Page History
| Table of Contents | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
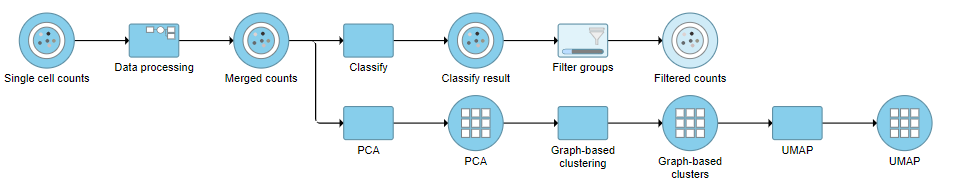
Next, we will filter out certain cells and re-split the data. Re-splitting the data can be useful if you want to perform differential analysis and downstream analysis separately for proteins and genes. For your own analyses, re-splitting the data is optional. You could just as well continue with differential analysis with the merged data if you prefer.
Filter Groups
Because we have classified our cells, we can now filter based on those classifications. This can be used to focus on a single cell type for re-clustering and sub-classification or to exclude cells that are not of interest for downstream analysis.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
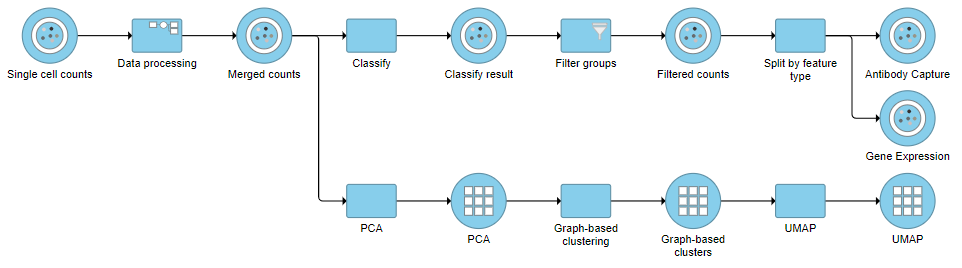
Re-split the Matrix
For this tutorial, we will re-split the protein and gene expression data prior to performing differential analysis. This is useful if you want to perform differential analysis and downstream analysis separately for each feature type. The split data nodes will both retain cell classification information.
For your own analyses, re-splitting the data is optional. You could just as well continue with differential analysis with the merged data if you prefer.
