Page History
...
Under Exploratory Analysis tasks is the Clonotype Frequency Plot task which will summarize the V(D)J node into plots of interest in the Data Viewer. Similar manual The same or different comparisons can be made in the Data Viewer (see Tips for Figure Making below). These may include determining the T cell receptor and B cell receptor chains that make up clonotypes in the samples, quantifying the clone diversity by frequency, comparing the immune repertoire between samples, and visualizing clones and gene expression data together on scatterplots like a UMAP.
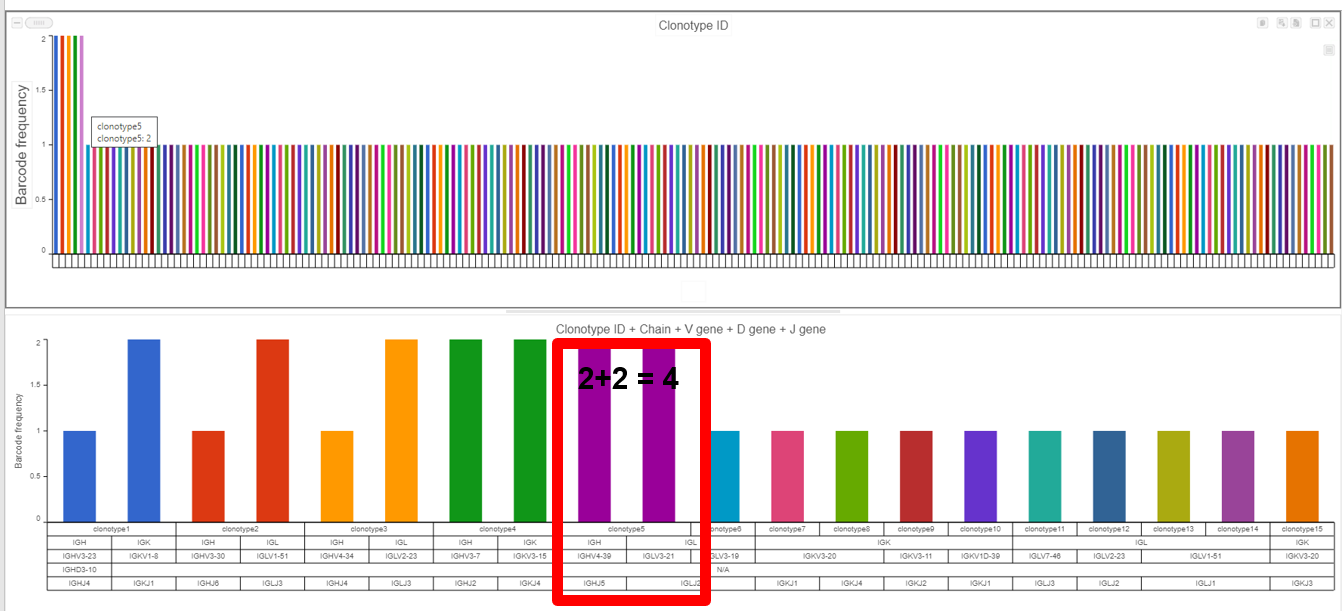
- The example below shows the results from the Clonotype Frequency Plot task which is accessed by choosing to perform this task from the Single cell V(D)J node then modified and will automatically open in the data viewer for modification. In this case, the barcode frequency is the number of clonotypes per cell because the barcode usually represents a single cell, so there are two cells which have clonotype5 (purple bar with information from hovering) and clonotype 5 is made of two compositions (a frequency of four for clonotype5 from the V(D)J node) witnessed by the with a Chain, V gene, D gene, and J gene as seen below the bars and by hovering.
- Plotting Clonotype ID frequency, as seen below, for the gene expression node (Cell counts as the top bar chart) and VDJ node (VDJ counts as the bottom bar chart), highlights the difference between the two nodes (where the top plot is the number of cells per clonotype and the bottom plot is the number of V(D)J clonotypes present). Note that Cell Ranger does not always call the barcode as a cell and this can affect these frequencies when making comparisons between cell frequency per clonotype and barcode frequency per clonotype (an example of this would be clonotype1 when comparing the figure above and below).
