Page History
...
The reads are first aligned to the genome and initially . The unaligned reads resulting from this initial alignment are then split into multiple 25 bp sequences which are, in turn, aligned to the genome by Bowtie. The TopHat-Fusion algorithm then identifies the cases where the first and the last 25 bp segment segments are aligned to either two different chromosomes or two locations on the same chromosome (spacing is defined by the user). The whole read is then used to identify a fusion point. After the initial fusion candidates are defined, all the segments from the initially unaligned reads are realigned against the fusion points (as well as intron boundaries and indels) and the . The resulting alignments are combined to with the full read alignments.
The most up to date TopHat-Fusion version implemented in Partek® Flow® when the manual was written (2.1.0) focuses on fusions due to chromosomal rearrangements, while fusions resulting from read-through transcription or trans-splicing were not supported. For details as well as discussion of TopHat-Fusion options, see TopHat-Fusion home page (4).
...
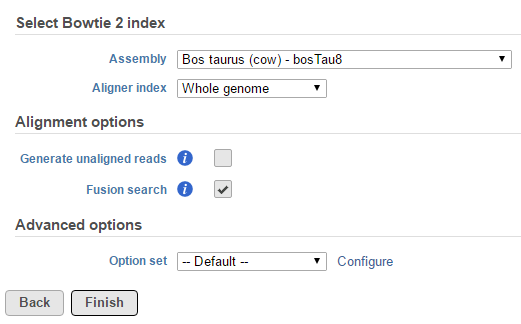
TopHat-Fusion is integrated with in the TopHat 2 task and fusion detection is activated invoked by using the Fusion search check box in the TopHat 2 Alignment options dialog (Figure 1).
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
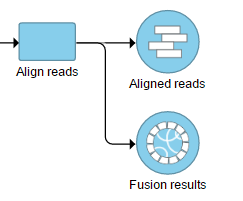
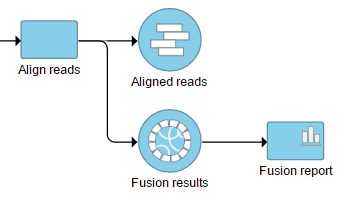
The output is dumped to the generated as a new data node Fusion results (Figure 2) , which is a stemming as part of the if the TopHat 2 results align reads task (in addition to Aligned reads node and, optionally, Unaligned reads node).
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
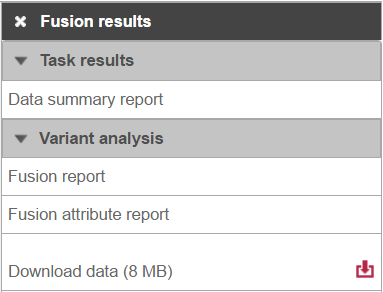
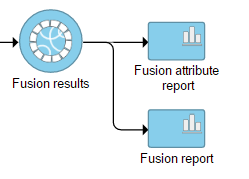
Selecting the Fusion results data node opens the toolboxtask menu, with four options (Figure 3): Data summary report, Fusion report, Fusion attribute report, and Download data.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Clicking on the Download data results in download of downloads a *.fusion file to the local computer. The file is human readable and can be opened in a text editor (example in Figure 4). For details refer to TopHat-Fusion documentation.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
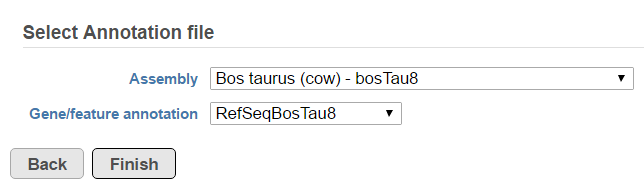
A list of annotated fusion genes, in a form of Fusion report can be obtained by first selecting the Fusion report task node (Figure 2) and then the Task report link from the task menu (Figure 3). Since the task provides an annotated report on detected fusion genes. For that purpose , an annotation file needs to be specified first (Figure 5).