- Click the Classified groups data node
- Click Pre-analysis tools
- Click Split matrix
This will produce two data nodes, one for each data type (Figure ?). The split data nodes will both retain cell classification information.
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...
Differential Analysis, Visualization, and Pathway analysis - Gene Expression Data
We can use a similar approach to analyze the gene expression data.
- Click the project name to return to the Analyses tab
- Click the Gene Expression data node
- Click Differential analysis
- Click GSA
- Check Cell type to include it in the statistical test
- Click Next
- Check Activated B cells in the top panel
- Check Mature B cells in the bottom panel
- Click Add comparison
- Click Finish to run the statistical test
As before, this will generate a GSA task node and a GSA data node.
- Double-click the GSA task node to open the task report (Figure ?)
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
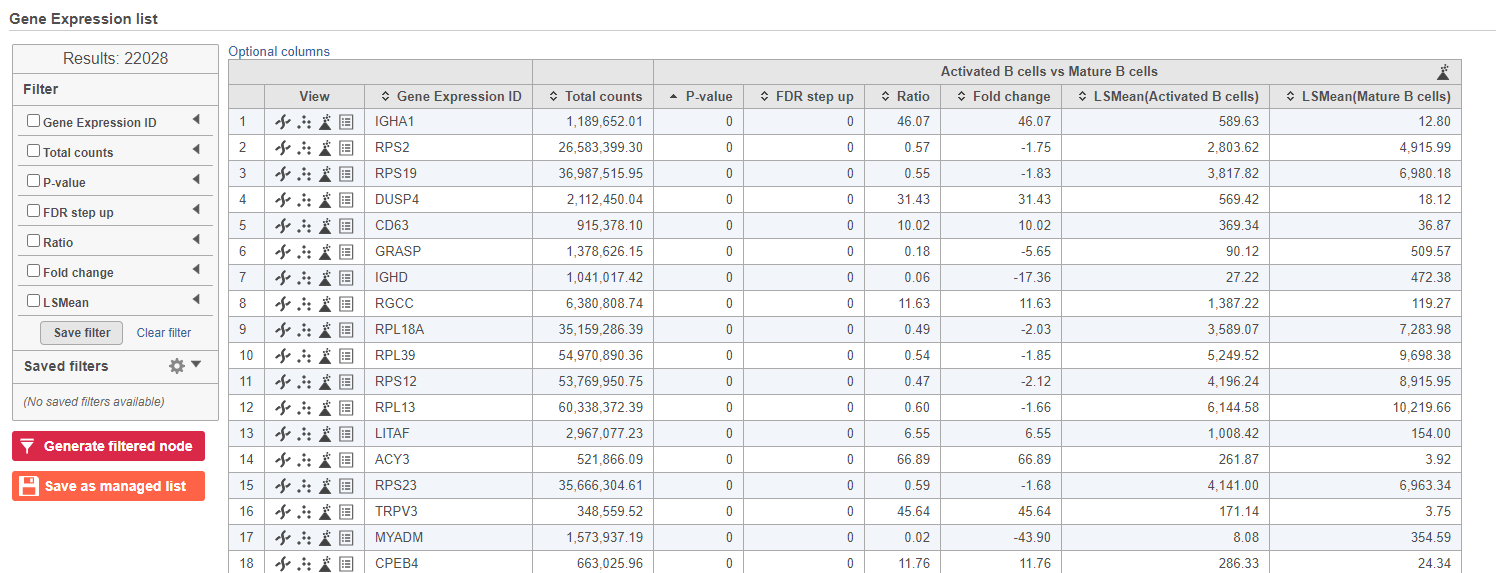
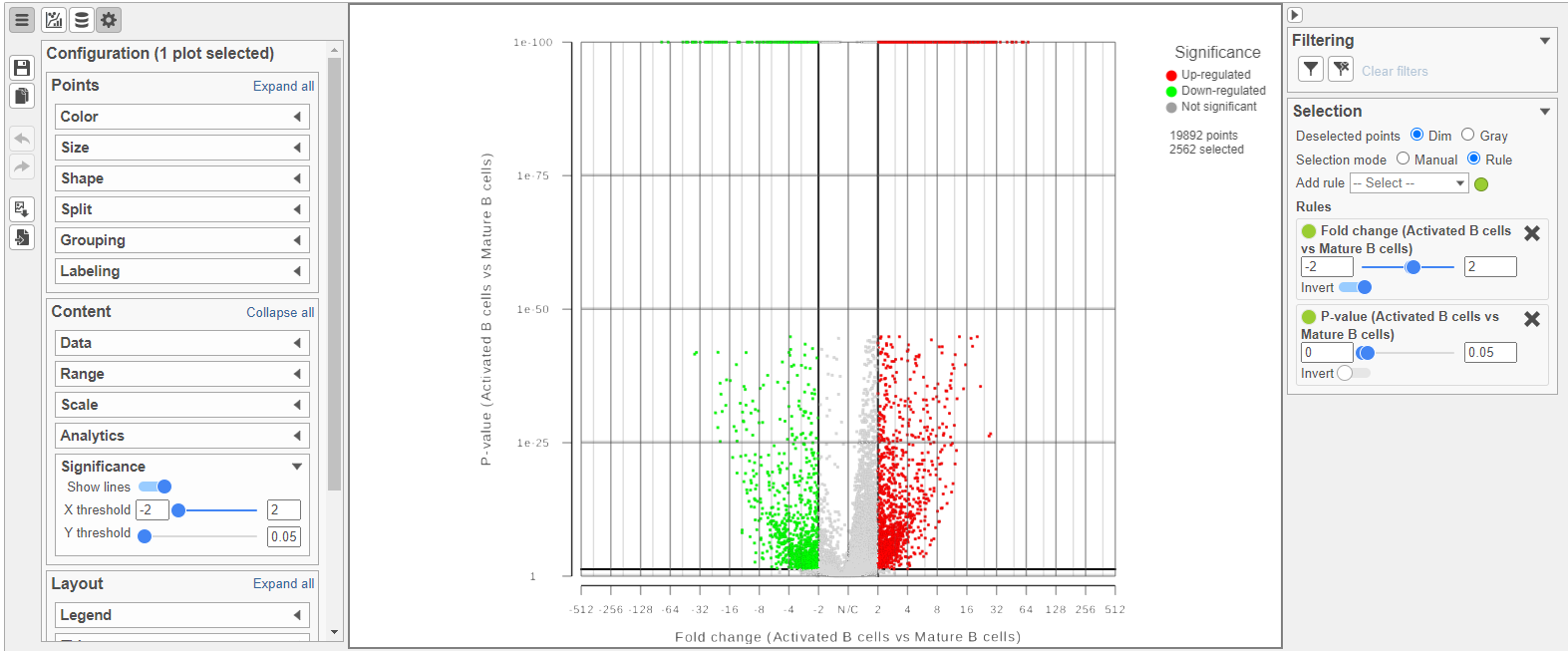
Because more than 20,000 genes have been analyzed, it is useful to use a volcano plot to get an idea about the overall changes.
