Page History
...
Multi-omics single cell analysis is based on simultaneous detection of different types of biological molecules on the same cells. Common multi-omics techniques include feature barcoding or CITE-seq (cellular indexing of transcriptomes and epitopes by sequencing) technologies, which enable parallel assessment of gene and protein expression. Specific bioinformatics tools have been developed to enable scientists to integrate results of multiple assays and learn relative importance of each type (or each biological molecule) in identification of cell types. Partek Flow supports weighted nearest neighbour (WNN) analysis (1), which can help combine output of two molecular assays.
Invoking Find Multimodal Neighbours
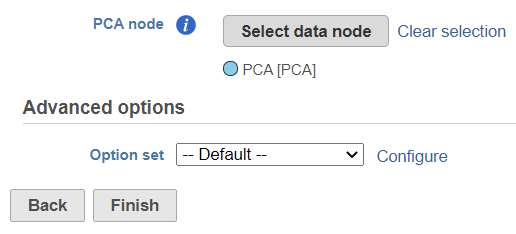
To start, select a PCA data node of one of the assays (e.g. gene expression) and go to Exploratory analysis > Find multimodal neighboursneighbors in the toolbox. On the task setup page, use the Select data node button to point to the PCA data node of the other assay (e.g. protein expression) (Figure 1).
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
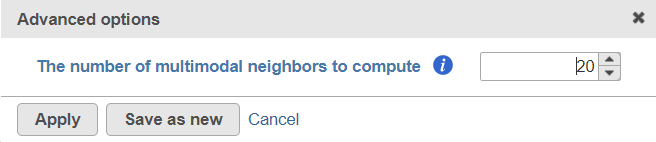
To customize the Advanced options, select the Configure link (Figure 3). At present you can only change the number of nearest neighbors for each modality (-k.nn option of the Seurat package); the default value is 20 (Figure 4). An illustration on how to use that option to assess the robustness of WNN analysis, please see Hao et al. (1).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
To launch the Find multimodal neighbors task, click the Finish button on the task setup page (Figure 3). For each cell, the WNN algorithm calculates its closest neighbors based on a weighted combination of RNA and protein similarities. The output of the Find multimodal neighbors task is a WNN data node.
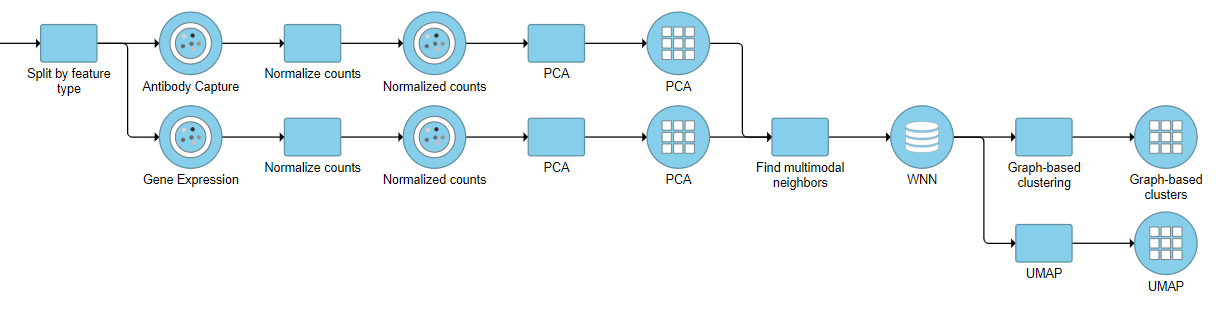
For downstream analysis, you can launch a UMAP or graph-based clustering tasks on a WNN node. For example, Figure 5 shows a snippet of analysis of a feature barcoding data set; gene expression and protein expression data were processed separately, and then Find multimodal neighbors was invoked on two respective PCA data nodes.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
For an illustration on advantages of WNN algorithm for identification of cell types, please see this blog post.
References
- Hao Y, Hao S, Andersen-Nissen E, et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell. 2021;184(13):3573-3587.e29. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.048
...