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
The resulting Fusion report task task node as seen in (Figure 6) can be double clicked to reveal the full table (Figure 7).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
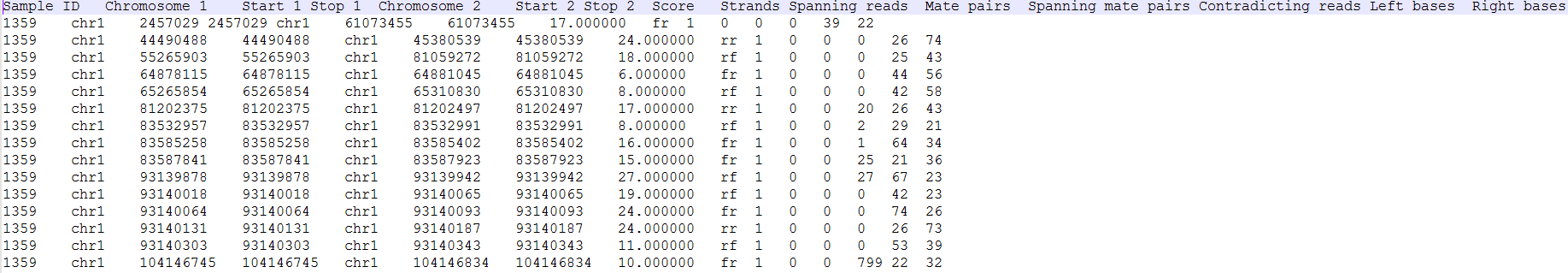
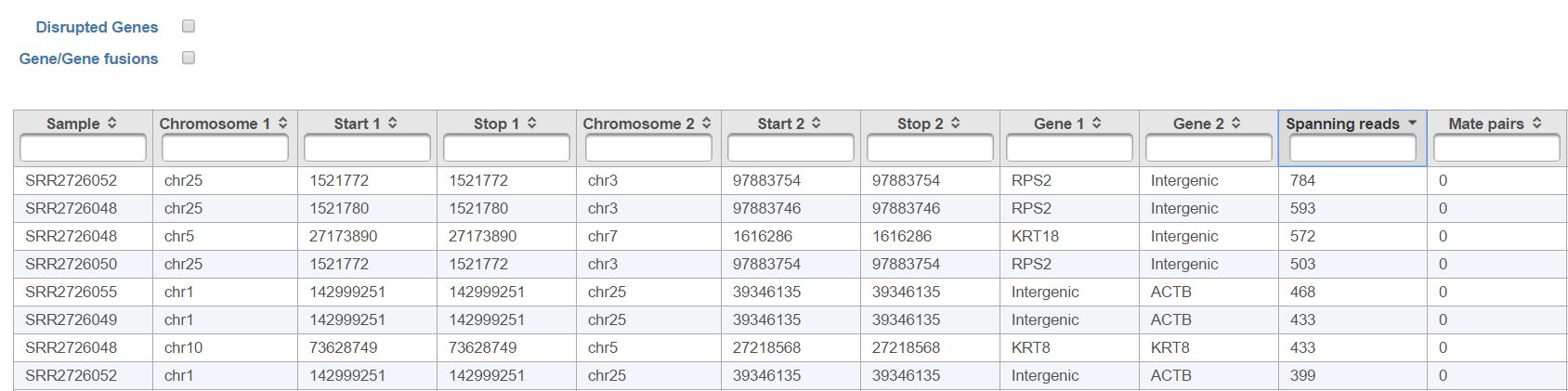
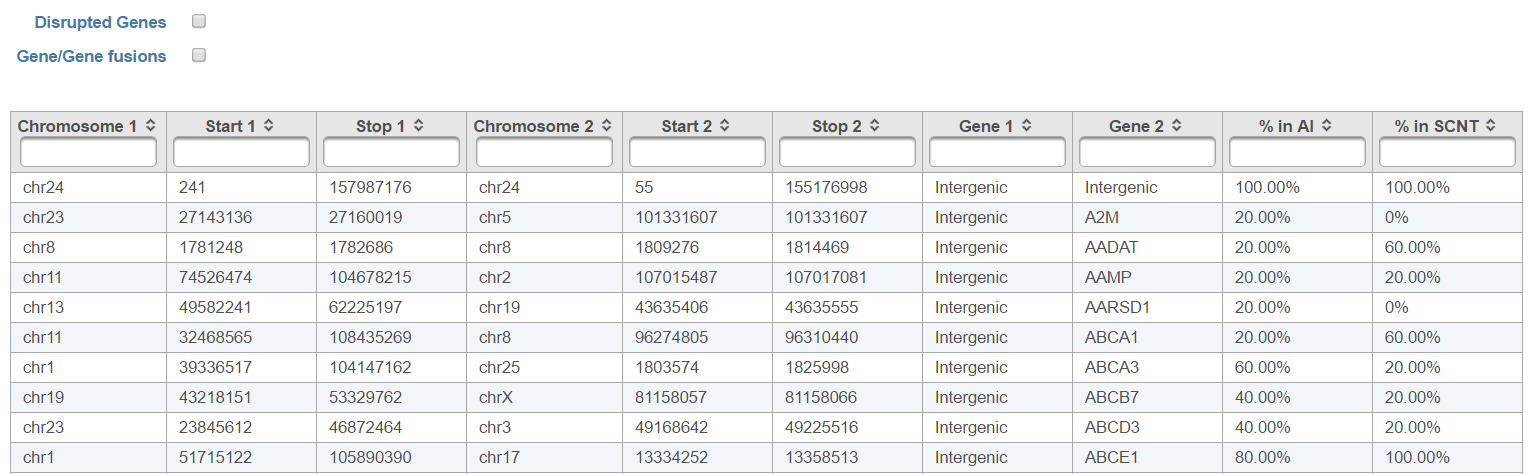
Each row of the table in Figure 7 is a potential fusion event, with the columns providing the following information.
- Sample ID: sample in which the fusion event was identified;
- Chromosome 1: chromosome hosting the first (left) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Stop 1: end of the first (left) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Chromosome 2: chromosome hosting the second (right) part of the fusion transcript;
- Start 2: beginning of the second (right) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Gene1: gene on the left side of the fusion;
- Gene2: gene on the right side of the fusion;
- Spanning reads: number of reads which were unaligned during the initial phase of TopHat and where only one mate is used as evidence of the fusion event;
- Mate Pairs: number of reads which were unaligned during the initial phase of TopHat and where both mates are used as evidence of the fusion event;
- Spanning mate pairs: number of reads where both mates were aligned during the initial phase of TopHat, but their pairing is discordant (e.g. different chromosomes, different orientation etc.);
- Contradicting reads: number of reads which do not support the fusion;
- Left bases: number of bases on the left side of the fusion;
- Right bases: number of bases on the right side of the fusion.
