Page History
With the Partek ® Flow ® Microarray Toolkit, you can import and analyze microarray data with the same ease as any sequencing analysis pipeline. This document covers the following parts.
...
For custom-made Affymetrix .CEL and Illumina .idat or AVGSignal data generated from Genome Studio files, refer to the documentation on Importing Custom Microarrays for additional instructions regarding the probe files.
...
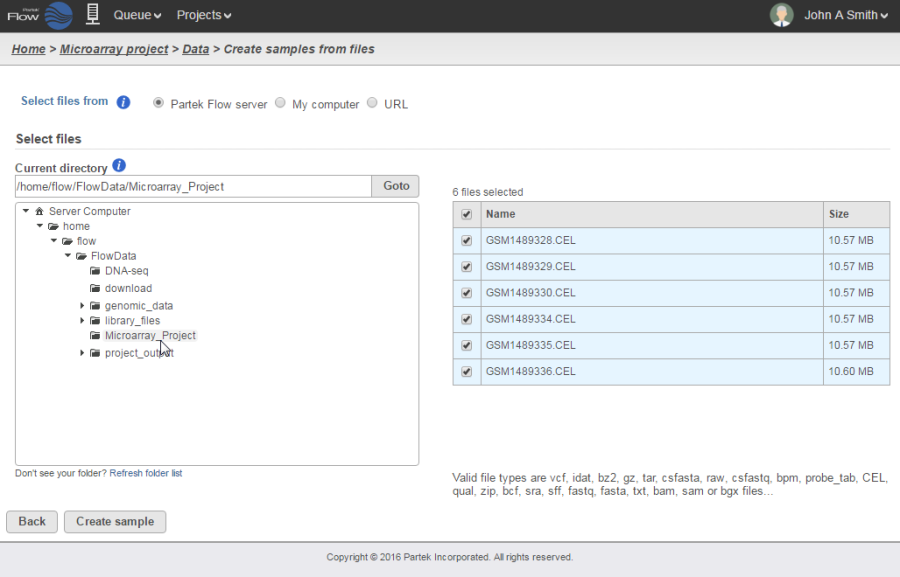
The most efficient way of importing array data would be to import them directly from your Partek Flow server. When you select this option, navigate to the folder containing your data files. Valid file types will be selectable for upload. Click on the files you would like to import into the project and select the Create sample button (Figure 1).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
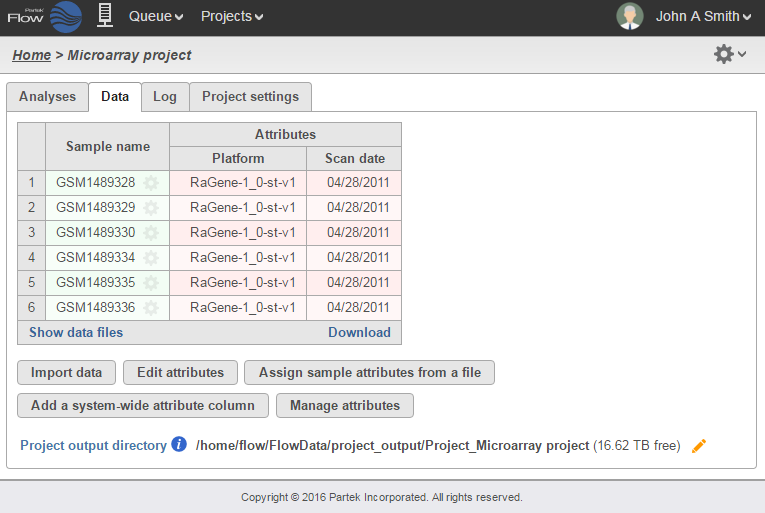
Once the samples have been uploaded, the Data tab will list each sample along with the Platform associated with each sample. If Affymetrix .CEL files were uploaded, it will also include the date that the array was scanned (Figure 2). This information may be helpful in assessing possible batch effects.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
You can now add additional sample attributes to your microarray project. For more information on how to set up your project, please refer to the documentation on Creating a project.
...
Partek Flow also supports custom-made Affymetrix and Illumina arrays. Once the data files have been uploaded, you will also need to supply a custom annotation file which contains information on the probe sequences associated with the array. Please refer to the document on Importing Custom Microarrays for additional information on how to create and upload these annotations.
...