- Click in the top right corner of the table to open a volcano plot
The Volcano plot opens in a new data viewer session, in a new tab in the web browser. It shows each gene as a point with cutoff lines set for P-value (y-axis) and fold-change (x-axis). By default, the P-value cutoff is set to 0.05 and the fold-change cutoff is set at |2| (Figure ?).
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Click the GSA report tab in your web browser to return to the full report
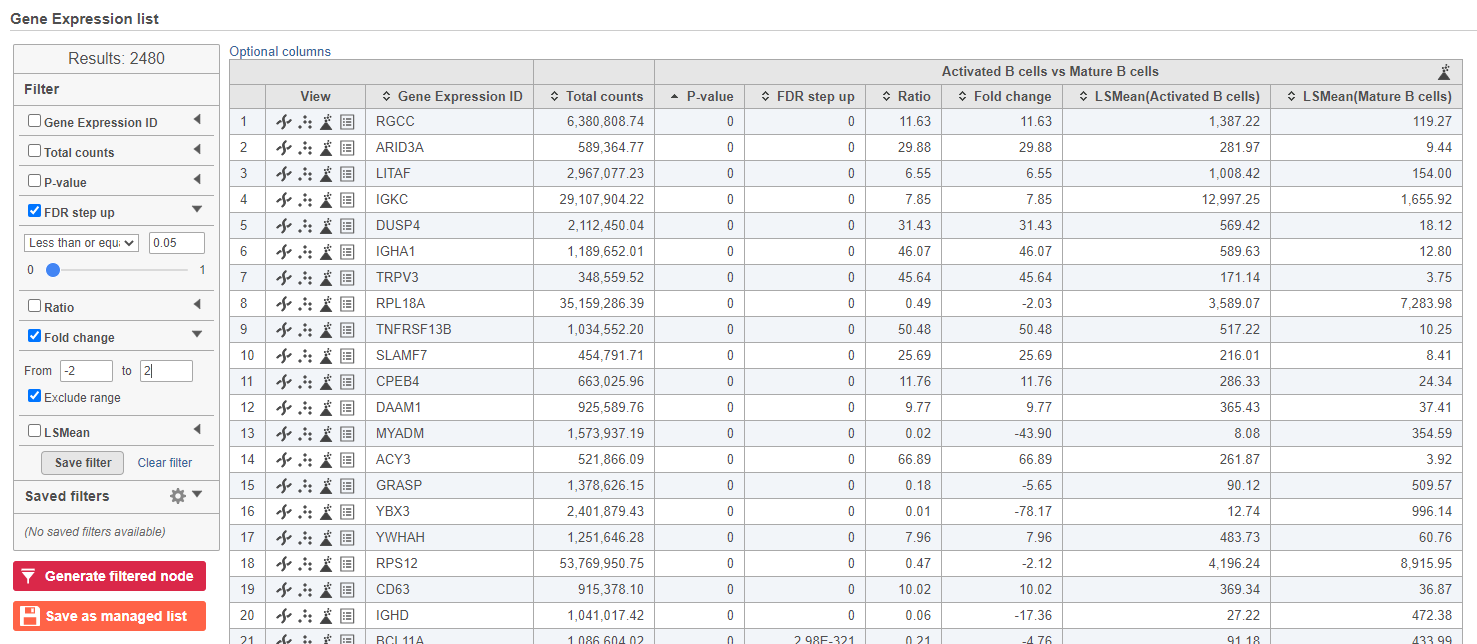
We can filter the full set of genes to include only the significantly different genes using the filter panel on the left.
- Click FDR step up
- Type 0.05 for the cutoff and press Enter on your keyboard
- Click Fold change
- Set to From -2 to 2 and press Enter on your keyboard
The number at the top of the filter will update to show the number of included genes (Figure ?).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
- Click to create a new data node including only these significantly different genes
A task, Differential analysis filter, will run and generate a new Filtered Feature list data node. We can get a better idea about the biology underlying these gene expression changes using gene set or pathway enrichment. Note, you need to have the Pathway toolkit enabled to perform the next steps.