Tips for Figure Making
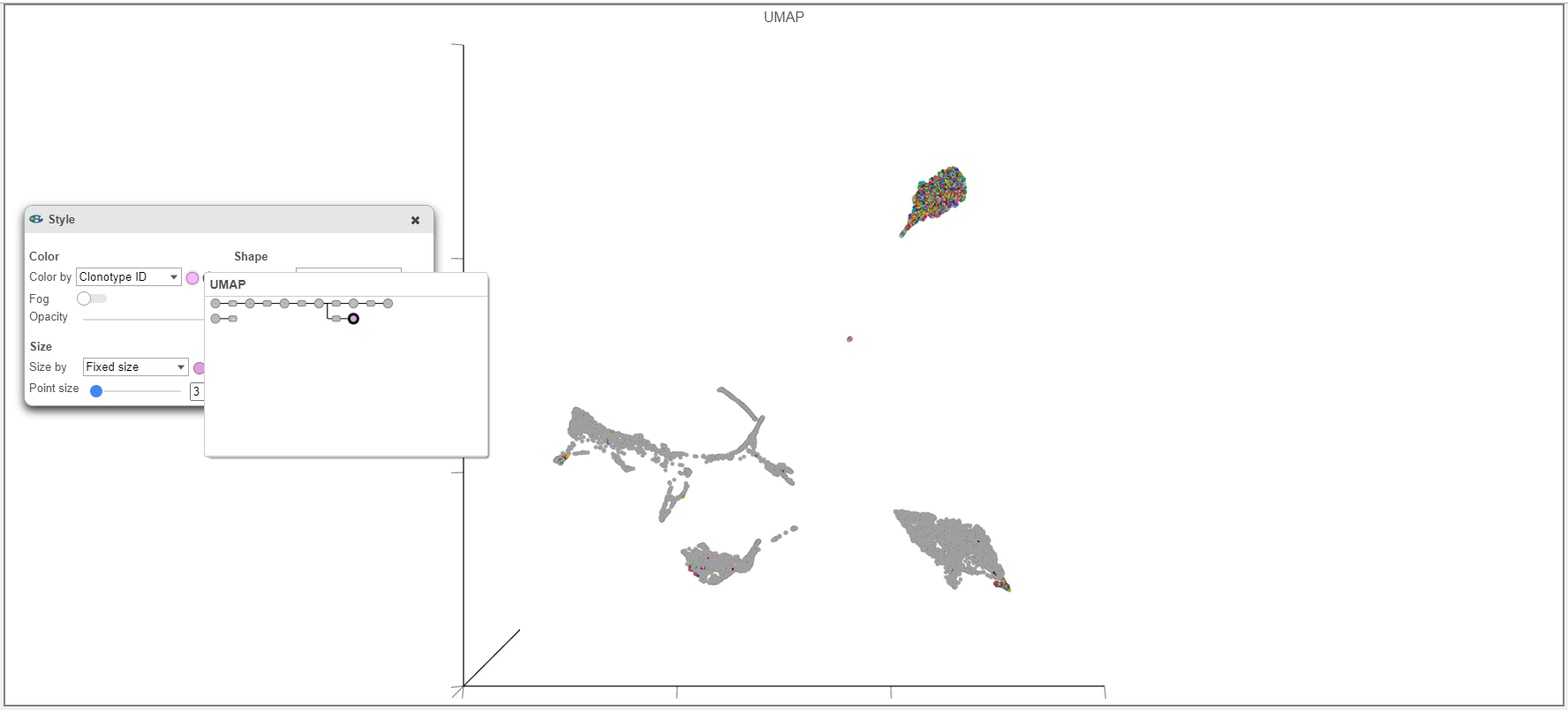
- When overlaying the Clonotype ID on plots from the Single cell counts analysis pipeline (such as the UMAP example below), make sure that the Clonotype ID from the Single cell counts node and not the VDJ node is used.
- B cell isotypes are defined by the Chain and C gene. In the example examples below, Chain and C gene are plotted by Barcode frequency. On the lefttop, no selection and filtering has been performed. On the bottom plot on the right, the heavy chain has been selected and filtered by in the data. By using select Select & filter, criteria can be selected and focused on.
- In the left plot belowBelow, CDR3 abundance is plotted by barcode frequency and colored by Clonotype ID in the top plot. In the bottom example on the right, the plot is instead colored by Chain and other modifications have been made such as axis ticks and the number of groups per page. Note that the predicted CDR3 amino acid sequence is plotted here, but the predicted CDR3 nucleotide sequence (cdr3_nt) as well as information for other Complementarity-Determining Regions is also available.
- In the plot on the left belowGene usage plots for the V, D, and J genes can be plotted many ways, as seen by the examples below for the V gene. In the top plot, barcode frequency for V genes is sorted by frequency in descending order and colored by Chain. The transposed plot on the right below shows all of the groups sorted by ascending value and the heavy chain has been excluded. Gene usage plots for the D and J genes can be quickly shown by changing the data dropdown.
References
- Tonegawa, S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature 302,575–581 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/302575a0
- https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-vdj/software/pipelines/latest/output/annotation#contig-annotation
- https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-vdj/software/overview/welcome
- https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/software/pipelines/7.0/advanced/h5_matrices
- https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/software/pipelines/7.0/output/matrices
- https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-vdj/software/pipelines/latest/algorithms/annotation#productive
- https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-vdj/software/pipelines/latest/using/vdj
- https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-vdj/software/pipelines/latest/using/multi