Page History
The Peak calling task is used to detect enriched genomic regions on reads generated from nucleic acid enrichment experiments such as ChIP-seq, DNase-seq, and MeDIP-seq. experiments. Partek® Flow® provides the widely used method of MACS2-model-based analysis1 (http://liulab.dfci.harvard.edu/MACS/) to find peaks. It can be performed with or without control sample.
MACS2 dialog
Selecting MACS2 from the context sensitive menu will bring up the MACS2 task dialog. The interface will appear differently depending on the input aligned data node and whether there are sample attributes available in the Data tab.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
The Effective genome size must be configured prior to running the peak caller. It refers to the size of the genomic regions that are actually mappable. This size is smaller than the actual size of an organism's whole genome because of the presence of repetitive features. They are typically about 70%-90% of the whole genome. The MACS2 authors1 have recommended presets available for four different species. Select from the drop-down menu the preset that best describes the genome you are working with. They are as follows:
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
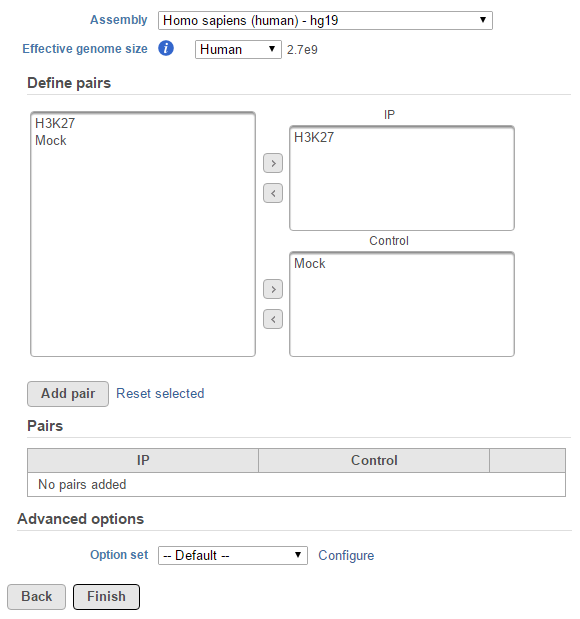
For data where no sample attributes are specified, the peak detection pairs need to be manually defined. In the example in Figure 1, there only two samples. Under the Define pairs section, the left panel lists all the sample names uploaded to the project (H3K27 and Mock). Add one pair at a time by dragging the corresponding samples to either the IP panel on the top-right or the Control panel on the bottom-right. If no control samples are present in the experiment, leave the Control panel blank. If more than one ChIP or Control samples are added, the samples will be combined (or pooled) during the analysis. After defining a pair, click the Add pair button.
...
| Numbered figure captions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
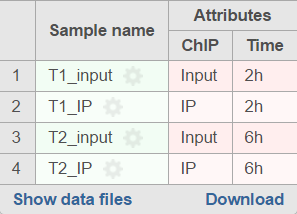
When running the MACS2 task, sample attributes will be used to define the multiple pairs (Figure 4). There is an IP-Input pair for each time point, so the Pair attribute is the Time attribute. The Control attribute is the attribute that differentiates between the Input and IP groups, and in this example, it is the ChIP attribute. Finally, the Control term is labeled as Input in the example.
...
If multiple pairs are added in the Pairs table, the peak detection is performed on each pair independently.
Peaks report
In the task report, each pair will generate a list of peaks displayed in a table (Figure 6). Use the drop down menu next to Peaks detected for... to select the pair.
...
Click the Download button at the lower-right corner to download the peaks in a text file.
References
- Zhang Y, Liu T, et al. Model-based Analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 2008;9(9):R137.
...