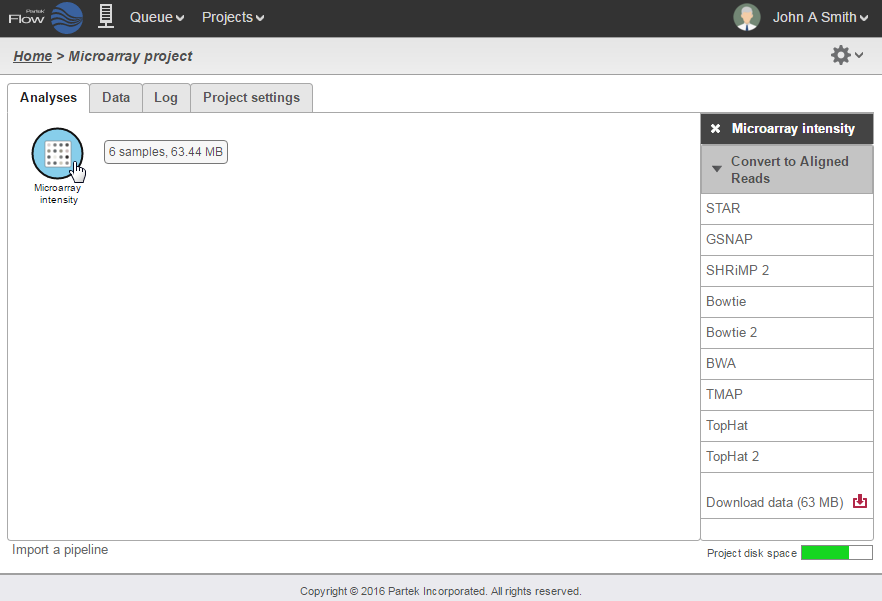
Once the microarray data has been uploaded, the Microarray intensity data node will appear in the Analyses tab. To convert this data to aligned reads, select the Microarray intensity data node and select the aligner you would like to use for conversion (Figure 3).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
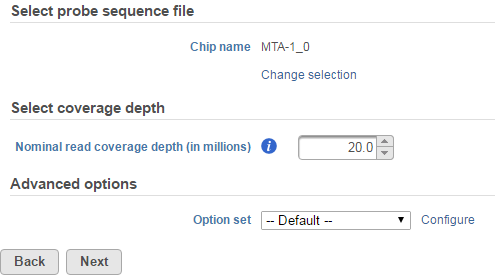
Selecting an aligner will bring up the Microarray Conversion options page (Figure 4). Under the Select probe sequence file section, make sure that the correct Chip name is specified. For non-custom arrays, these should be set automatically to the platform detected upon importing the array.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
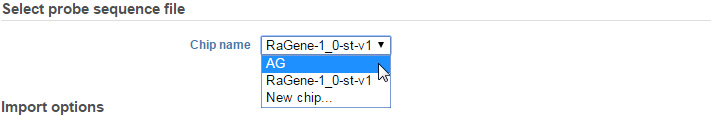
If for some reason you wish to override that selection, then click the Change selection link and select the chip name in the drop-down menu or select New chip… if you would like to upload a different chip annotation (Figure 5).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
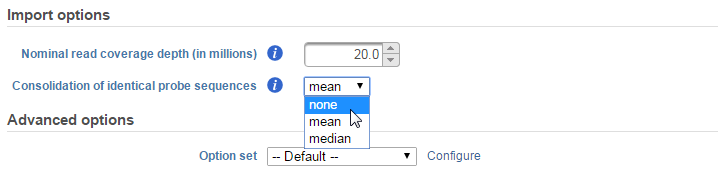
In the Select coverage depth section, you can set the nominal read coverage depth for your array. This is by default set at 20 million reads. However, you can adjust this number for better accuracy or if you are evaluating low-expressing genes. If you are comparing the microarray data with a corresponding NGS dataset, you can use this option to scale your data to a more comparable order of magnitude. Take note that setting this to a higher number will result in longer computation times overall.
...
