Page History
...
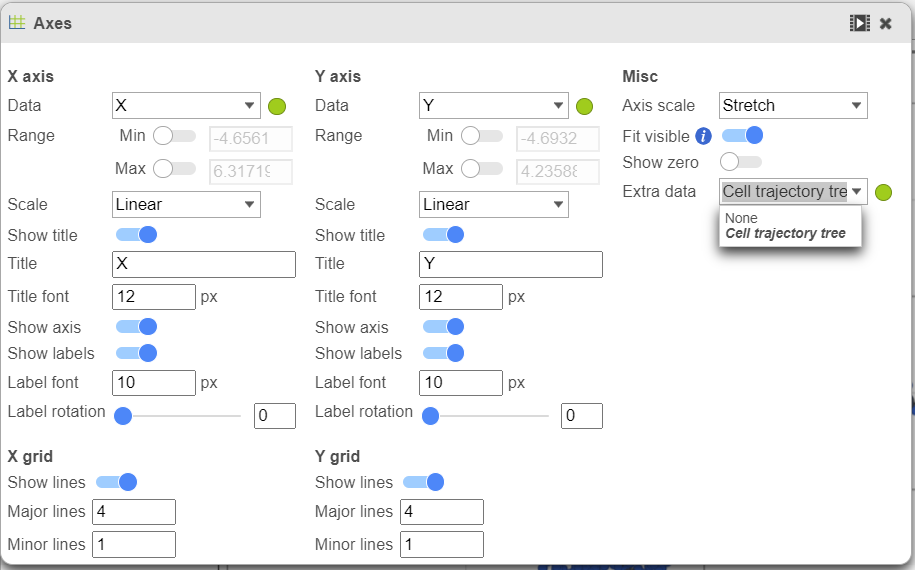
To show / hide cell trajectory tree and trajectory nodes, use the Extra data option on the Content card select Axes in Configure section and on the upper-right corner of the dialog, select the Extra data drop-down options (Figure 2).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Pseudotime Analysis
...
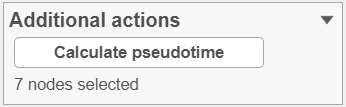
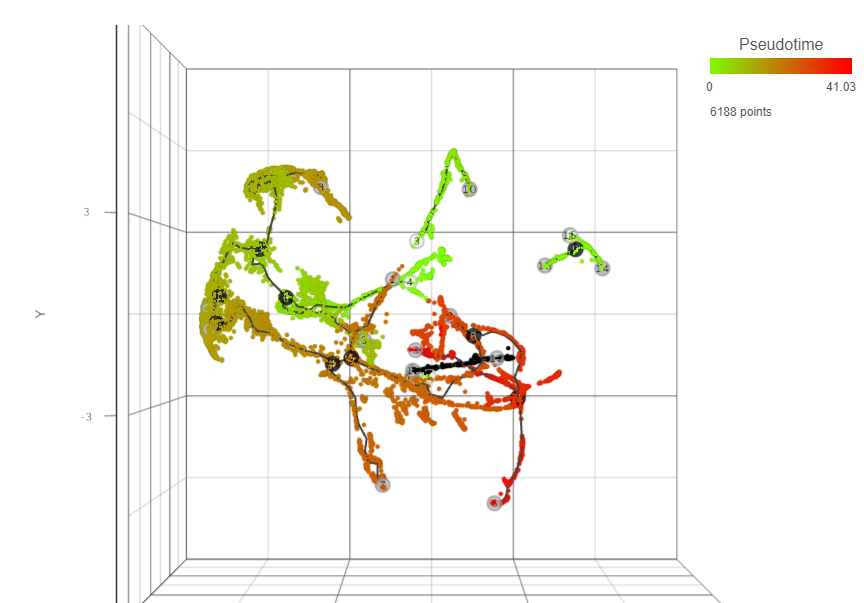
To start, select the root cell nodes (gray circles in trajectory tree) by left-clicking. If the trajectory result consists of more than one trajectory tree, you can specify more than one root node, e.g. one root node per trajectory tree (ctrl & click). If no root node is specified for a tree, that tree will not be included in the pseudotime calculation. Figure 4 shows an example where seven root nodes were identified.
...
Once you have identified all the root nodes, click on Additional button in Tools section on the left panel, push the Calculate pseudotime button in the Selection panel dialog (Figure 5).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
As a result, the cells will be annotated by pseudotime, using green to red gradient (start and end, respectively) (Figure 6). If, for a particular tree, no root node has been identified, those cells will be omitted from the pseudotime calculation and will be colored in black (Figure 9).
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
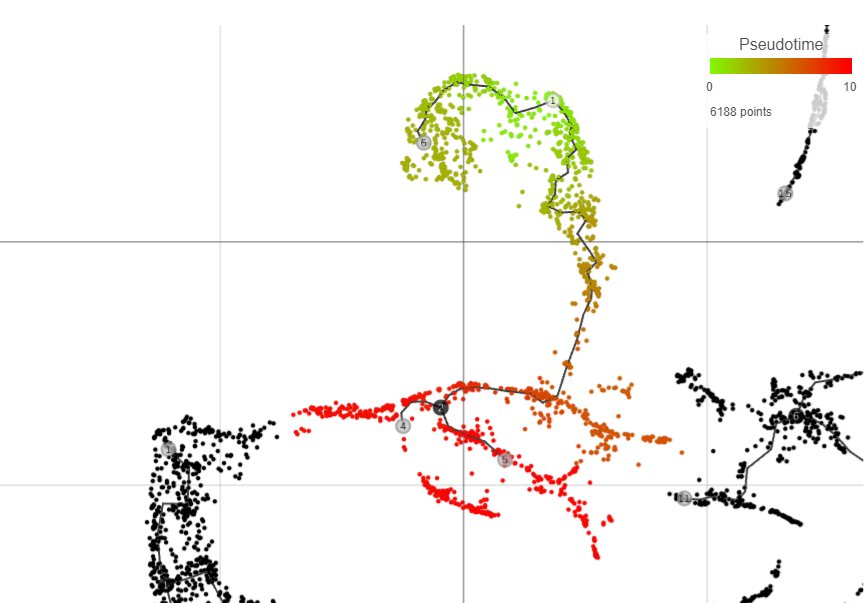
Following pseudotime calculation, three types of cell nodes will be annotated on the plot.Pseudotime calculation display the structure of the graph using black lines. The circles with numbers (cell nodes) on the black lines represent special points. There are three types of cell nodes:
- Root node (white). Root nodes are start points of the pseudotime and were defined by the user in the previous step (e.g. node 4 in Figure 7).
- Branch node (black). Branch nodes indicate where the trajectory tree forks out; i.e. each branch represents a different cell fate or different trajectory (e.g. nodes 3-6, and 8 in Figure 7).
- Leaf (light gray). Leaves correspond to different cell fates / different trajectory outcomes (e.g. nodes 5, 9, and 12 in Figure 7). The leaves correspond to cell states of Monocle 2.
The numbers within the circles are provided for reference purposes only. The intermediate nodes from the previous step have been removed.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
References
- Cao J, Spielmann M, Qiu X, Huang X, Ibrahim DM, Hill AJ, Zhang F, Mundlos S, Christiansen L, Steemers FJ, Trapnell C, Shendure J. The single-cell transcriptional landscape of mammalian organogenesis. Nature. 2019 Feb;566(7745):496-502. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0969-x. Epub 2019 Feb 20. PMID: 30787437; PMCID: PMC6434952.
...