All the columns can be sorted by using the arrow buttons in column headers, while the type-in boxes can be used for searching. TopHat-Fusion does not report exact start and stop position for each side of the fusion event. It has a single location for the end of the upstream segment (Stop 1) and the beginning of the downstream segment (Start 2). Therefore, columns Start 1 and Stop 2 are added for (internal) consistency with other Partek Flow tools.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Checkboxes The checkboxes Disrupted Genes and Gene/Gene fusions are filter tools. When selected, Disrupted Genes removes all the rows (fusion events) which have no gene genes assigned to it, i.e. which those that merge two intergenic regions. However, if there is a fusion between a gene and an intergenic region, it will be kept in the table. The Gene/Gene fusions filters in only those fusion events which have an annotated gene on both sided sides of the breakpoint. In the other words, only gene to gene fusions are kept in the table.
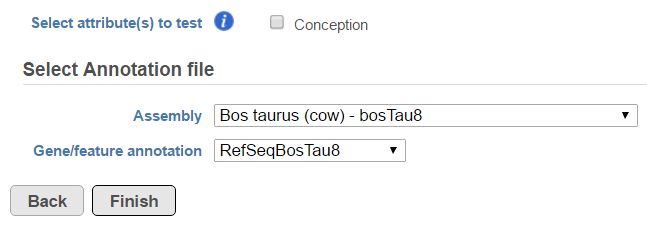
Another table which can be generated based on a Fusion results node is the Fusion attribute report (Figure 3). When the option is selected, it brings up the dialog shown in Figure 8. First, you need to specify one or more categorical attributes (Select attribute(s) to test), which have at least two categories (see Data tab). Second, you need to specify an annotation file, using the Assembly and Gene/feature annotation drop-down lists.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
A new data node, Fusion attribute report, is generated in the Analysis tab (Figure 9) and it provides access to the Task report link in the toolboxtask menu.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The output, Fusion report table (Figure 10) resembles the basic TopHat-Fusion output (Figure 7); each row of the table is a single fusion event while the information on the merged segments is on the columns.
