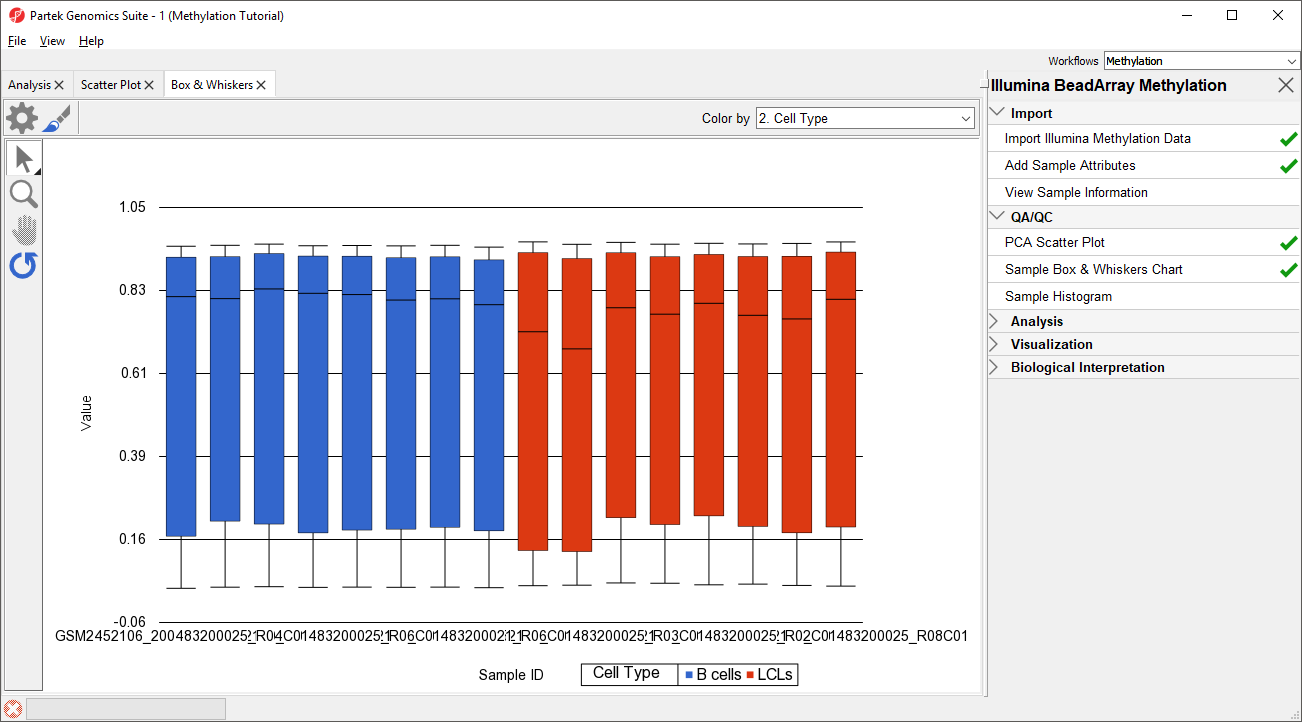
Next, distribution of M-beta values across the samples can also be inspected by a box-and-whiskers plot: QA/QC > Plot Sample Box & Whiskers Chart. .
- Select Sample Box and Whiskers Chart from the QA/QC section of the Illumina BeadArray Methylation workflow to bring up a Box and Whiskers tab
Each box-and-whisker is a sample and the y-axis shows Mbeta-valuesvalue ranges. Samples in this data set seem reasonably uniform and no outliers can be detected (Figure 2).
| Numbered figure captions | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
|
...
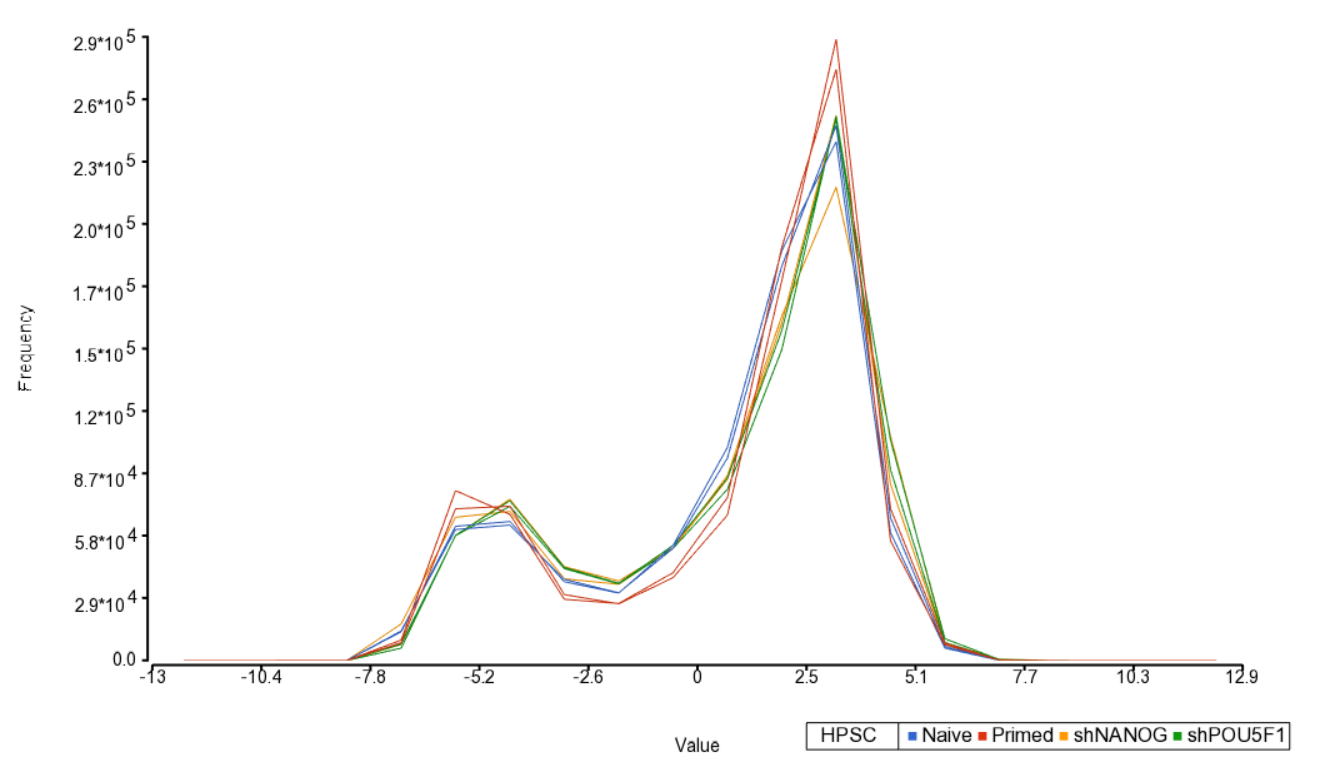
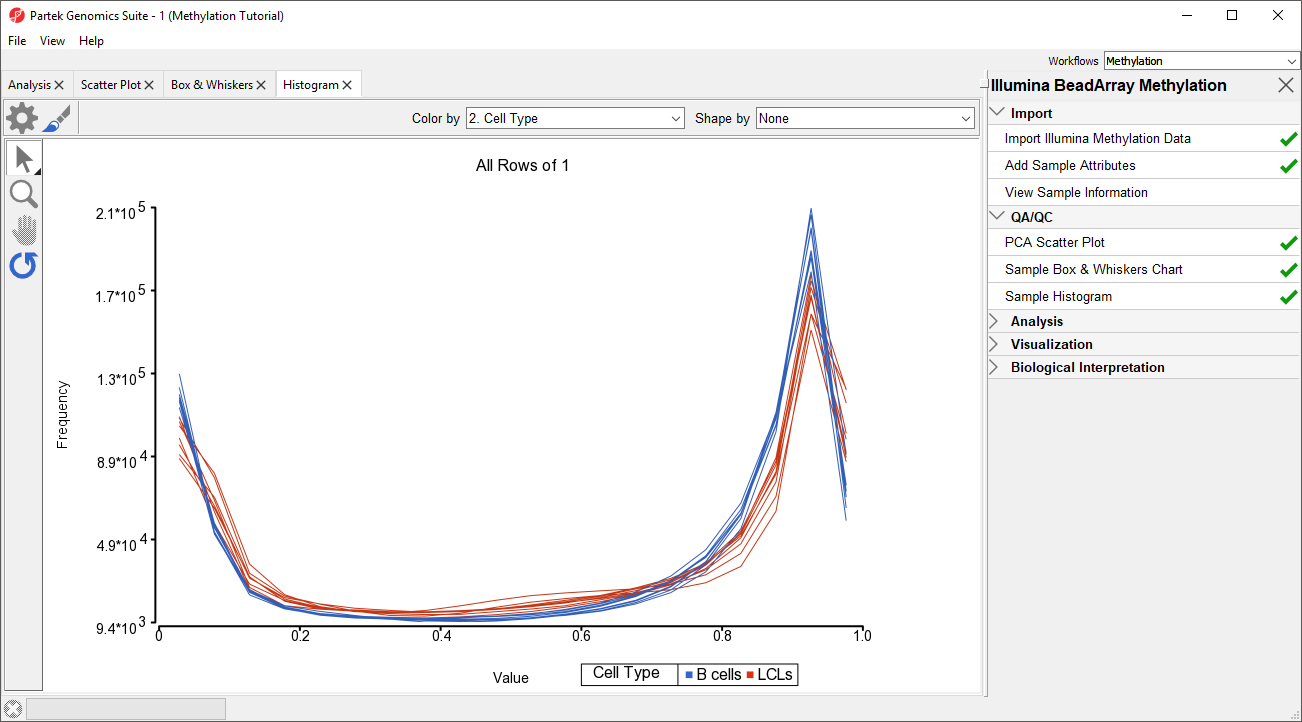
An alternative way to take a look at the distribution of Mbeta-values is a histogram (QA/QC > Plot Sample Histogram). .
- Select Sample Histogram from the QA/QC section of the Illumina BeadArray Methylation workflow to bring up a Histogram tab
Again, no sample in the tutorial data set stands out (Figure 3).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Section Heading
Section headings should use level 2 heading, while the content of the section should use paragraph (which is the default). You can choose the style in the first dropdown in toolbar.
| Page Turner | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Additional assistance |
|---|
|
| Rate Macro | ||
|---|---|---|
|