Page History
...
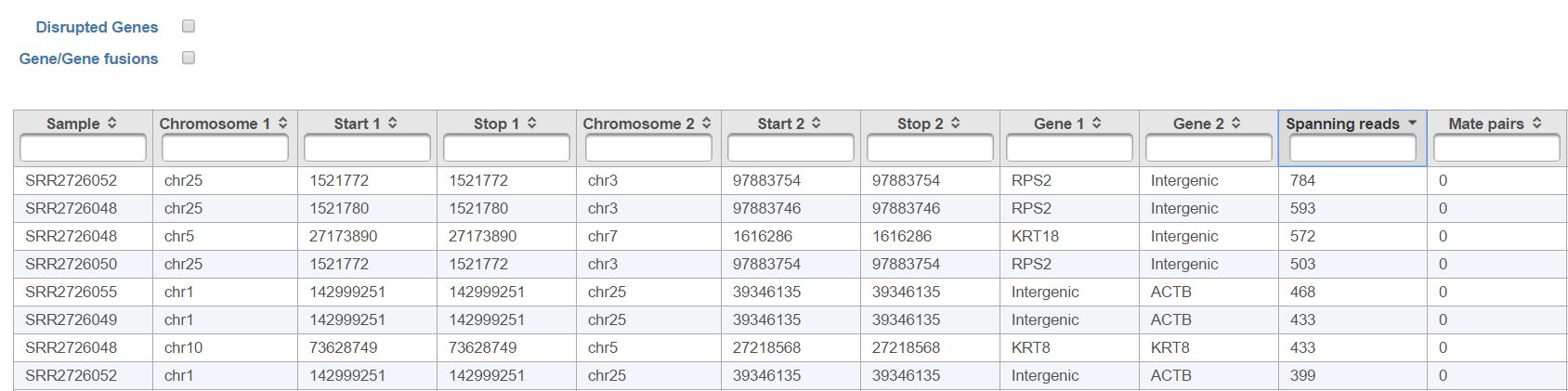
- Sample ID: sample in which the fusion event was identified;
- Chromosome 1: chromosome hosting the first (left) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Stop 1: end of the first (left) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Chromosome 2: chromosome hosting the second (right) part of the fusion transcript;
- Start 2: beginning of the second (right) segment of the fusion transcript;
- Gene1: gene on the left side of the fusion;
- Gene2: gene on the right side of the fusion;
- Spanning reads: number of reads which were unaligned during the initial phase of TopHat and where only one mate is used as evidence of the fusion event;
- Mate Pairs: number of reads which were unaligned during the initial phase of TopHat and where both mates are used as evidence of the fusion event;
- Spanning mate pairs: number of reads where both mates were aligned during the initial phase of TopHat, but their pairing is discordant (e.g. different chromosomes, different orientation etc.);
- Contradicting reads: number of reads which do not support the fusion;
- Left bases: number of bases on the left side of the fusion;
- Right bases: number of bases on the right side of the fusion.
All the columns can be sorted by using the arrow buttons () in in column headers, while the type-in boxes can be used for searching. TopHat-Fusion does not report exact start and stop position for each side of the fusion event. It has a single location for the end of the upstream segment (Stop 1) and the beginning of the downstream segment (Start 2). Columns Start 1 and Stop 2 are added for (internal) consistency with other Partek Flow tools.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
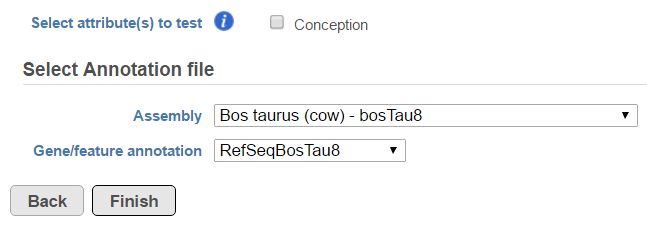
Moreover, Fusion attribute report, when invoked from the Fusion results node, displays a report on attributes of detected fusion genes. Attributes to be tested for association with the fusion should be specified first (Figure 12).Checkboxes Disrupted Genes and Gene/Gene fusions are filter tools. When selected Disrupted Genes removes all the rows (fusion events) which have no gene assigned to it, i.e. which merge two intergenic regions. However, if there is a fusion between a gene and an intergenic region, it will be kept in the table. Gene/Gene fusions filters in only those fusion events which have an annotated gene on both sided of the breakpoint. In the other words, only gene to gene fusions are kept in the table.
Another table which can be generated based on a Fusion results node is Fusion attribute report (Figure 3). When the option is selected, it brings up the dialog shown in Figure 8. First, you need to specify one or more categorical attributes (Select attribute(s) to test), which have at least two categories (see Data tab). Second, you need to specify an annotation file, using the Assembly and Gene/feature annotation drop-down lists.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
A new data node, Fusion attribute report, is generated in the Analysis tab (Figure 139) and it provides access to the Task report link in the toolbox.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
The output, Fusion report table (Figure 14) resembles the basic TopHat-Fusion output (Figure 11); each row of the table is a single fusion event and three right-most columns are as follows:
...