- Chromosome 1: chromosome hosting the first (left) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Start 1: beginning of the first (left) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Stop 1: end of the first (right) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Chromosome 2: chromosome hosting the second (right) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Start 2: beginning of the second (right) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Stop 2: end of the second (left) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Gene1: gene on the left side of the fusion;
- Gene2: gene on the right side of the fusion;
- % in (category name): fraction of samples within the category with the fusion event.
Checkboxes The checkboxes Disrupted Genes and Gene/Gene fusions are filter tools. When selected selected, Disrupted Genes removes all the rows (fusion events) which have no gene genes assigned to it, i.e. which those that merge two intergenic regions. However, if there is a fusion between a gene and an intergenic region, it will be kept in the table. The Gene/Gene fusions filters in only those fusion events which have an annotated gene on both sided sides of the breakpoint. In the other words, only gene to gene fusions are kept in the table.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
STAR Algorithm
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
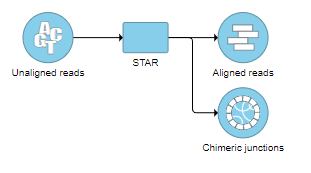
The output is associated with the Chimeric results data node (Figure 12), which is a part of STAR results (in addition to Aligned reads node and, optionally, Unaligned reads node).
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Selecting the Chimeric results node opens the toolbox (Figure 13) with twooptions: Data summary report or Download data.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
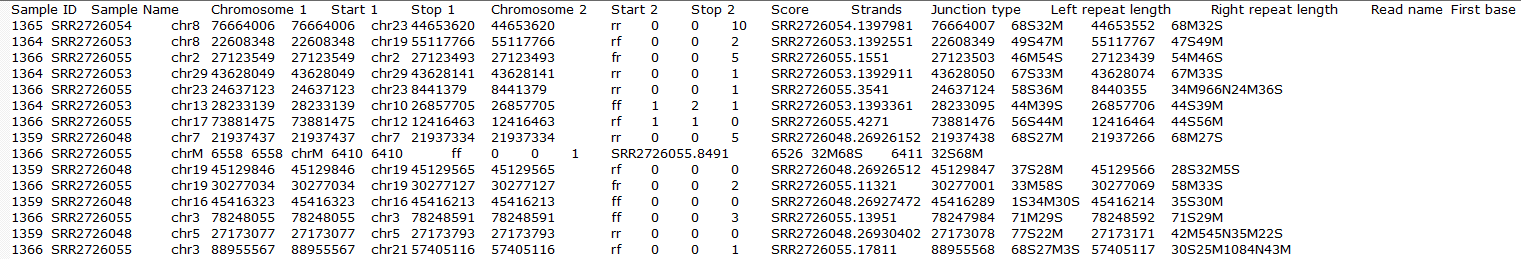
Clicking on the Download data results in download of a .fusion file to the local computer. The file is human readible and can be opened in a text editor (example in Figure 14). For details refer to STAR's documentation.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
References
- Annala MJ, Parker BC, Zhang W, Nykter M. Fusion genes and their discovery using high throughput sequencing. Cancer Lett. 2013;340:192-200.
- Costa V, Aprile M, Esposito R, Ciccodicola A. RNA-Seq and human complex diseases: recent accomplishments and future perspectives. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013;21:134-142.
- Kim D, Salzberg SL. TopHat-Fusion: an algorithm for discovery of novel fusion transcripts. Genome Biology. 2011;12:R72
- TopHat-Fusion. An algorithm for discovery of novel fusion transcripts. http:// http://tophat.cbcb.umd.edu/fusion_index.html Accessed on April 25, 2014
- Dobin A, Davies CA, Schlesinger F et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:15-21.
...