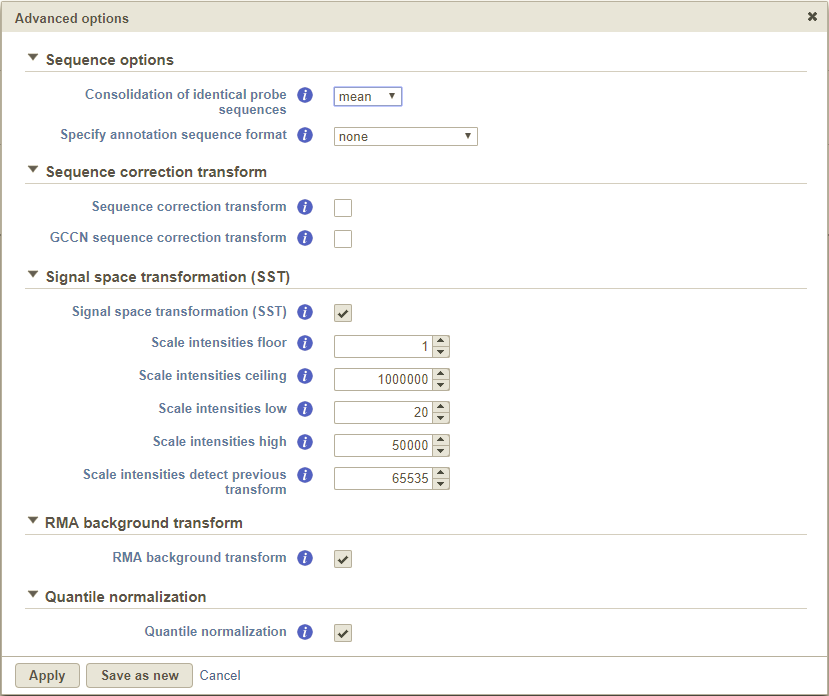
Clicking the Configure link under the Advanced options section to view the advanced options that can be modified. These are generally transformations applied to microarray data (Figure 6). Note that both interrogating and control (if present) probes are used during fitting and adjustment.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The Specify annotation sequence format drop-down menu allows you to specify the format of the probe sequences associated with your microarrays. Please consult with the manufacturer of your microarrays to determine the exact specification of their probe annotation files. The options available for sequence annotation include:
...
By default, this is set to take the mean of the intensities the probes and utilizes that to calculate the read count for the probe sequence. Clicking on the drop-down menu allows you to either turn off this feature (none) or use the median instead (Figure 6).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The Clicking the Sequence correction transform checkbox corrects intensity values for sequence-specific effects. It is turned off by default and we only advise that you select this option if there are wide differences in the GC content of your probes.
The Both the GCCN sequence correction transform and Scale intensity transform was transforms were developed by Affymetrix [1]. GCCN scales the intensities with respect to the difference in probe affinity associated with Guanine and Cytosine (GC) content. On the other hand, the Scale intensity transform was developed improve inter-platform comparisons between microarray and RNA-seq data. Specifically, the algorithm stretches the intensity distribution to a common range with a power law mapping that decompresses fold change ratios [1] . This ultimately simplifies fold change comparisons between different technologies.
The RMA background transform check box applies robust multi-array average (RMA) normalization to your microarray samples [2]. This is a well-accepted method of background correction for microarray intensities.
The Quantile normalization check box performs quantile normalization on all microarray intensities. This is important in making sure that signals from any two arraysare arrays are comparable.
Any combination of these advanced options can be saved as its own option set. Once the option set has been created, it will be available in the Option set drop-down menu for use in future projects.
After you have finished configuring all microarray conversion options. Click the Next button to configure the parameters for the aligner you have chosen to use. Please refer to the documentation on Alignment for more information about configuring aligners.
...
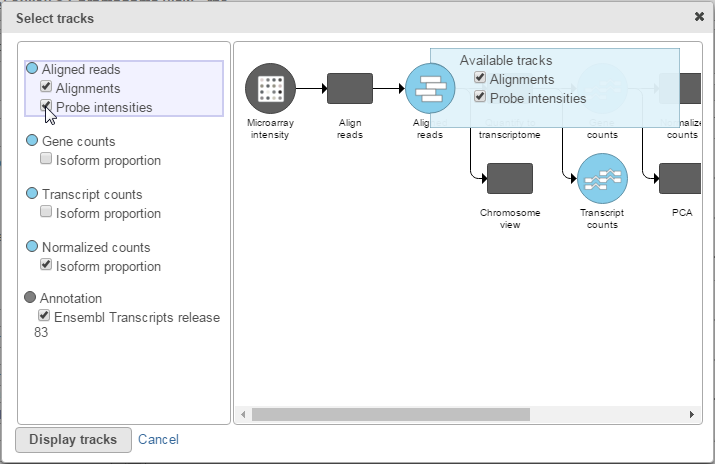
To visualize microarray probes in Partek Flow's Chromosome viewer, click the Select tracks button at the top left corner of the viewer. Select the Probe intensities check box to display microarray probes (Figure 8).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
This will display microarray probes aligned to the reference genome (Figure 9). By default, the probes are colored by their intensities with darker shades signifying higher probe intensities.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
References
- Affymetrix Whitepaper on Microarray normalization using Signal Space Transformation with probe Guanine Cytosine Count Correction. Accessed February 17, 2016
- Irrizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F et al. Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostat. 2003; 4:249-264.
...
...
| Additional assistance |
|---|
| Rate Macro | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...