- Click the Filtered feature list data node
- Click Biological interpretation in the toolbox
- Click Pathway enrichment
- Make sure that Homo sapiens is selected in the Species drop-down menu
- Click Finish to run
- Double-click the Pathway enrichment task node to open the task report
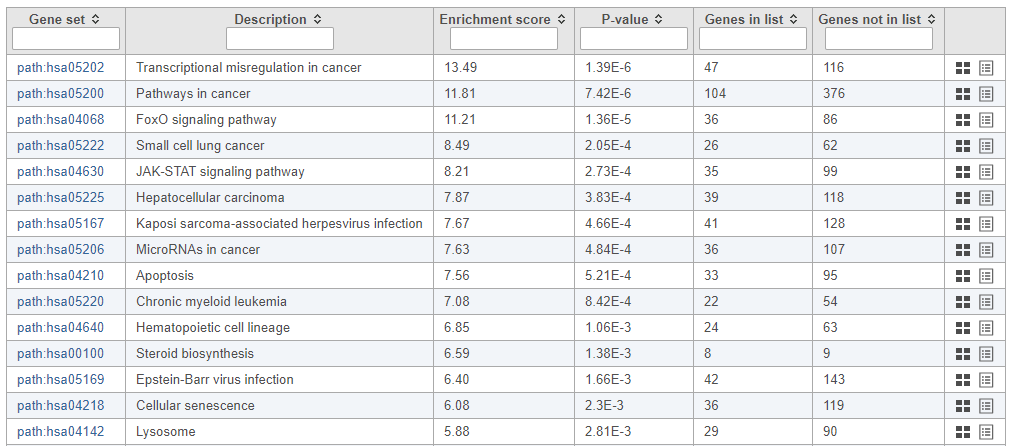
The pathway enrichment results list KEGG pathways, giving an enrichment score and p-value for each (Figure ?).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
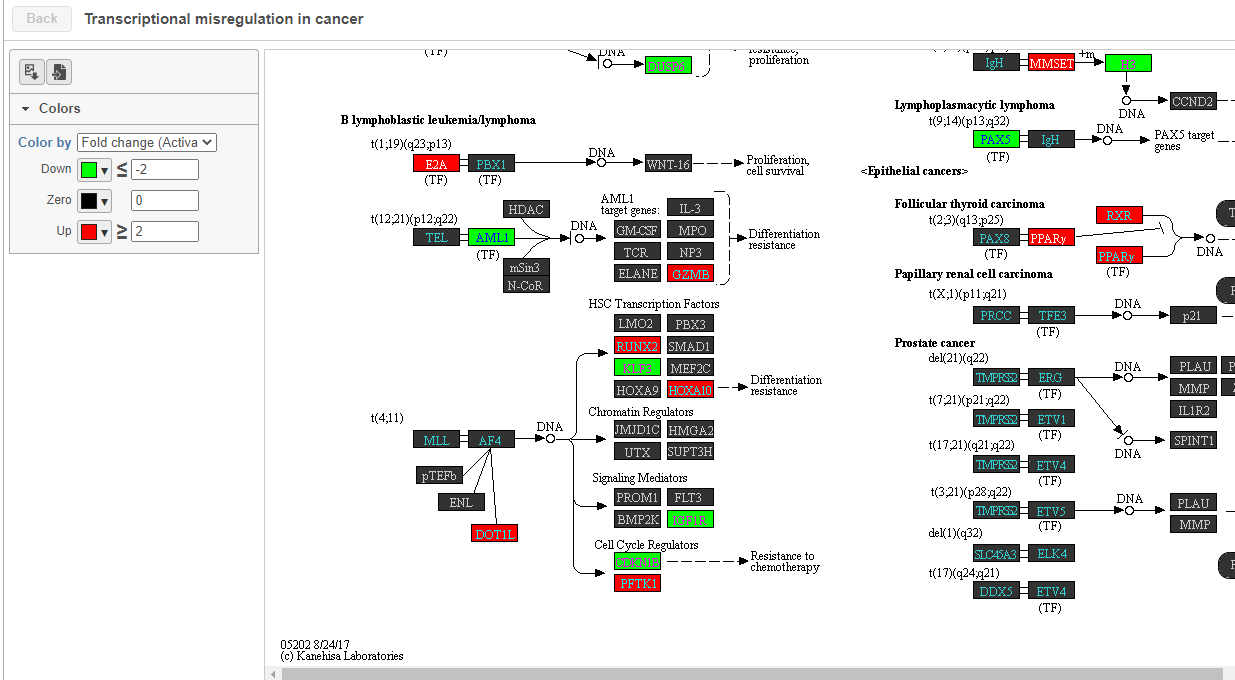
To get a better idea about the changes in each enriched pathway, we can view an interactive KEGG pathway map.
- Click path:hsa05202 in the Transcriptional misregulation in cancer row
The KEGG pathway map shows up-regulated genes from the input list in red and down-regulated genes from the input list in green (Figure ?).
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
...